Soil conditioner capable of reducing activity of heavy metals, preparation method and soil improvement method
A soil conditioner and heavy metal technology, applied in the field of soil, can solve the problems of not being widely used, serious harm to the human body, low operability, etc., and achieve the effects of strong operability, low cost, and reducing the amount of chemical fertilizers used.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
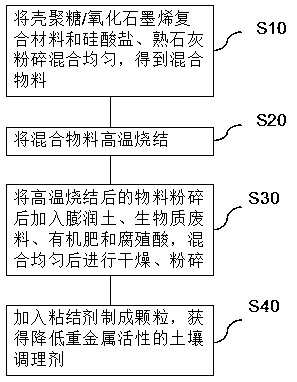
[0037] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of the soil conditioner that reduces heavy metal activity according to the embodiment of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step S10, pulverizing and mixing the chitosan / graphene oxide composite material, silicate, and slaked lime uniformly to obtain a mixed material;
[0039] Step S20, sintering the mixed material at high temperature;
[0040] Step S30, crushing the high-temperature sintered material, adding bentonite, biomass waste, organic fertilizer and humic acid, mixing evenly, drying and crushing.
[0041] Step S40, adding a binder to form granules to obtain the soil conditioner with reduced activity of heavy metals.
[0042] In other words, according to some specific embodiments of the present invention, chitosan / graphene oxide composite material, silicate, slaked lime, bentonite, biomass waste, organic fertilizer and humic acid are used as raw materials to make soil conditioners that r...
Embodiment 1
[0055]First, 20 parts of chitosan / graphene oxide composite material, 5 parts of silicate, and 15 parts of slaked lime were selected and mixed after pulverization, wherein the slaked lime was passed through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0056] The mixed material is sintered at a high temperature of 500°C.
[0057] Secondly, crush the material after high-temperature sintering, add 3 parts of bentonite, 5 parts of biomass waste, 20 parts of organic fertilizer and 1 part of humic acid after crushing, mix well and then dry and pulverize. The drying temperature can be 45°C.
[0058] Then, 3 parts of binder were added to the dried mixed material to form granules to obtain the soil conditioner B1 for reducing the activity of heavy metals.
Embodiment 2
[0060] First, 25 parts of chitosan / graphene oxide composite material, 8 parts of silicate, and 20 parts of slaked lime were selected and mixed after pulverization, wherein the slaked lime was passed through a 40-mesh sieve.
[0061] The mixed material is sintered at a high temperature of 500°C.
[0062] Secondly, crush the material after high-temperature sintering, add 4 parts of bentonite, 7 parts of biomass waste, 22 parts of organic fertilizer and 2 parts of humic acid after crushing, mix well and then dry and pulverize. The drying temperature can be 45°C.
[0063] Then, 3 parts of binder were added to the dried mixed material to form granules to obtain the soil conditioner B2 for reducing the activity of heavy metals.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com