A set of microbial interaction network markers for screening disease-related bacterial flora and its application
An interactive network and marker technology, applied in the fields of bioinformatics and medical health, can solve problems such as the application limitations of microbial flora research, and achieve the effect of reliable technical support and rapid screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Comparing the number of special trios in the intestinal flora network of HIV positive and negative persons
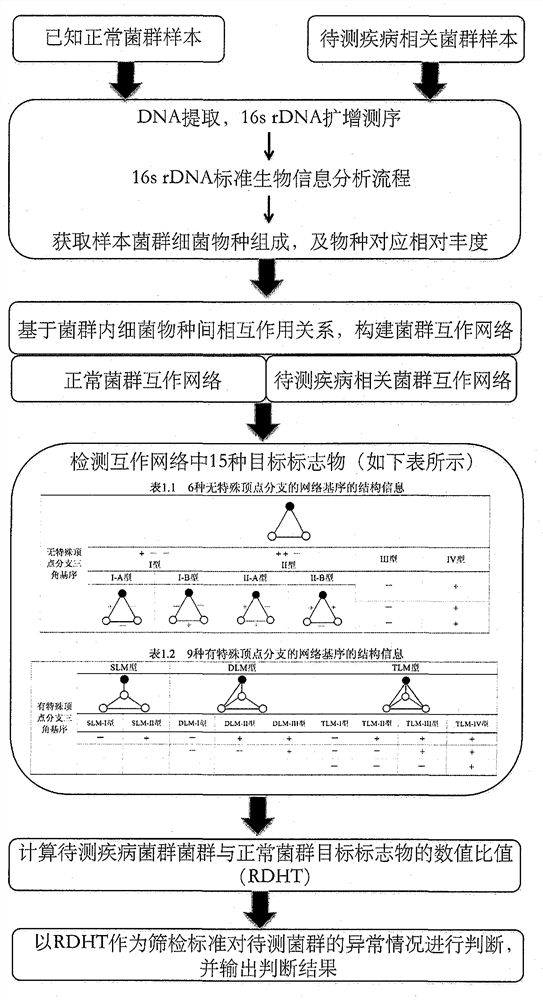
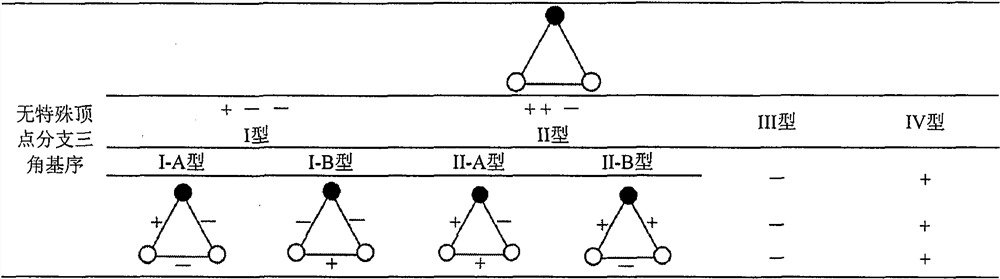
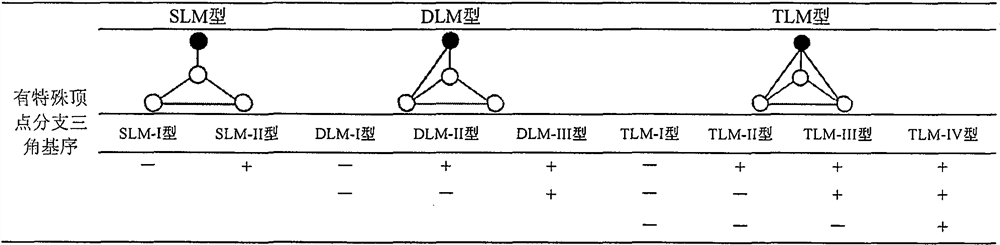
[0020] The calculation process of the present invention is as accompanying drawing figure 1 shown
[0021] Data Sources:
[0022] In 2013, McHardy et al. published the microbial data of HIV-positive and negative individuals. The samples were collected from the intestinal mucosa of 20 HIV patients who had not received antiretroviral treatment and 20 healthy people. 16S rDNA fragments were amplified from the sample DNA using universal primers, sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencing platform, and microbial operational taxonomic units (operational taxonomic units, OTUs) with 97% similarity were obtained through subsequent bioinformatics analysis, in which each An OTU represents a species, and the sequencing content of the OTU in each sample represents the species abundance of the OTU in the sample.
[0023] Construct the intestinal flora int...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Comparing the number of special trios in the oral flora interaction network of smokers and non-smokers
[0031] The calculation process of the present invention is as accompanying drawing figure 1 shown
[0032] Data Sources:
[0033] Lazarevic et al published the oral saliva microbial data of smokers and non-smokers in 2010, and collected oral saliva samples of two non-smoking individuals and three smoking individuals at three time points within 29 days. The 16S rDNA fragment was amplified from the sample DNA using universal primers, and the sequence was sequenced on the Genome Sequencer FLX system, and the microbial operational taxonomic unit (OTU) with 97% similarity was obtained through subsequent bioinformatics analysis, in which each An OTU represents a species, and the sequencing content of the OTU in each sample represents the species abundance of the OTU in the sample.
[0034] Build an oral flora interaction network:
[0035] Based on the abundanc...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Comparing the number of special trios in the skin flora interaction network of AD patients and healthy people
[0041] The calculation process of the present invention is as accompanying drawing figure 1 shown
[0042] Data Sources:
[0043] The skin microbiome data of AD patients and healthy people published by Kong et al. in 2012, samples were collected from the skin samples of 12 AD patients aged 2-15 years and 11 healthy people. 16SrDNA fragments were amplified from the sample DNA using universal primers. After sequencing, microbial operational taxonomic units (operational taxonomic unit, OTU) with 97% similarity were obtained through bioinformatics analysis. Each OTU represented a species, and each The sequence content of the OTU in a sample represents the species abundance of the OTU in the sample.
[0044] Build a skin flora interaction network:
[0045] Based on the abundance of OTUs, the Spearman correlation coefficient R between OTUs in the skin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com