Single cream cheese and preparation method of using ultrahigh-pressure sterilization and normal temperature whey draining
A technology of ultra-high pressure sterilization and cream, applied in cheese substitutes, dairy products, applications, etc., can solve the problems of destroying cheese structure, flavor and mouthfeel, uneven distribution of colloidal agglomerates, protein denaturation when heated, etc., to achieve Suitable for large-scale continuous production, maintaining flavor and taste, and smooth taste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
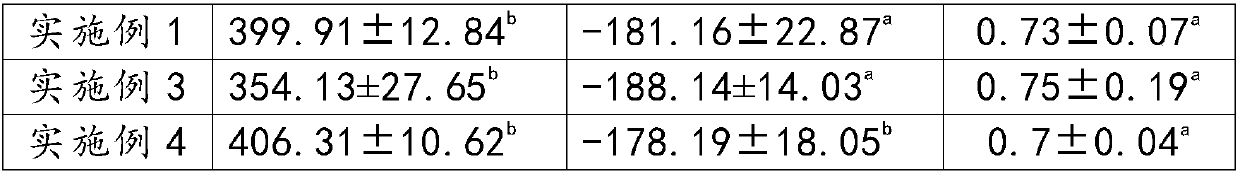
Embodiment 1
[0030] In the cream cheese raw material of this embodiment, cream: fat content is 40%, dosage is 25kg; fresh milk: protein content is 3%, dosage is 75kg; the direct throw starter used in the fermentation process is extracellular For the mixture of polysaccharide starter of lactic acid bacteria and medium temperature lactic acid bacteria starter, the amount of starter is 4g; the amount of table salt is 600g. Among them, the starter of lactic acid bacteria that produces extracellular polysaccharides is R-704, and the starter of medium temperature lactic acid bacteria is MM100, and the mass ratio of the two is 1:10.
[0031] The preparation method of cream cheese in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0032] (1) Standardize the fresh milk and cream, and mix them thoroughly and stir to dissolve to obtain a mixture;
[0033] (2) Heat the mixture to 55°C for homogenization, and the homogenization pressure is 100bar; the homogenized material is vacuum-packed and then subjected ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In the cream cheese raw material of this embodiment, cream: fat content is 34%, dosage is 35kg; fresh milk: protein content is 3.4%, dosage is 66kg; the direct-input starter used in the fermentation process is extracellular A mixture of polysaccharide lactic acid bacteria starter and medium temperature lactic acid bacteria starter, the amount of starter is 4g; the amount of table salt is 650g. Among them, the starter of lactic acid bacteria that produces extracellular polysaccharides is R-704, and the starter of medium-temperature lactic acid bacteria is LL-50, and the mass ratio of the two is 1:10.
[0039] The preparation method of cream cheese in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0040] (1) Standardize the fresh milk and cream, and mix them thoroughly and stir to dissolve to obtain a mixture;
[0041] (2) Heat the mixture to 60°C for homogenization, and the homogenization pressure is 130bar; the homogenized material is vacuum-packed and then subjected to ultr...
Embodiment 3
[0046] In the cream cheese raw material of this example, cream: fat content is 38%, dosage is 30kg; fresh milk: protein content is 3.2%, dosage is 70kg; the direct throw starter used in the fermentation process is extracellular A mixture of polysaccharide lactic acid bacteria starter and medium temperature lactic acid bacteria starter, the amount of starter is 5g; the amount of table salt is 770g. Among them, the starter of lactic acid bacteria producing extracellular polysaccharides is MM100, and the starter of medium temperature lactic acid bacteria is R-704, and the mass ratio of the two is 1:10.
[0047] The preparation method of cream cheese in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) Standardize the fresh milk and cream, and mix them thoroughly and stir to dissolve to obtain a mixture;
[0049] (2) Heat the mixture to 60°C for homogenization, and the homogenization pressure is 200bar; the homogenized material is vacuum-packaged and then subjected to ultra-hig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com