OFDM Peak-to-Average Ratio Suppression Method Based on Alternating Direction Multiplier Method
A technology of alternating direction multiplier and peak-to-average ratio suppression, which is applied in the field of OFDM peak-to-average ratio suppression based on the alternate-direction multiplier method, can solve the problems of high computational complexity and reduce the peak-to-average ratio of OFDM signals, and achieves computational complexity. The effect of low and low bit error rate and excellent bit error performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
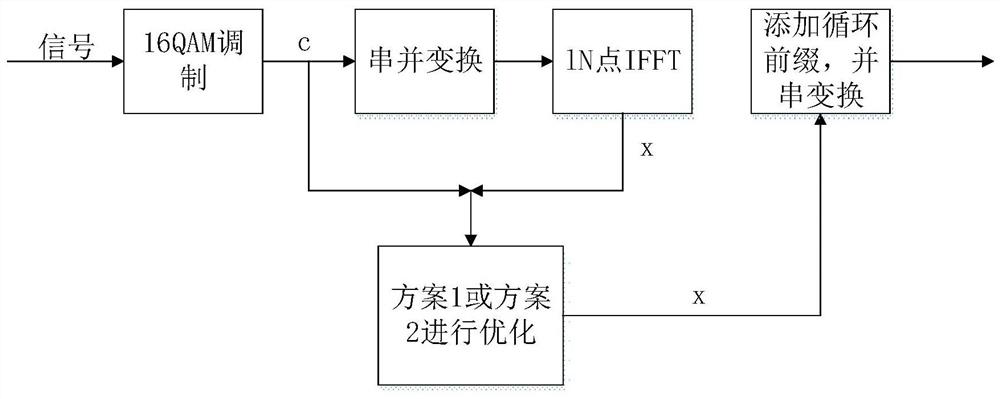
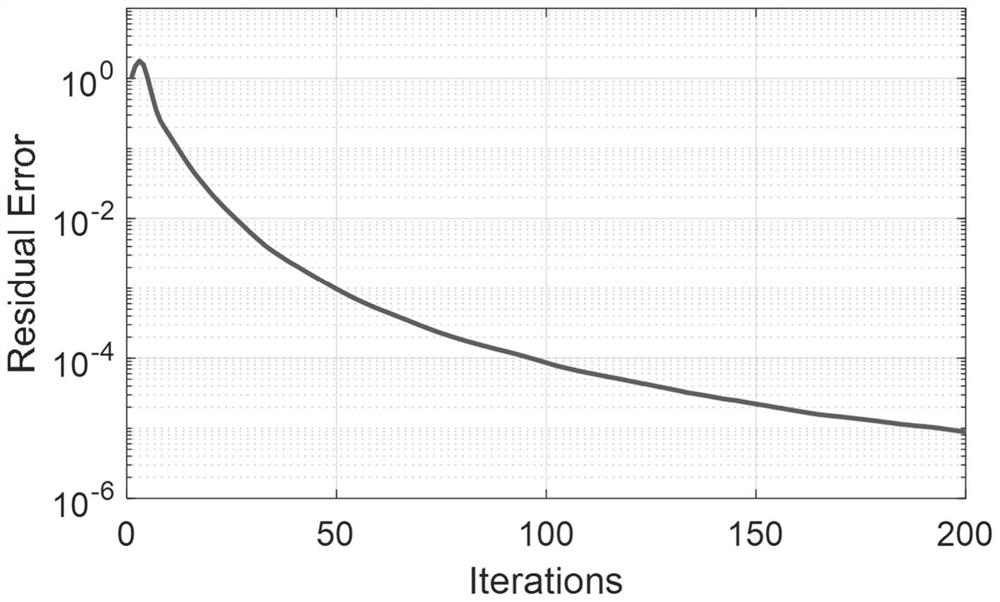
[0029] Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is an important multi-carrier modulation technology, which has been widely used in modern wireless communication systems. One of the biggest disadvantages of OFDM is that it results in a large peak-to-average ratio of the signal. However, the power amplifier of the transmitter is limited in power, and a large peak-to-average ratio will cause the power amplifier to enter the nonlinear saturation region, causing in-band interference and out-of-band radiation of the signal. Some methods in the prior art can effectively reduce the peak-to-average ratio of OFDM signals and obtain a better system bit error rate, but their computational complexity is relatively high, which hinders practical engineering applications. The present invention conducts research on this, takes minimizing data carrier interference as the objective function, peak-to-average ratio and free carrier power as constraint conditions, and establishes a non-con...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The OFDM peak-to-average ratio suppression method based on the alternating direction multiplier method is the same as embodiment 1, and the optimization with one of the schemes in the two schemes described in step (3) is modeling, solving, and obtaining the optimal solution, wherein the scheme The modeling and solving process of 1 includes the following steps:
[0040] (3.1.a) Establish a direct model: the objective function is set to minimize data carrier interference, and the following direct model is established with the peak-to-average ratio and free carrier power as constraints, which is model :
[0041] Objective function:
[0042] Restrictions:
[0043]
[0044] Ac=x
[0045]Among them, N is the number of subcarriers, l is the oversampling factor, c∈C N Represents OFDM frequency domain signal, x∈C lN represents the corresponding time-domain signal. In the objective function, c represents the optimized OFDM signal, and c o is the original OFDM signal;...
Embodiment 3
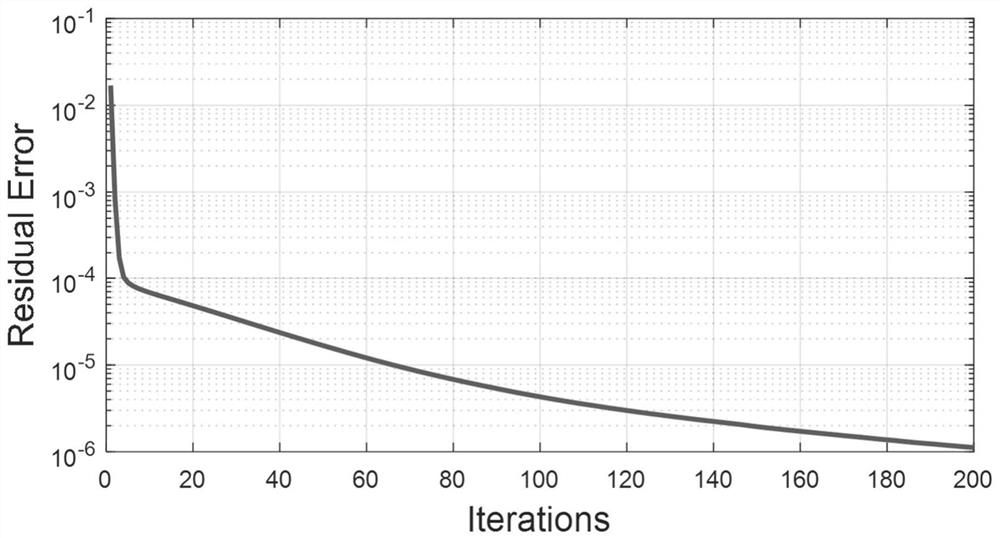
[0065] The OFDM peak-to-average ratio suppression method based on the alternating direction multiplier method is the same as embodiment 1-2, and the modeling of the present invention's scheme 2 includes the following steps:
[0066] (3.2.a) Establish a relaxation model: introduce two auxiliary variables u and w, use the first and second auxiliary variables to relax the direct model in (3.1.a), and obtain the following relaxation model, which is model:
[0067] Objective function:
[0068] Restrictions:
[0069]
[0070] Ac=u
[0071] x=w
[0072] in, is the penalty parameter.
[0073] The augmented Lagrangian function to establish the relaxation model is as follows:
[0074]
[0075] Among them, y 1 ∈C lN ,y 2 ∈C lN are the Lagrangian multipliers corresponding to the constraints Ac=u and x=w, respectively.
[0076] (3.2.b) Apply the ADMM method to the relaxed model to obtain a relaxed ADMM model: apply the ADMM method to the relaxed model obtained in (3....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com