Preparation method of clinical cord blood monocytes
A mononuclear cell and cell technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems that do not meet clinical applications, and achieve the effects of avoiding acute renal failure, short time consumption, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038]This embodiment provides a method for preparing umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for clinical use, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1: Preliminary screening and storage of umbilical cord blood: screening and collection of umbilical cord blood from healthy full-term maternal volunteers, and storing in blood bags at 7°C.
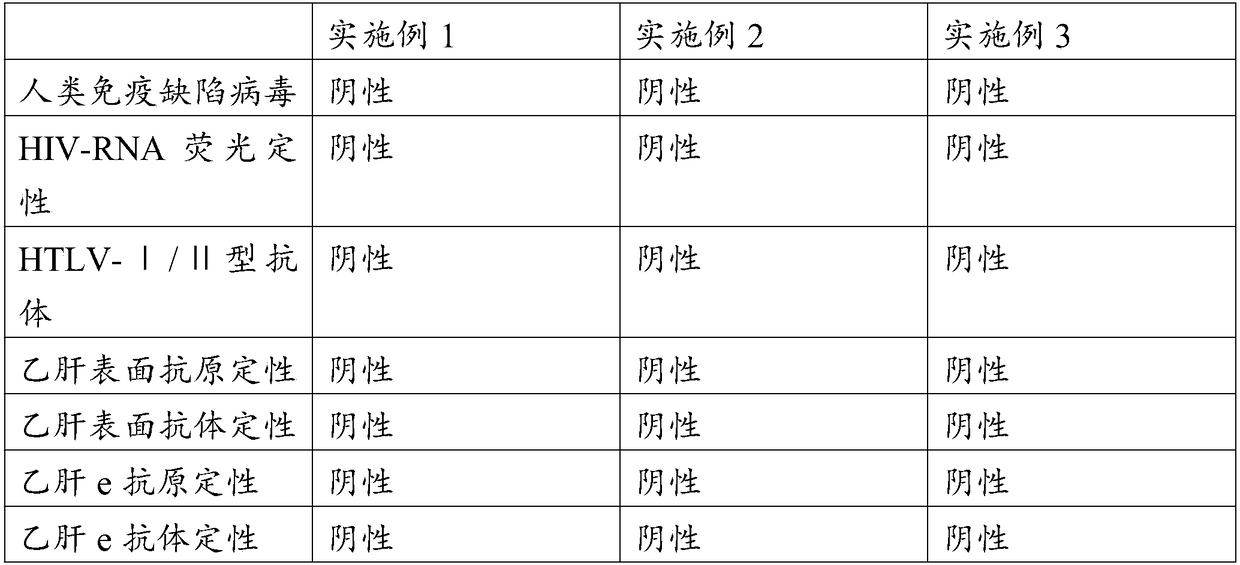
[0040] At the same time, a tube of maternal blood was collected for re-examination. The re-examination items were viral immunological detection and genetic detection of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, and syphilis.
[0041] Step 2: Cultivation: put the umbilical cord blood sample in a culture dish containing RPMI-1640 medium, and incubate for 2 hours at 37° C. in a cell culture incubator containing 5% CO2.
[0042] Step 3: Absorption: After the monocytes adhere to the wall, discard the suspended cells in the upper layer, wash gently with PBS buffer twice, add a small amount of RPMI-1640 medium, and scrape off the adher...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment provides a method for preparing umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for clinical use, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0049] Step 1: Preliminary screening and storage of umbilical cord blood: Screening and collection of umbilical cord blood from healthy full-term maternal volunteers, and storing in blood bags at 5°C.
[0050] At the same time, a tube of maternal blood was collected for re-examination. The re-examination items were viral immunological detection and genetic detection of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, and syphilis.
[0051] Step 2: Cultivation: put the umbilical cord blood sample in a petri dish containing RPMI-1640 medium, and incubate for 3 hours at 37° C. in a cell culture incubator containing 6% CO2.
[0052] Step 3: Absorption: After the monocytes adhere to the wall, discard the suspended cells in the upper layer, wash gently with PBS buffer twice, add a small amount of RPMI-1640 medium, and scrape off the adhere...
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment provides a method for preparing umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for clinical use, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0059] Step 1: Preliminary screening and storage of umbilical cord blood: screening and collection of umbilical cord blood from healthy full-term maternal volunteers, and storing in blood bags at 6°C.
[0060] At the same time, a tube of maternal blood was collected for re-examination. The re-examination items were viral immunological detection and genetic detection of hepatitis B, hepatitis C, AIDS, and syphilis.
[0061] Step 2: Incubation: Place the cord blood sample in a petri dish containing RPMI-1640 medium at 37°C with 4% CO 2 Incubate for 1 h in a cell culture incubator.
[0062] Step 3: Absorption: After the monocytes adhere to the wall, discard the suspended cells in the upper layer, wash gently with PBS buffer twice, add a small amount of RPMI-1640 medium, and scrape off the adherent cells with a cell scr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com