Improved method for planning paths of driverless vehicles by aid of rapidly random-exploring trees
A technology for path planning and unmanned vehicles, applied in vehicle position/route/height control, motor vehicles, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve problems such as inability to follow, follow, and non-smooth paths, and achieve smoothness Direct followable path effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0039] The present invention provides a two-way pruning optimization RRT path planning algorithm based on non-holonomic constraints of unmanned vehicles, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0040] S1: Use the RRT algorithm to search for a path:
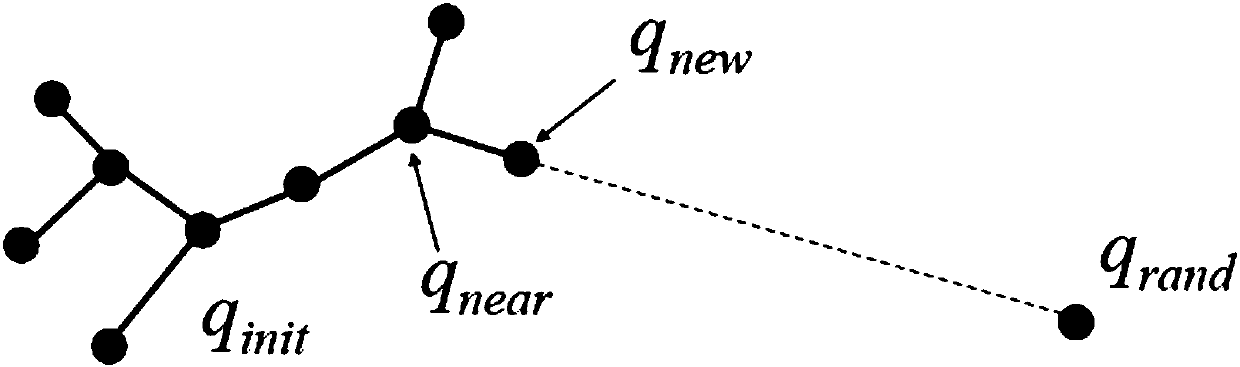
[0041] Such as figure 1 The schematic diagram of the RRT algorithm node expansion is shown. The algorithm takes the starting point as the root node, generates a sampling node uniformly and randomly each time, and selects the point closest to it on the tree. From this point to the direction of the sampling point, follow a fixed step Long expand the next node, and repeat the above process until the target node is added to the tree, and a path from the start point to the end point is found.
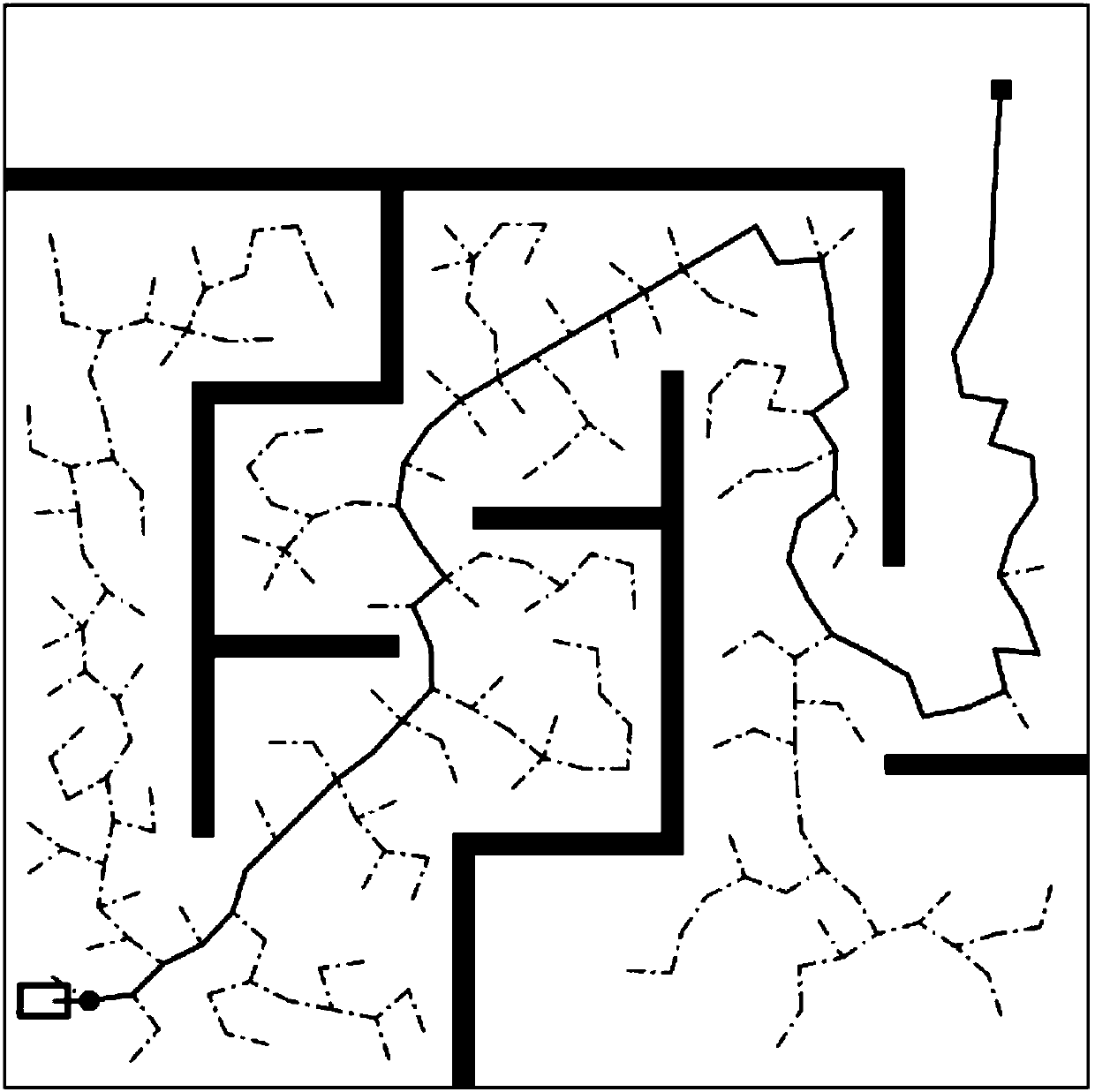
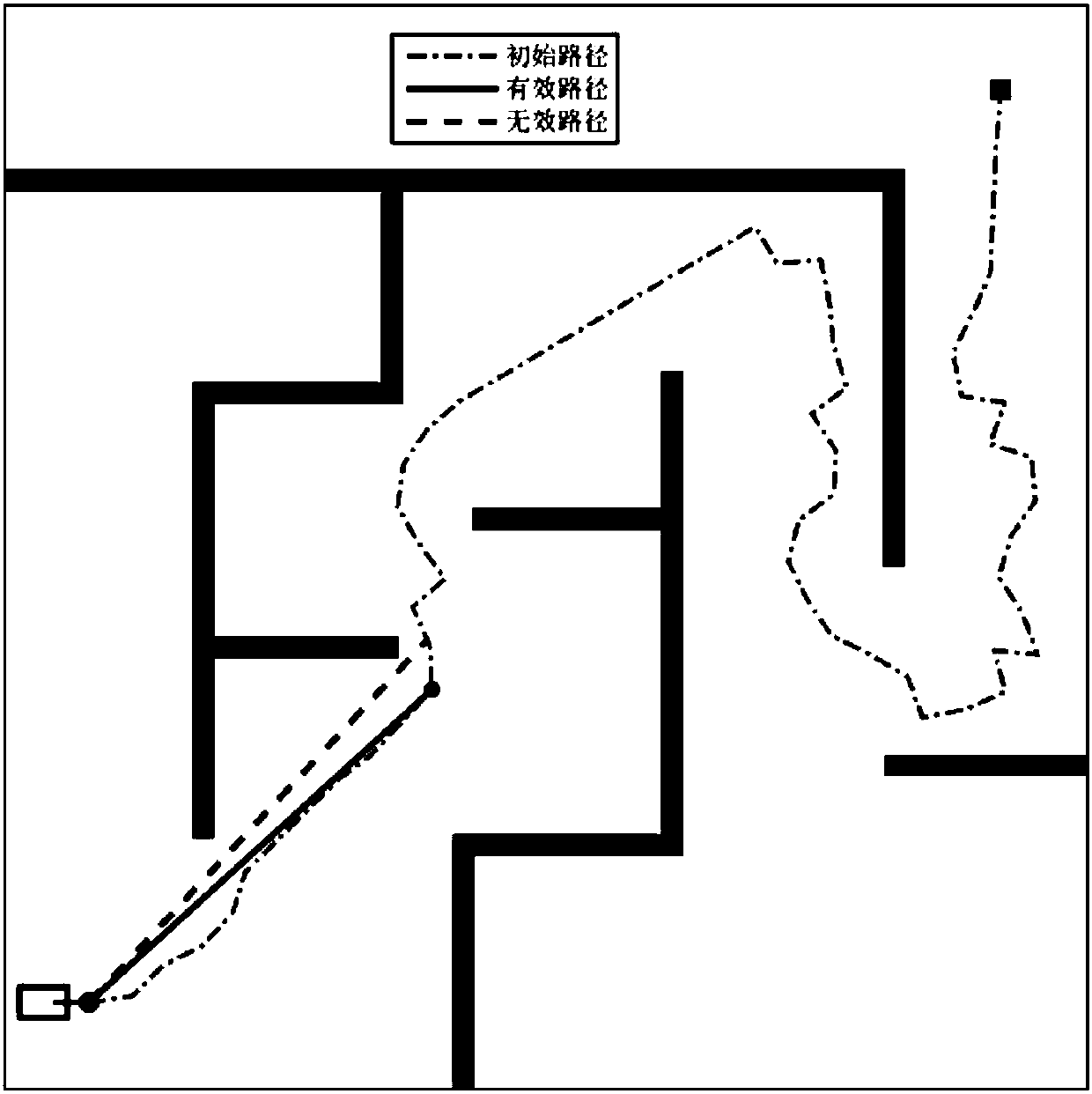
[0042] In the obstacle environment, the path generated by using the above RRT planning algorithm is as follows: figure 2 shown. figure 2 , the black bar area is the obstacle space, the white area is the free space, the dot in the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com