Projection method and back projection method for panoramic videos and pictures
A panoramic video and back-projection technology, which is applied in picture duplicators, color TV components, image reproducers using projection devices, etc., can solve uneven pixel distribution, redundant pixel data, and affect the image quality of panoramic images, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of uniform distribution of pixels and uniform distribution of good pixels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] The flow of the method for projecting a spherical image or video image in this embodiment is as follows:
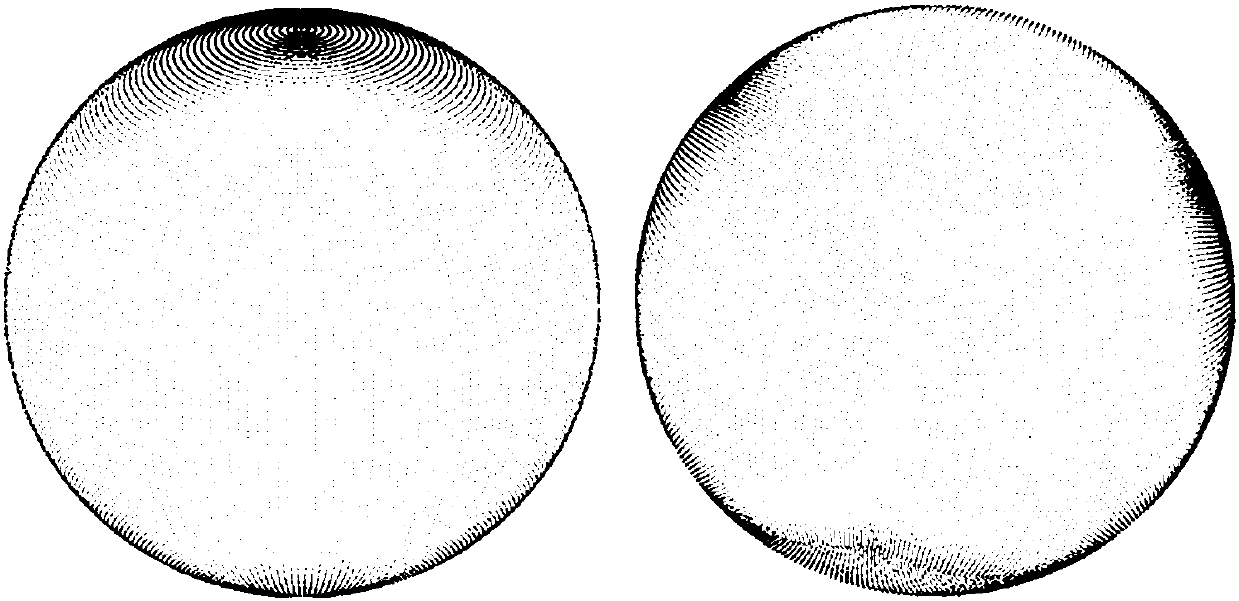
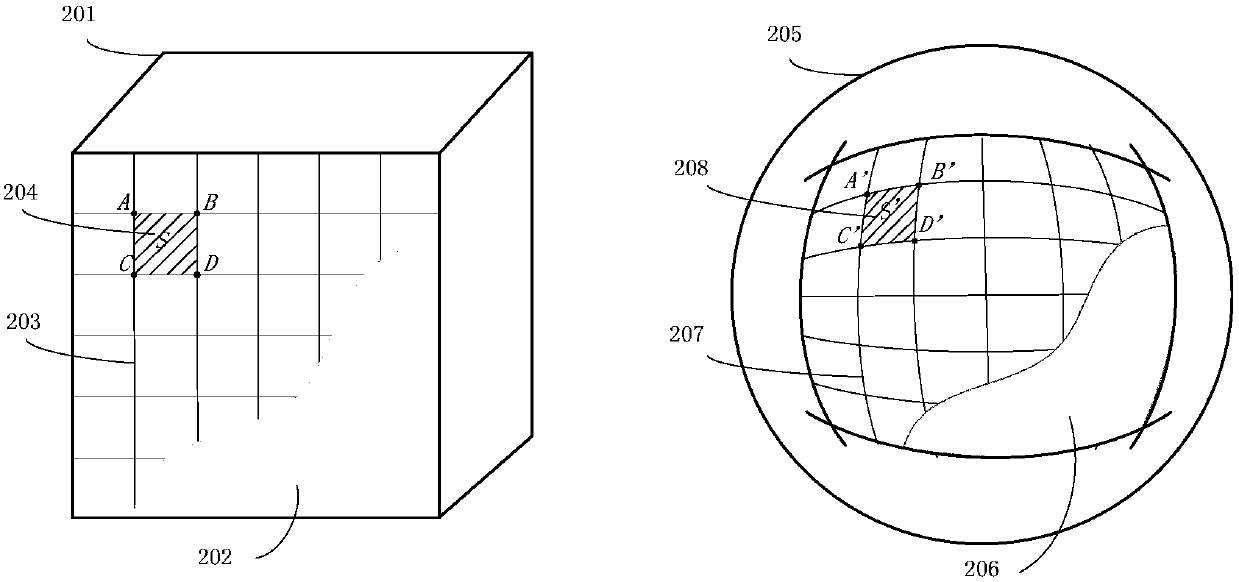
[0125] Step S101, creating a cube, wherein the surface area of the cube is the same as the surface area of the sphere where the spherical image is located. Divide the spherical image into surfaces by cubic spherical projection. This embodiment adopts a cube, and any regular polygon, polygon, etc. can be used in this embodiment. But in terms of calculation and utility, regular polygons including cubes have the best utility.
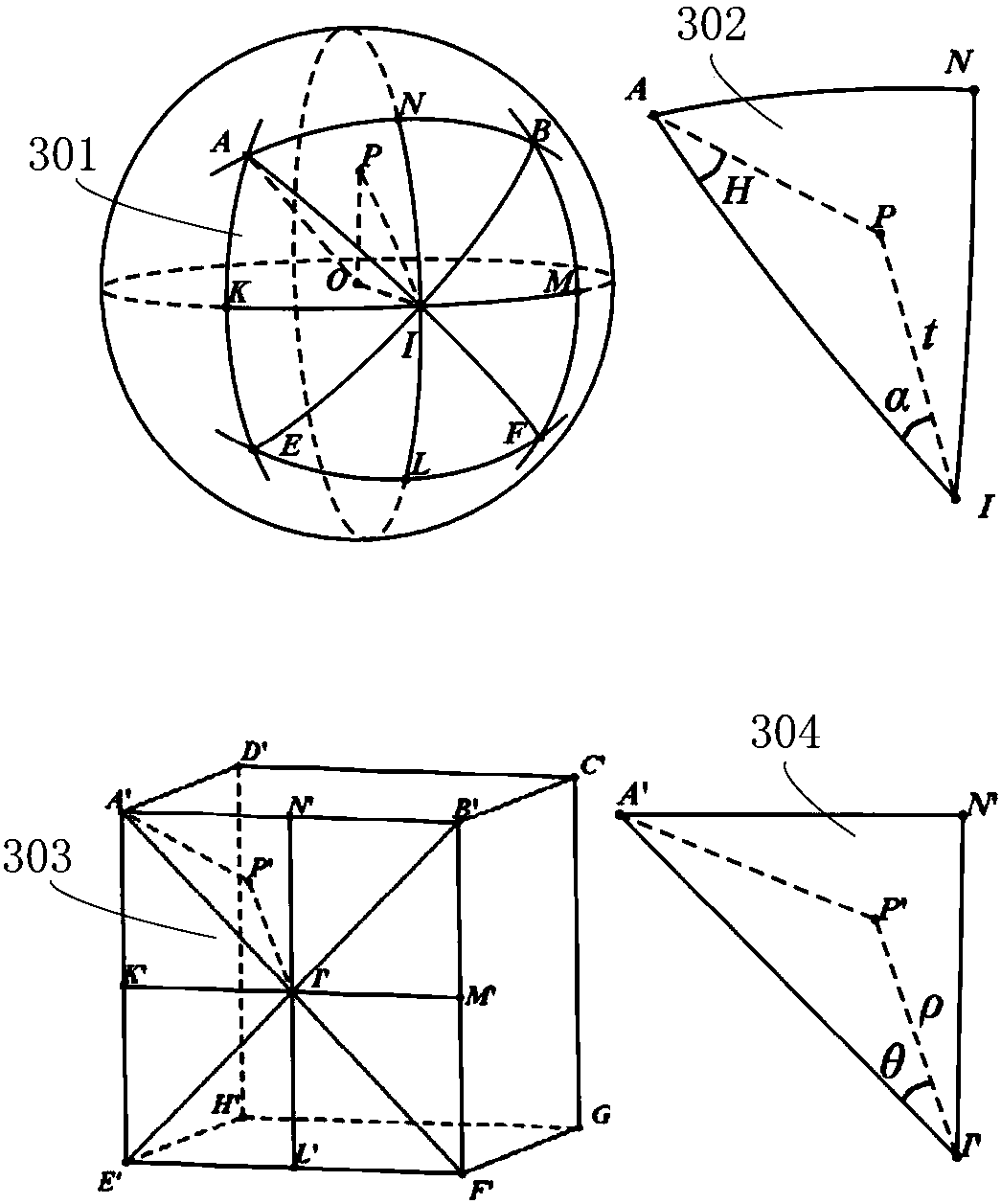
[0126] The specific segmentation of the spherical image further includes step S1011, setting the polyhedron in the sphere where the spherical image is located, and taking the center of the sphere as the center point.
[0127] Step S1012, mapping each vertex and edge of the polyhedron to a spherical image.
[0128] Step S1013, each vertex and edge mapped to the spherical image divides the spherical image into multiple surfaces.
[0129] ...
Embodiment 2
[0162] The method for projecting a spherical image or video image in this embodiment is based on the projection method in Embodiment 1, and further divides and maps the surface projected from the spherical surface to a cube, thereby further improving the distribution uniformity of pixels. The specific method flow is as follows:
[0163] Step S201, creating a cube, wherein the surface area of the cube is the same as the surface area of the sphere where the spherical image is located. Divide the spherical image into surfaces by cubic spherical projection.
[0164] The specific segmentation of the spherical image further includes step S2011, setting the polyhedron inside the sphere where the spherical image is located, and taking the center of the sphere as the center point.
[0165] Step S2012, mapping each vertex and edge of the polyhedron to a spherical image.
[0166] Step S2013, each vertex and edge mapped to the spherical image divides the spherical image into multipl...
Embodiment 3
[0182] The method for projecting a spherical image or video image in this embodiment is based on the projection method in Embodiment 2, and again divides and maps the surface projected from the spherical surface to a cube, thereby improving the uniformity of pixel distribution. The specific method flow is as follows:
[0183] Step S301, mapping each vertex and edge of the polyhedron to a spherical image.
[0184] Step S302, each vertex and edge mapped to the spherical image divides the spherical image into multiple surfaces.
[0185] Step S303, through the Snyder transformation, respectively establish the mapping relationship between each surface of the spherical image and each surface of the polyhedron. The mapping method is the same as step S202 in Embodiment 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0186] Step S304, perform the following steps for each pair of the surface of the spherical image and the face of the polyhedron that have a mapping relationship:
[0187] S3041. D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com