High angular stability frequency selective surface based on 2.5d braided structure
A frequency selective surface and stability technology, applied in the field of antenna and wireless communication, can solve the problems of insufficient angular stability and reduction of equivalent electrical length, etc., to achieve the reduction of equivalent electrical size and resonance frequency point Offset, the effect of improving angular stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] refer to figure 1 , a frequency selective surface with high angular stability based on a 2.5D braided structure, including M×N frequency selective surface units arranged periodically, M=20, N=20. The passive resonant unit is a regular hexagonal prism unit, and the frequency selection surface composed of it is a honeycomb structure.
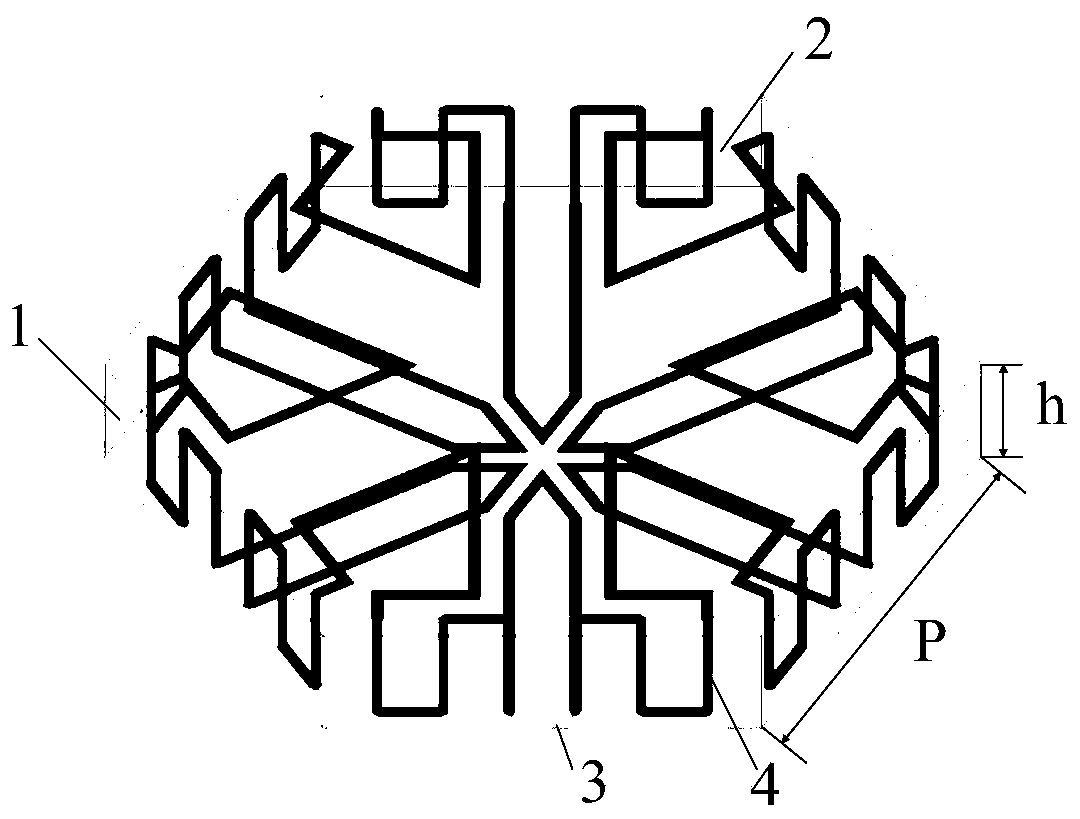
[0037] refer to figure 2 , the frequency selective surface unit includes a dielectric plate 1 with a regular hexagonal cross-sectional shape, a first metal patch 2 printed on the upper surface of the dielectric plate 1, a second metal patch 3 on the lower surface, and a metallized via hole 4 ,in:
[0038] The dielectric plate 1 has a side length of P=5mm, a thickness of h=1.5mm, and a relative permittivity of 4.4.
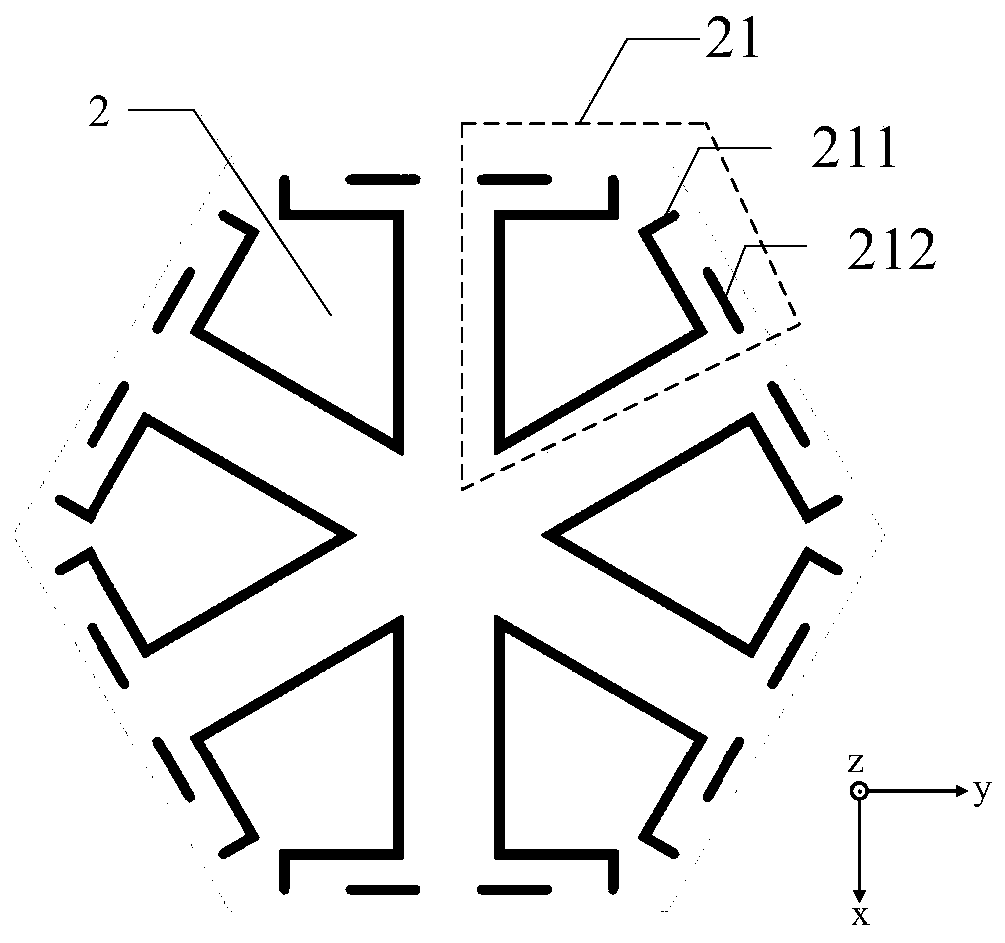
[0039] The first metal patch 2 has a structure such as image 3 As shown, it consists of six first strip groups 21 , and each first strip group 21 is composed of one open ring strip 211 and two first short strips 212 . The...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This example has the same structure as Example 1, only the following parameters have been adjusted:
[0050] M×N frequency selective surface units arranged periodically, M=6, N=6; the side length of the dielectric plate 1 is P=4.5mm, and the thickness h=1.5mm; the short side length L1 of the open ring strip 211=0.9mm , the length of the short strip is S=0.2mm; the length of the two parallel long strips of the quasi-V-shaped strip 311 is n1=1.5mm, and the distance is d=0.5mm; the radius of the metallized via hole 4 is R=0.1mm, and the center and The distance from the nearest edge of the dielectric plate 1 is g=0.2mm.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The structure of this example is the same as that of Example 1, and only the following parameters have been adjusted:
[0053] M×N frequency selective surface units arranged periodically, M=10, N=10; the side length of the dielectric plate 1 is P=9mm, the thickness h=2.5mm; the short side length L1=1.5mm of the open annular strip 211, The length of the short strip is S=0.45mm; the length of the two parallel long strips of the quasi-V-shaped strip 311 is n1=3.5mm, and the distance is d=1mm; the radius of the metallized via hole 4 is R=0.3mm, and the center and the nearest The edge distance of the dielectric plate 1 is g=0.3 mm.
[0054] Below in conjunction with simulation experiment, technical effect of the present invention is described further:
[0055] 1. Simulation conditions and content:
[0056] Utilize commercial simulation software HFSS_17.0 to carry out simulation calculation to the transmission coefficient under the different incident angles of embodiment 1,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com