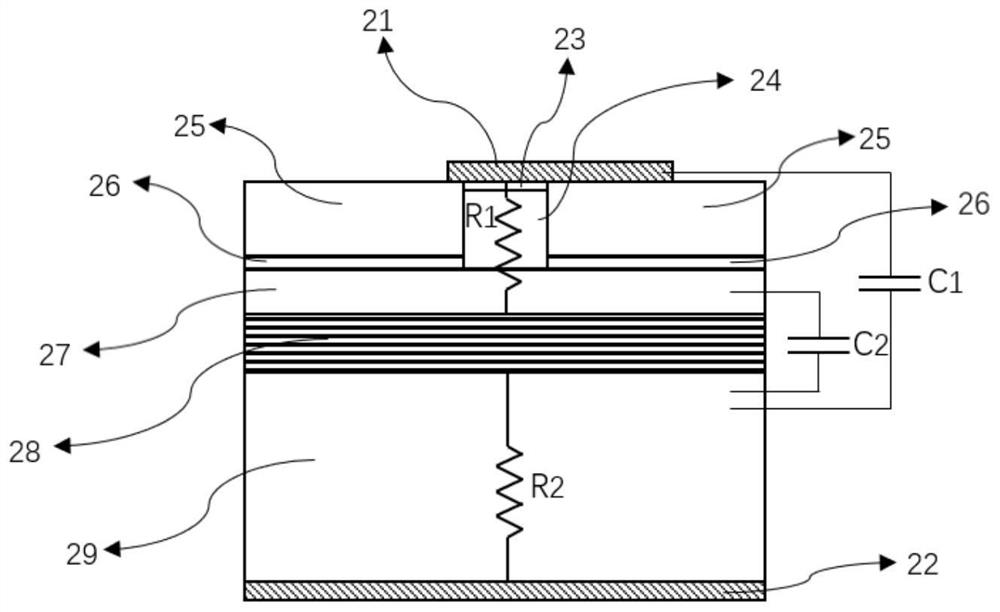
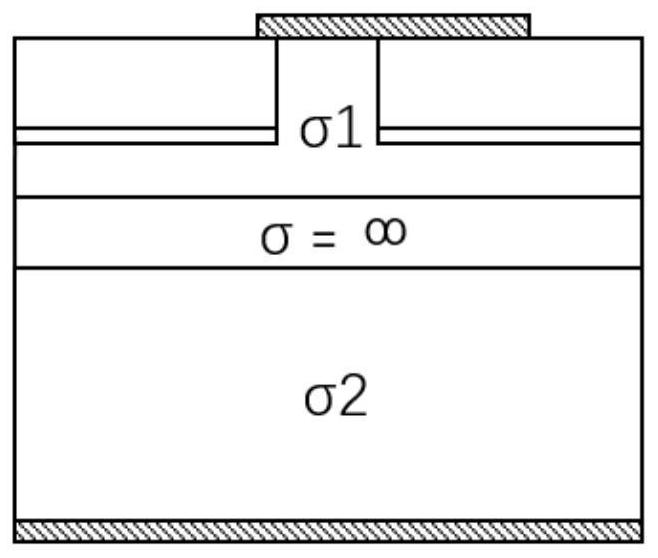
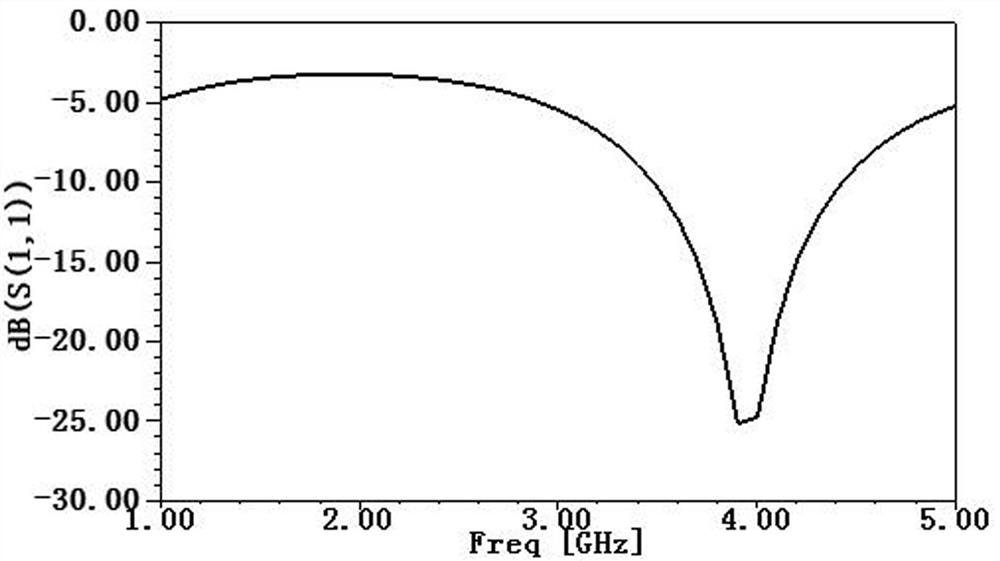
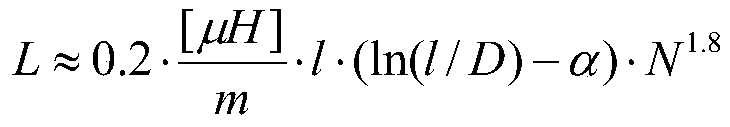Patents
Literature
31 results about "HFSS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HFSS is a commercial finite element method solver for electromagnetic structures from Ansys. The acronym stands for high-frequency structure simulator. HFSS is one of several commercial tools used for antenna design, and the design of complex radio frequency electronic circuit elements including filters, transmission lines, and packaging. It was originally developed by Professor Zoltan Cendes and his students at Carnegie Mellon University. Prof. Cendes and his brother Nicholas Cendes founded Ansoft and sold HFSS stand-alone under a 1989 marketing relationship with Hewlett-Packard, and bundled into Ansoft products. In 1997 Hewlett-Packard acquired Optimization Systems Associates Inc. (OSA), a company John Bandler founded in 1983. HP's acquisition was driven by the HP's need for an optimization capability for HFSS. After various business relationships over the period 1996–2006, HP (which became Agilent EEsof EDA division) and Ansoft went their separate ways: Agilent with the critically acclaimed FEM Element and Ansoft with their HFSS products, respectively. Ansoft was later acquired by Ansys.
Gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode millimeter wave and terahertz spectrum modeling method
ActiveCN104268355AExcellent indicatorsSpeed up developmentSpecial data processing applicationsThermionic emissionHFSS
The invention discloses a gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode millimeter wave and terahertz spectrum modeling method and relates to the diode modeling technical field. The gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode millimeter wave and terahertz spectrum modeling method comprises describing the nonlinear junction characteristics of a mixing schottky diode junction through a measurement based empirical formula and namely performing the formula description on the diode junction through a thermionic emission model; establishing a three-dimensional electromagnetic model of a gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode and obtaining an S parameter of parasitic parameters in the millimeter wave and terahertz spectrum through a commercial HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator); establishing a circuit level model corresponding to the gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode in circuit simulation software such as ADS; performing comparison on the established model and the actual encapsulation testing diode S parameter, correcting the empirical formula of the diode junction and obtaining an accurate model of the gallium arsenide base mixing schottky diode in the millimeter wave and terahertz spectrum.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
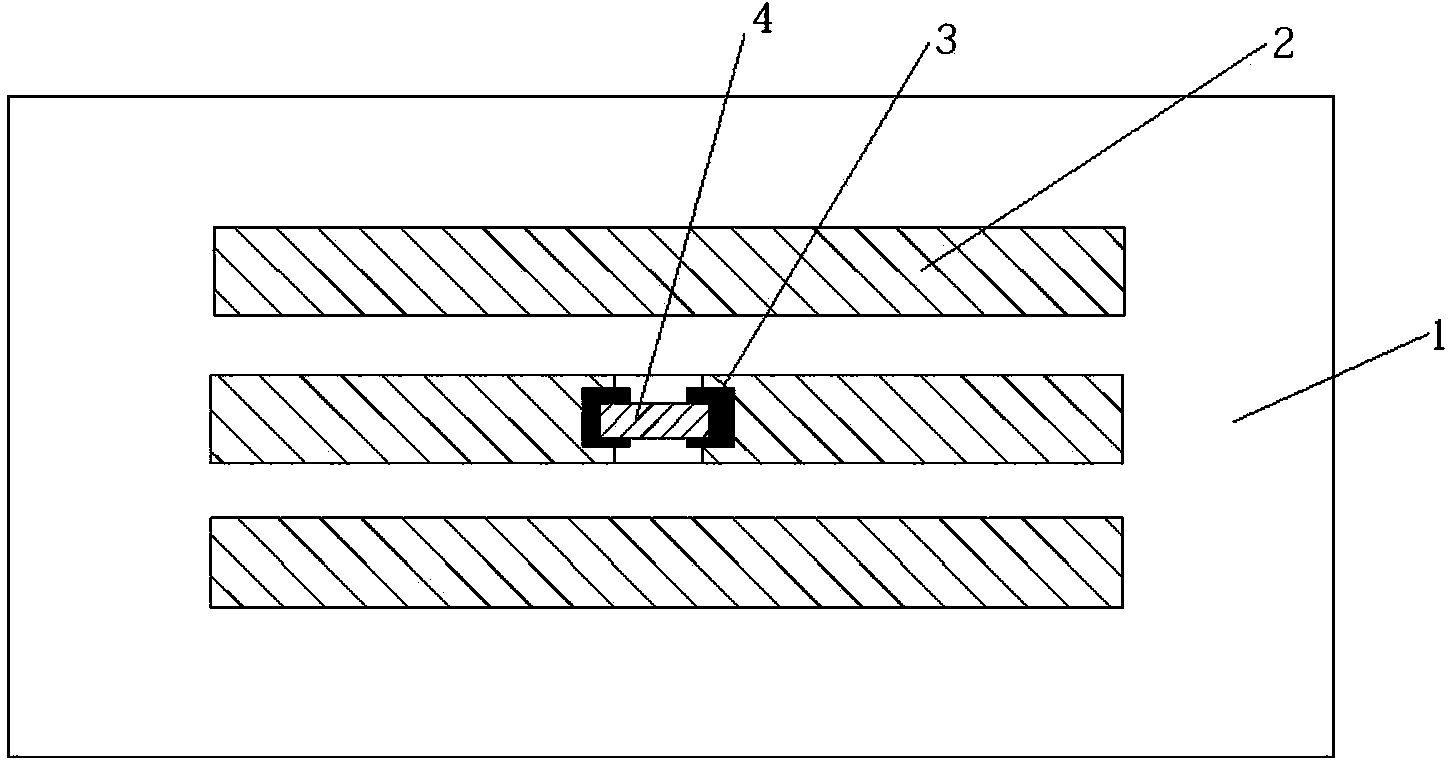
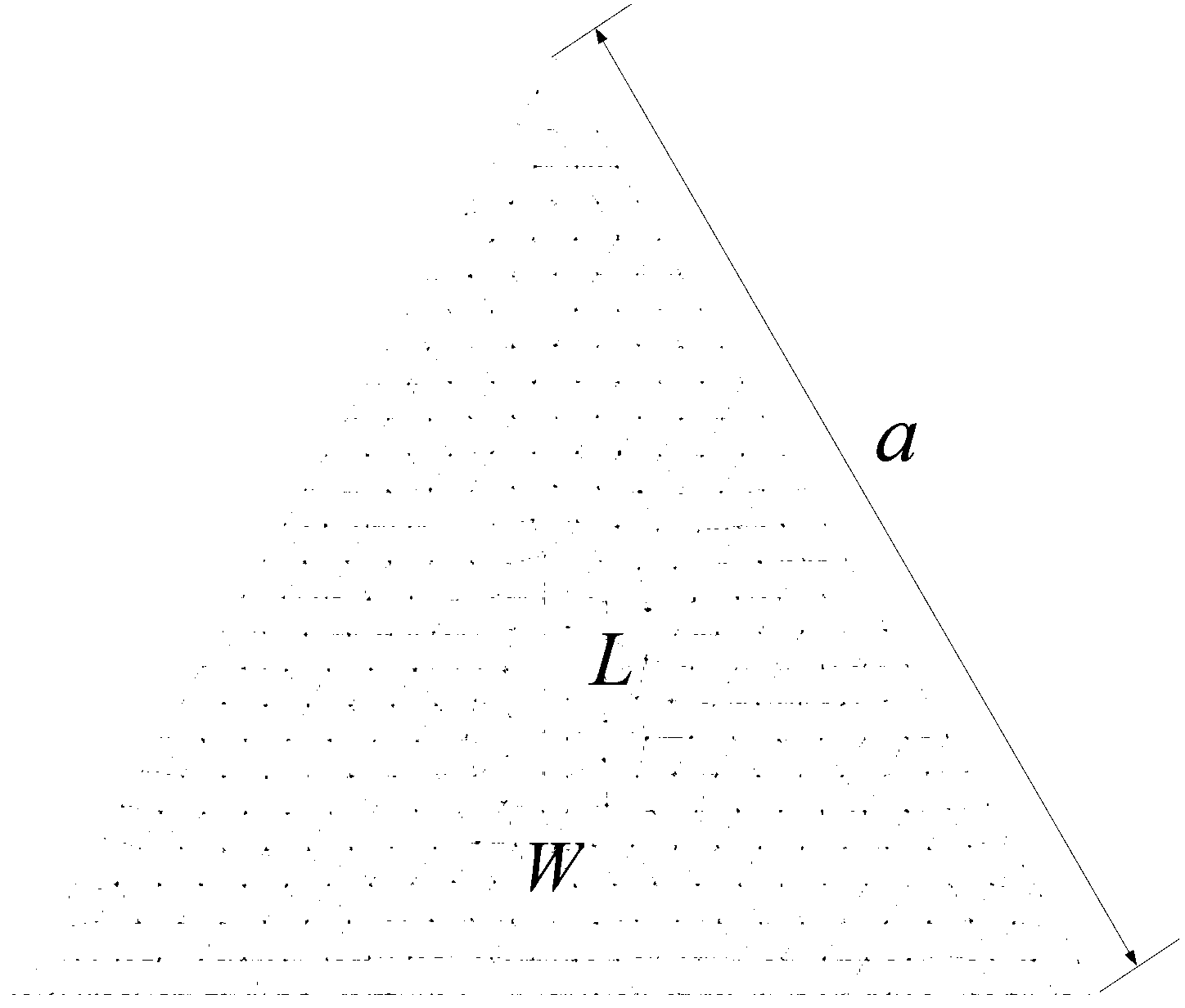
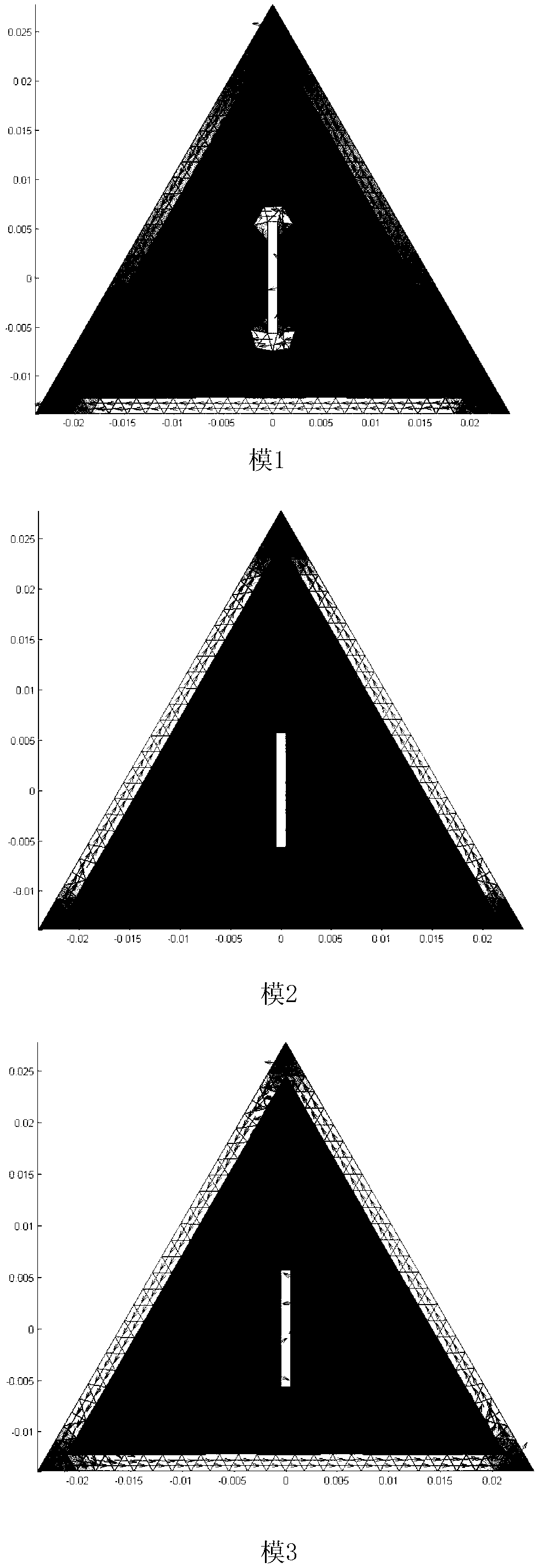
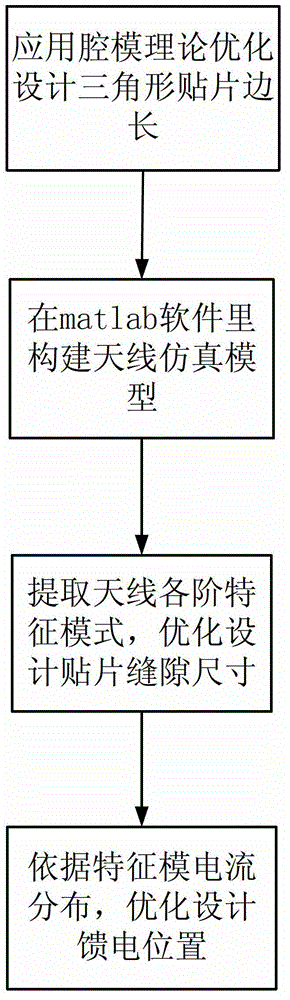
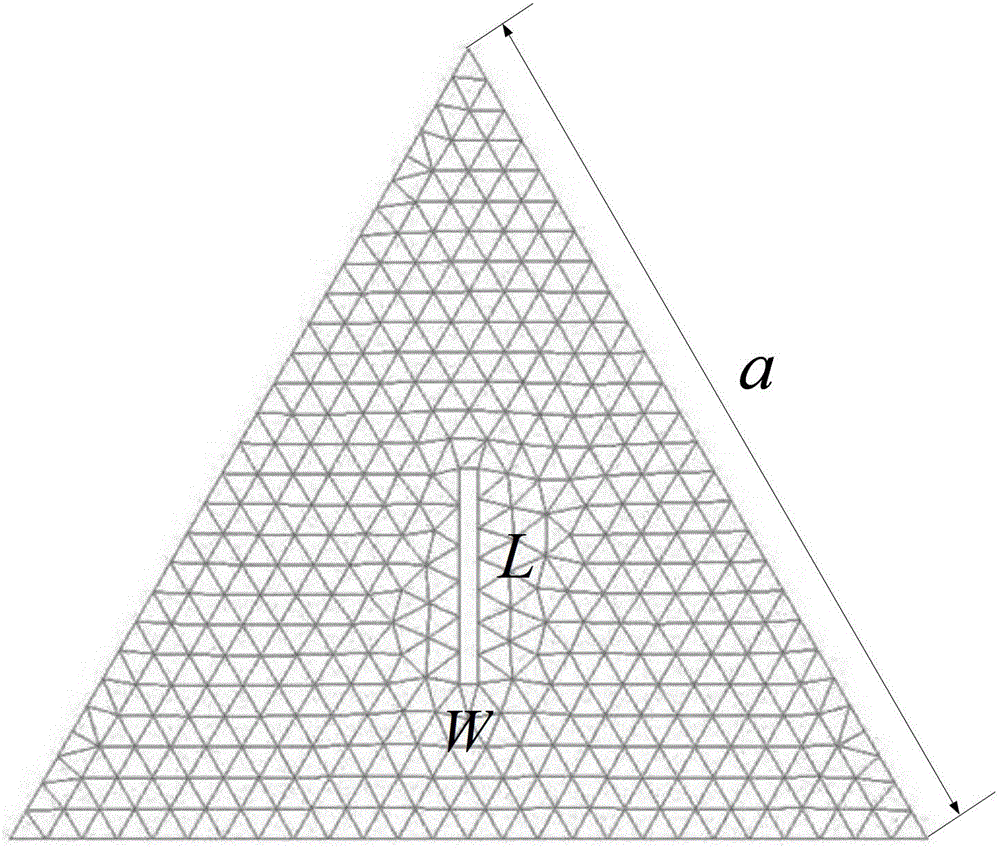
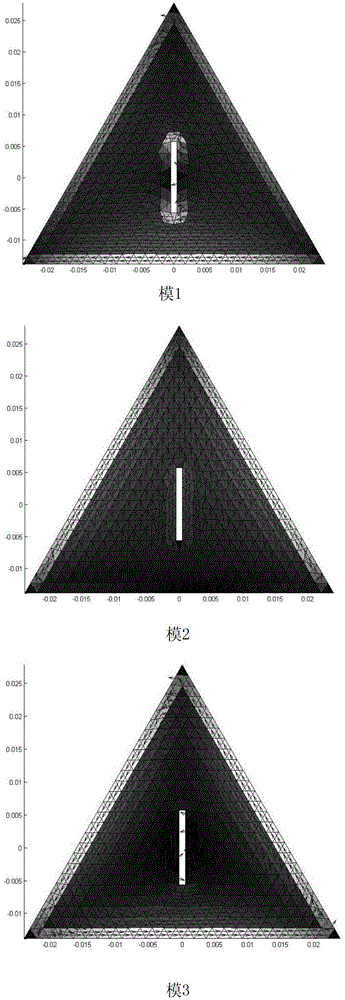
Optimum design method of circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna based on characteristic module theory
ActiveCN103311664AEasy to handleSatisfactory impedanceRadiating elements structural formsAdaptive controlAntenna feedOperating frequency
The invention discloses an optimum design method of a circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna based on a characteristic module theory. The optimum design method includes steps of 1 obtaining the optimum side length a of a triangular patch; 2 optimally designing the gap size of the patch; and 3 optimally designing the feed position. The single feed point circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna is simple in structure and easy to process and has satisfactory impedance and axial ratio bandwidth. The optimum design method can explain the working principle of the circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna in the aspect of the physical concept, designs the determined antenna feed position and working frequency, and greatly improves the efficiency compared with manual antenna parameter adjustment processing by aid of High Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) simulation software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
8mm wave dielectric loaded moment circle transition horn antenna
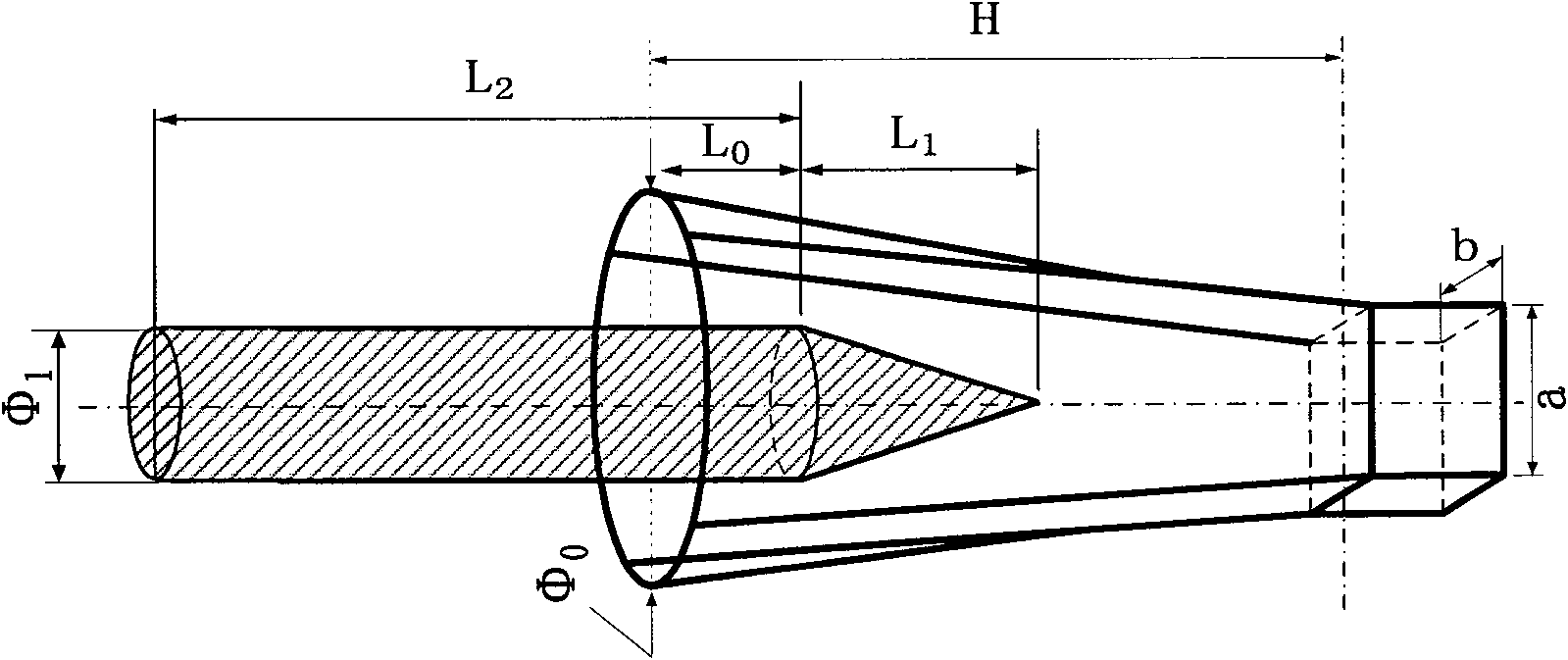
The invention relates to an 8mm wave dielectric loaded moment circle transition horn antenna. The antenna consists of a rectangular waveguide, a moment circle transition horn and a dielectric rod, wherein a moment circle transition section in the moment circle transition horn is in a smooth transition mode; the dielectric rod consists of a gradient taper section and a uniform cylindrical section, and is coaxial with the moment circle transition horn; the cylindrical section of the dielectric rod is extended into the moment circle transition horn mouth surface and is determined by a numerical analysis method; and the dielectric rod is made of polytetrafluoroethylene and a relative dielectric constant Epsilon r is 2. In the antenna, each parameter of the antenna is optimally designed by a finite element method of a high-frequency structure simulator (HFSS) for an electromagnetic field, so that the antenna can realize a narrow beam width under a smaller caliber, and the input standing wave ratio is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method of simulating the absorption of plane waves using fem software tools
InactiveUS20140180604A1Effective visualizationComponent separationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsValidation methodsImpedance matching
A novel and useful method of visualization by detection of EM radiation being irradiated or reflected from objects in the imager's field of view using Finite Element Method (FEM) simulation software tools. The methodology provides a verification method of antenna operation from an electrical point of view since bolometer performance cannot be estimated using regular antenna parameters such as directivity, gain, impedance matching, etc. as the bolometer does not behave as an antenna but rather behaves as an absorber. An incident wave is triggered on the absorber and the absorption of the bolometer structure is estimated using commercially available Finite Element Method (FEM) software (e.g., ANSYS HFSS, CST Microwave Studio, etc.). How much of the energy is reflected is subsequently measured. The energy which is not reflected is considered to be absorbed by the absorber.
Owner:IBM CORP
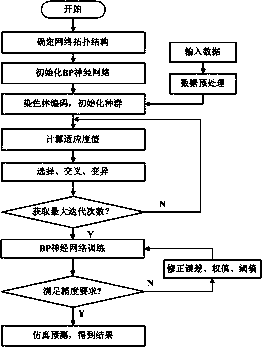
Spiral inductance optimization method based on HPSO algorithm and GA-BP algorithm
PendingCN110069805ANot easy to fall intoOptimize weightArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationTime efficientData set
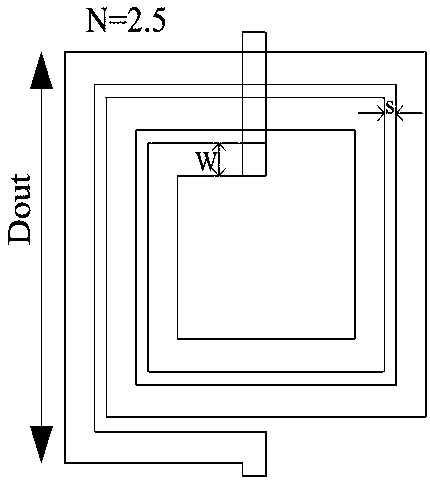
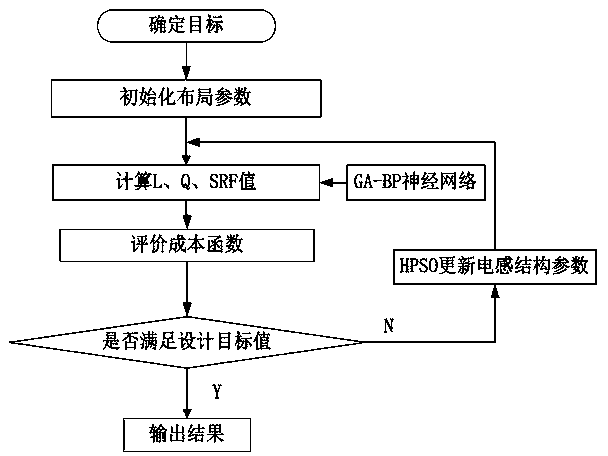
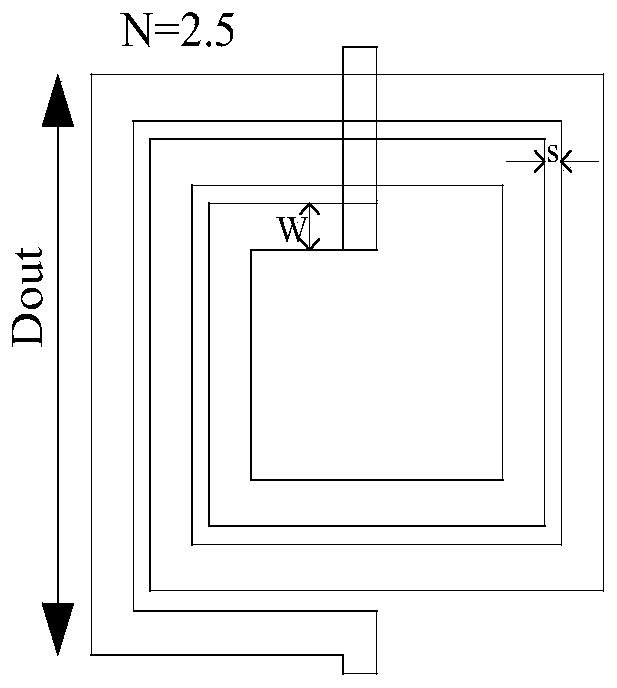
The invention discloses a spiral inductance optimization method based on HPSO algorithm and GA-BP algorithm. The spiral inductance optimization method comprises the steps that an on-chip spiral inductance data set is manufactured through electromagnetic simulation software HFSS, and data preprocessing is carried out; a genetic algorithm (GA) is adopted to optimize the BP neural network, then the optimized BP neural network is trained, and a GA-BP model is established; layout search is performed on the on-chip spiral inductor by adopting HPSO to obtain structure parameters meeting constraint conditions under a specific target inductance value; characterization parameter prediction is carried out on the structure parameters of the on-chip spiral inductor under the specific inductance value by using the GA-BP model. The method can help designers compromise and analyze the inductive performance and the inductive size, enables the circuit to have the optimal performance and the optimal size, not only guarantees the accuracy of the calculation result, but also can save time and cost, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
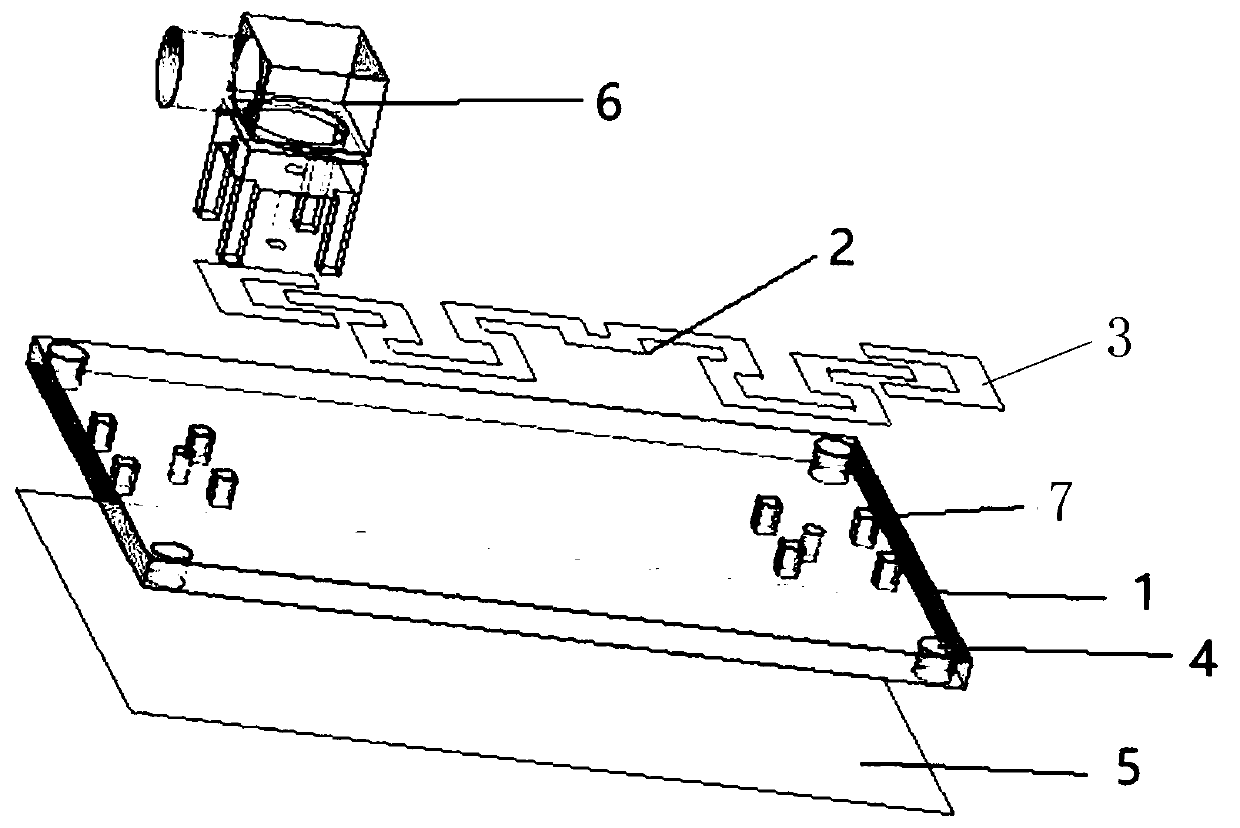
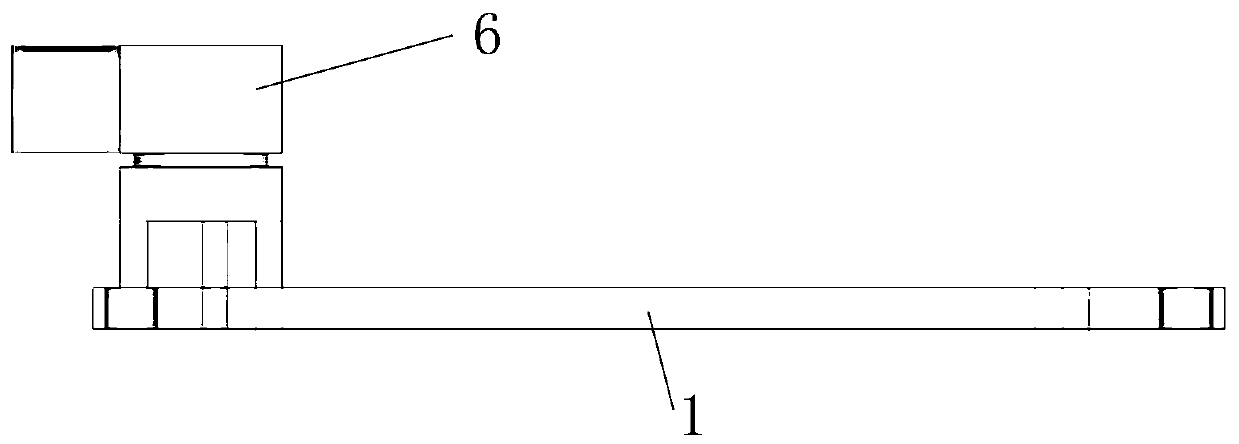
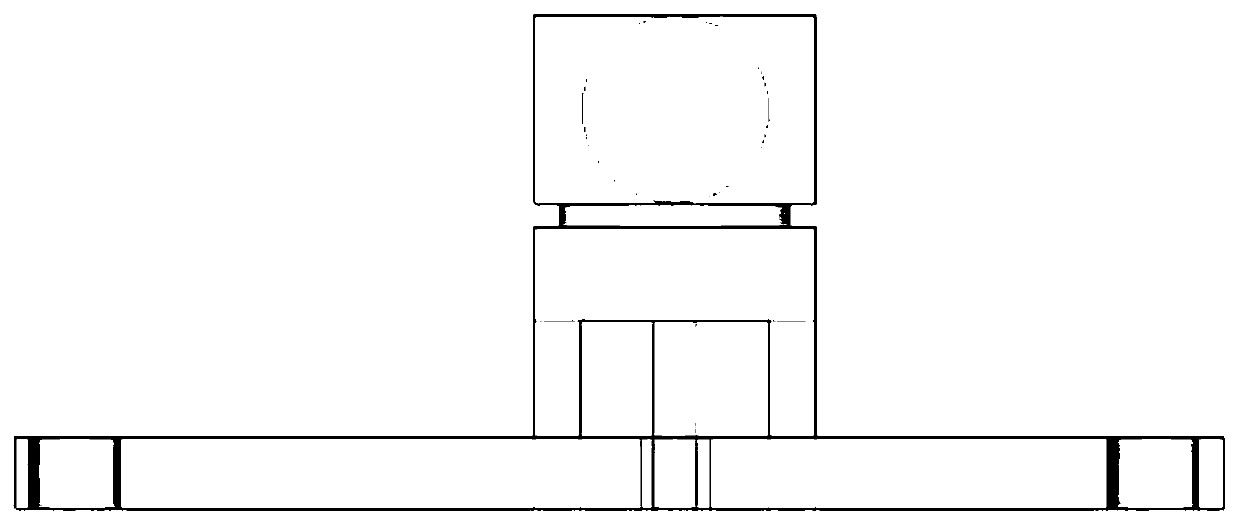
Planar microwave resonant antenna with dual frequency points and high radiation efficiency
ActiveCN110797653AShorten the lengthSmall footprintSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMetal foilDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a novel planar microwave resonant antenna with dual frequency points and high radiation efficiency, including a rectangular dielectric substrate, a grounding radiation patch onthe bottom surface of the substrate and a rectangular broken line symmetrically concave metal foil feeder line arranged on the upper surface of the dielectric substrate. A SMA joint is used to directly weld the inner part onto the feeder line and connect the grounding radiation patch. The simulation design is carried out by means of electromagnetic simulation software ANSYS HFSS, real-time simulation is carried out by changing the shape and size of a feed antenna, multi-parameter simulation data and simulation diagrams are combined for calculation, the structure, material and process of the antenna are optimized, and the reliability of a simulation result is confirmed. The effective radiation resistance of the antenna is increased, the generation of high-order modes is reduced, the radiation efficiency of the antenna is improved, the overall effect of the antenna system is improved, the requirements of double frequency points and high radiation efficiency are realized on the same substrate and the same plane, and the application of double frequency points is realized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Planar inverted F-shaped antenna resonant frequency prediction method based on semi-supervised learning
PendingCN111709192AImprove forecast accuracyShorten the timeDesign optimisation/simulationNeural learning methodsAlgorithmElectromagnetic optimization
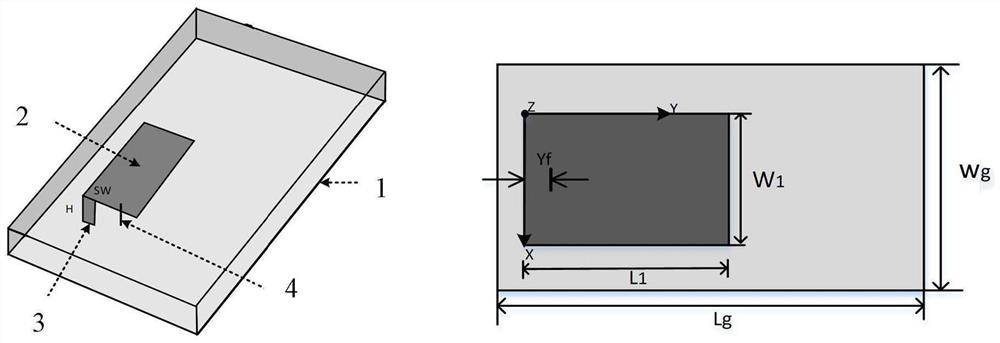
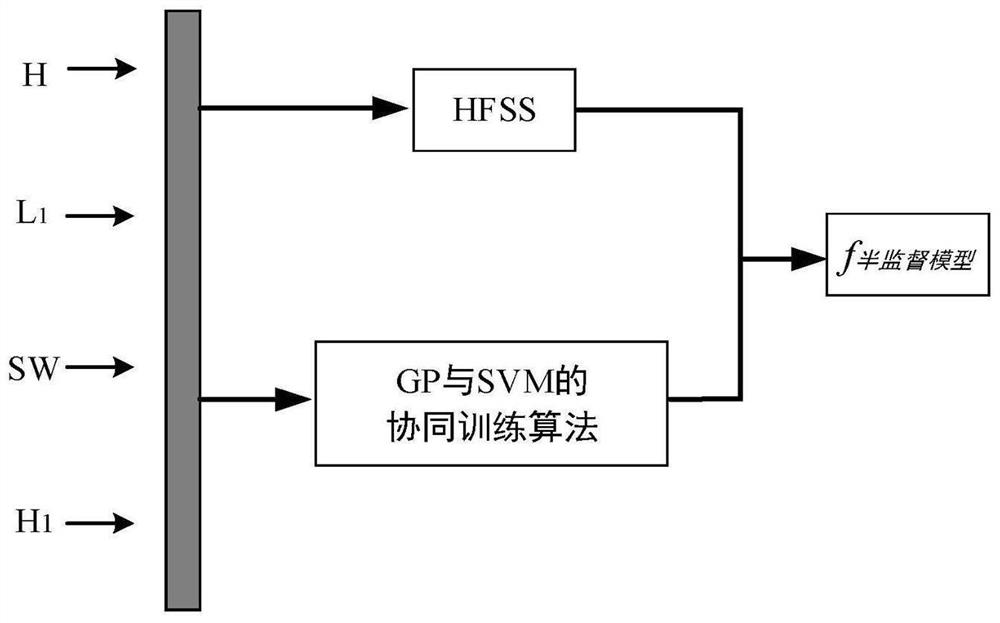
The invention discloses a planar inverted F-shaped antenna resonant frequency prediction method based on semi-supervised learning. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a mapping relationship between four related parameters of the width of a short-circuit metal sheet, the length of a radiation metal sheet, the width of the radiation metal sheet and the height of the radiation metal sheet of the planar inverted F-shaped antenna and an actually measured resonant frequency by using a Gaussian process and a support vector machine; carrying out iterative training by utilizing a cooperative training method of a Gaussian process and a support vector machine in combination with unmarked data, wherein the trained semi-supervised cooperative training model can be used for predictingresonant frequencies of other planar inverted F-shaped antennas. According to the method, the problems that in existing electromagnetic optimization design, more marking samples are needed during model training, electromagnetic simulation software HFSS needs to be called for multiple times, the calculation cost is high, and consumed time is long can be solved; compared with a modeling mode basedon traditional supervised learning, the resonant frequency prediction capability of the method has certain advantages.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Design method of anti-interference scatter communication system antenna array
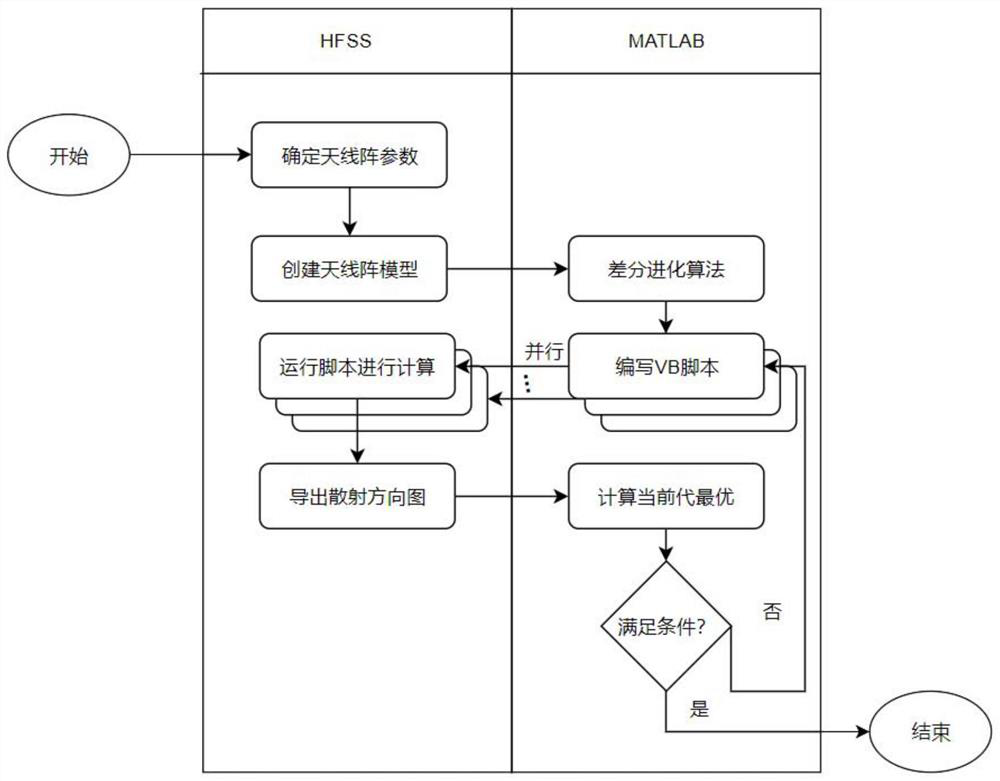
PendingCN111783301AQuality improvementIncrease distanceGeometric CADAntenna arraysCommunications systemInterference resistance
The invention provides a design method of an anti-interference scattering communication system antenna array, which is a communication system scattering field antenna array design method capable of enhancing scattering signal intensity and realizing scattering field beamforming, and the design can be used for a scattering communication system to improve communication performance such as communication radius expansion and interference resistance. The method is characterized in that a design method capable of realizing beamforming in any direction in a three-dimensional space is provided based on geometrical characteristics of the three-dimensional space and characteristics of an antenna array; MATLAB and HFSS are adopted to carry out joint design simulation; the HFSS establishes a scatter communication system antenna array model, the array element antenna spacing of the scatter communication system antenna array model is set to be a variable quantity, and MATLAB calculates the optimal array element antenna spacing by adopting a differential evolution algorithm and the HFSS in a combined manner. According to the method, the differential evolution algorithm and the HFSS are adopted onthe MATLAB for joint calculation, so that the antenna scattering direction in the scattering communication system antenna array can be centralized.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Ultra-wideband omnidirectional antenna applied to wideband electromagnetic environment monitoring system and design method
PendingCN112670706AWith ultra-wideband characteristicsGood omnidirectional characteristicsRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsUltra-widebandAntenna bandwidth
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband omnidirectional antenna applied to a wideband electromagnetic environment monitoring system and a design method. The antenna comprises a radiator, a metal floor, a coaxial feed structure and a feed probe. The method comprises the following steps: 1, designing initial parameters of a dipole structure of an antenna radiator; 2, creating an initial antenna model in three-dimensional electromagnetic simulation software HFSS, and performing simulation; 3, setting a parameter scanning interval of the feed probe according to the surface current distribution condition of the antenna, and performing parameter scanning; and 4, determining the optimal size of the antenna according to a parameter scanning result. The antenna can solve the problems that a traditional front-end receiving antenna is narrow in bandwidth and large in weight, has high performance and portability, has the ultra-wideband characteristic, and has the sound omni-directional characteristic within the wide frequency band.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Spiral inductor modeling method based on random forest
InactiveCN111191361ASimplify the development processSimplify optimizationDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designAlgorithmOriginal data
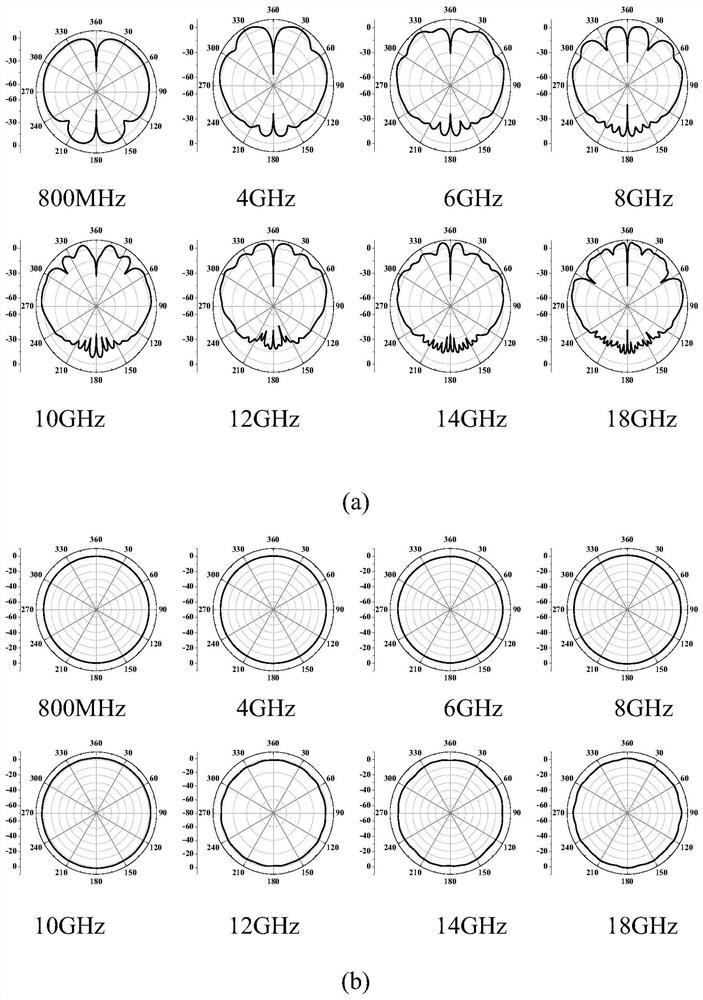
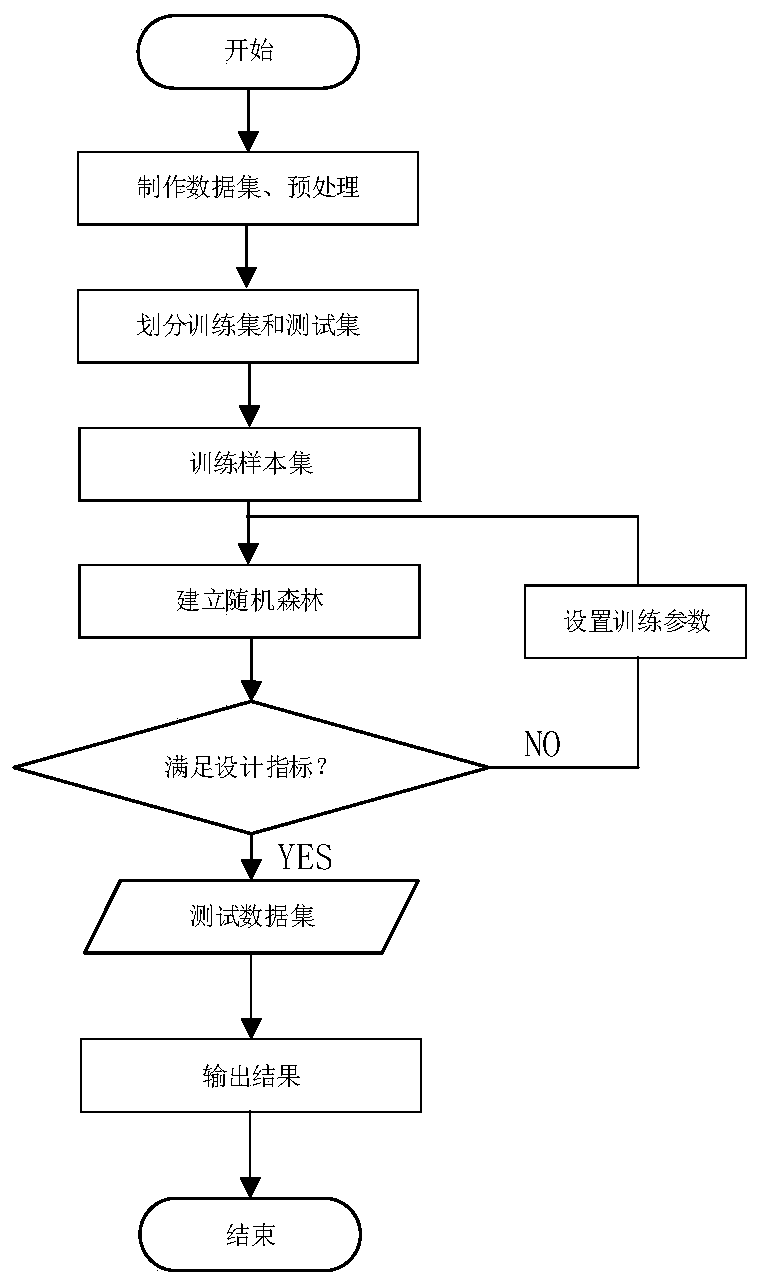
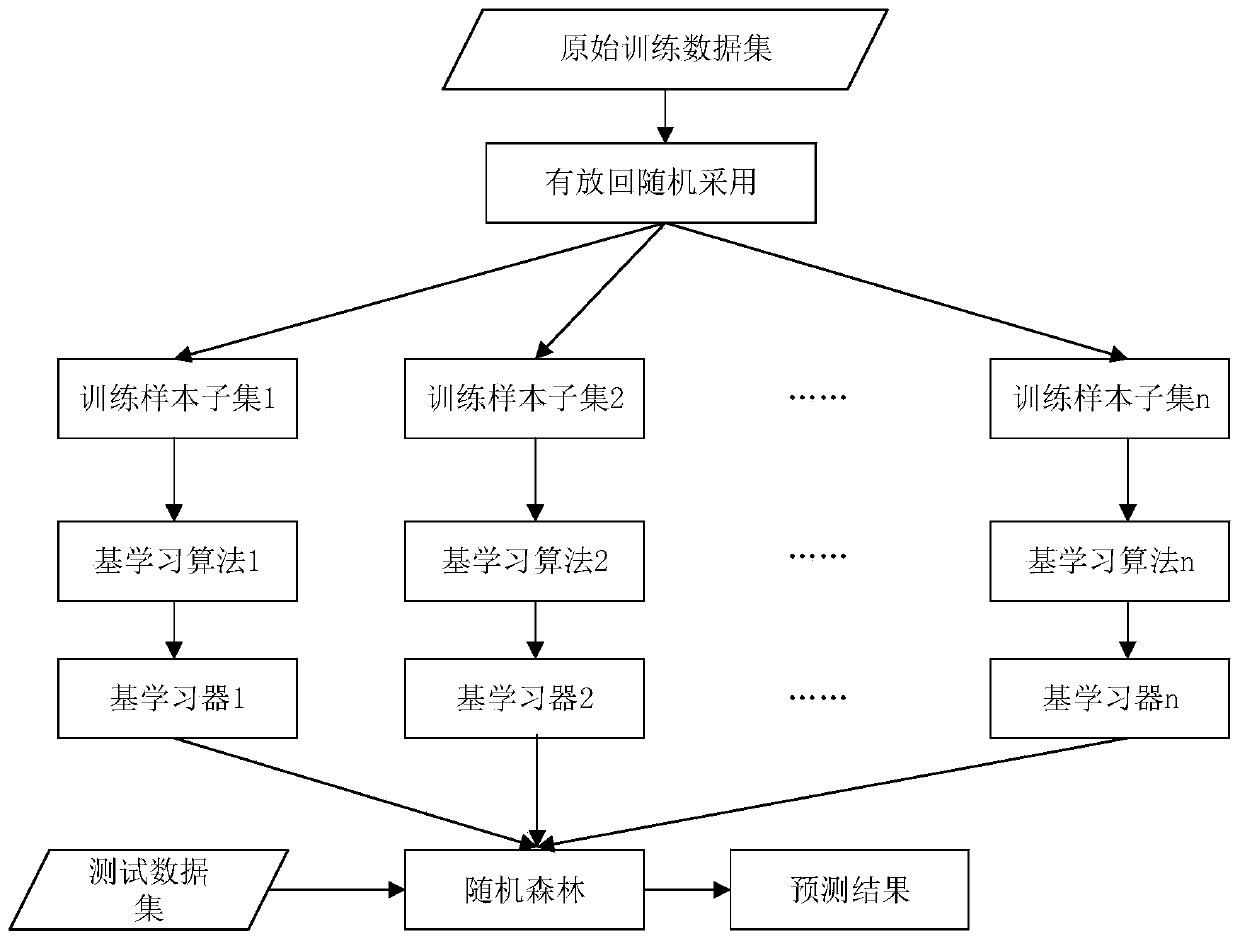
The invention discloses a spiral inductor modeling method based on a random forest, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining structural parameters and corresponding performance parameters of a spiral inductor through ANSYS HFSS electromagnetic simulation software, and constructing an original data set of the spiral inductor; 2, performing normalization processing on the originaldata set of the spiral inductor; 3, randomly dividing the normalized original data set into an original training sample set and a test sample set; 4, training the training sample set by using a randomforest algorithm, and obtaining a trained spiral inductance prediction model by using structural parameters of the spiral inductance as input and performance parameters as output; and 5, inputting the test sample set into the trained spiral inductance prediction model to obtain corresponding spiral inductance performance parameters, and evaluating the prediction precision of the model. The spiralinductor modeling method based on the random forest is established, the development and optimization of spiral inductors by designers are simplified, the research efficiency is improved, the cost issaved, and the integrated circuit design is accelerated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Passive intermodulation suppression method of circulator for communication
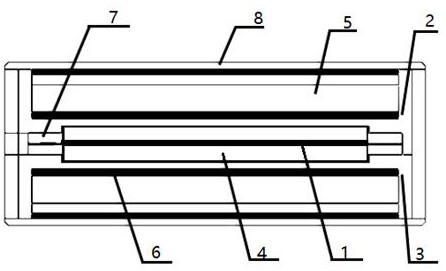
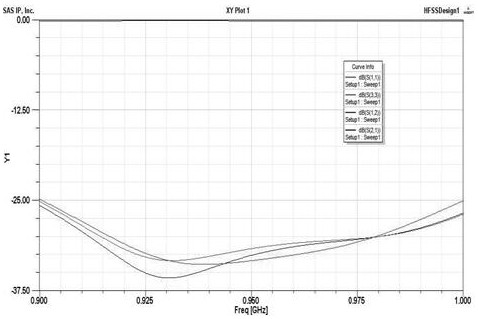
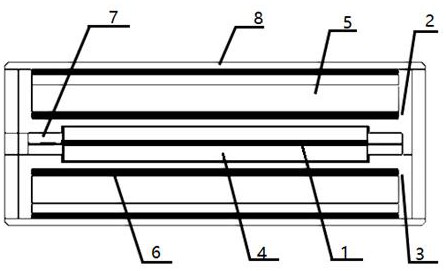
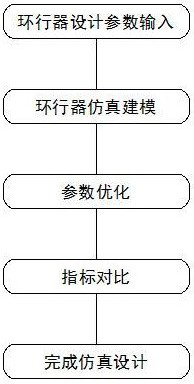
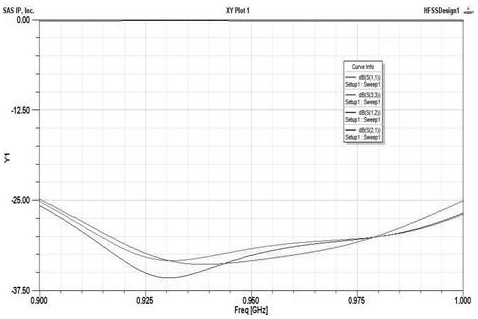
The invention discloses a passive intermodulation suppression method for a circulator for communication. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a frequency band and a power indexof a circulator to be machined, and an expected PIM value expected to be reached under the power index; (2) establishing a simulation model of the circulator in HFSS simulation software, and obtaining maximum field intensities A and B at (2f<1>-f<2>) and (2f<2>-f<1>) under the power index; (3) calculating a PIM value of the simulation model according to the A and the B, and marking the PIM valueas a simulation PIM value; and (4) comparing the simulation PIM value with the expected PIM value, and adjusting the structure of the simulation model in the HFSS simulation software according to a comparison result until conditions are met. According to the method of the invention, the determinant causing the passive intermodulation of the circulator is determined; and a method for quantitativelyanalyzing the passive intermodulation index of the circulator by using the determinant is provided; and the method is also suitable for other gyromagnetic ferrite material-based microwave passive devices with three-order passive intermodulation inhibition requirements.
Owner:中国电子科技集团公司第九研究所
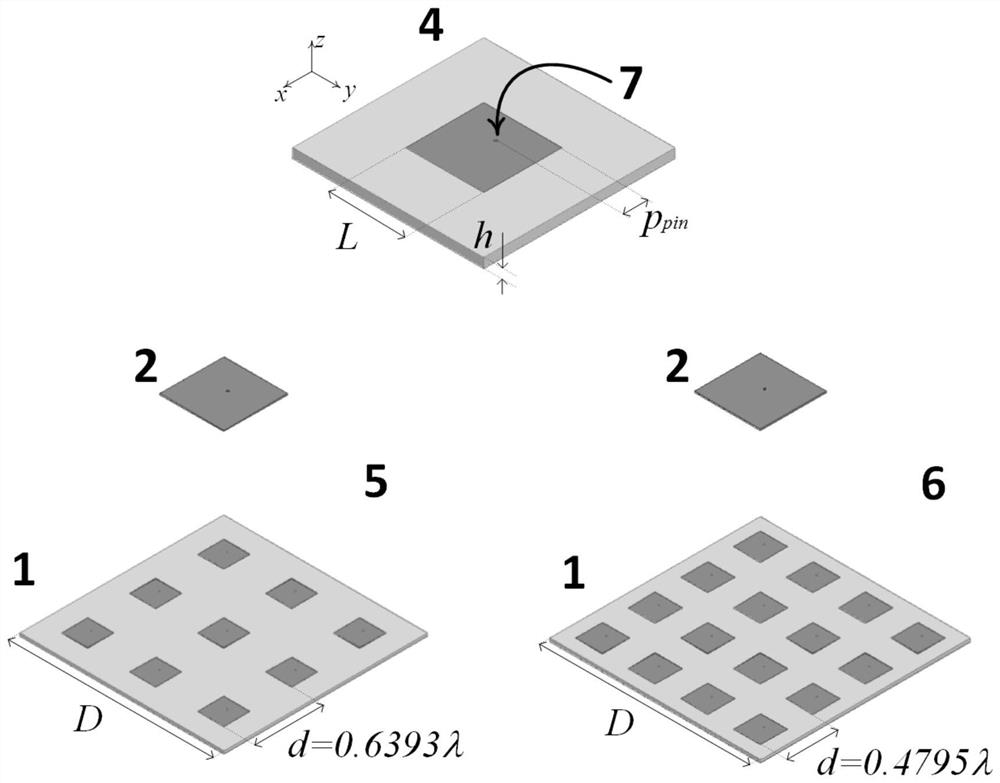
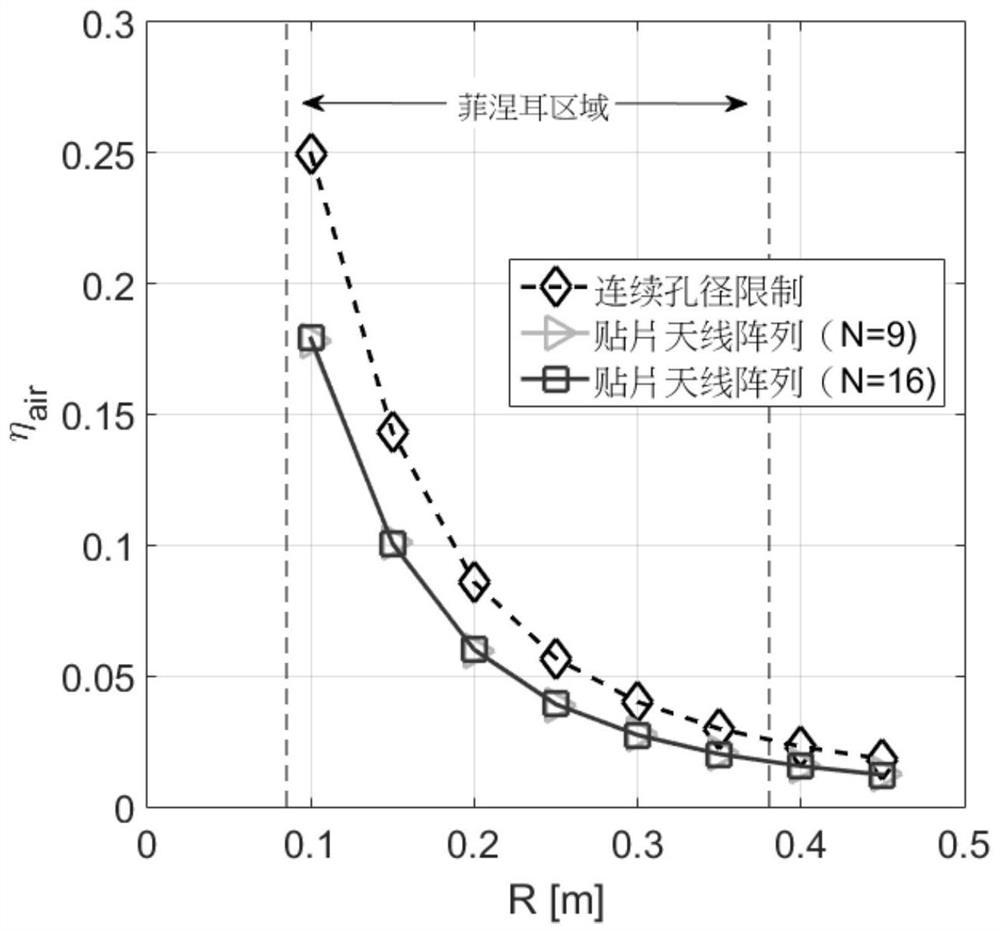
Metamaterial antenna array for efficient wireless energy transmission in Fresnel area
InactiveCN112531354AEasy to synthesizeExtended ellipsoidal wave functionParticular array feeding systemsDesign optimisation/simulationHFSSGenetics algorithms
The invention discloses a metamaterial antenna array for efficient wireless energy transmission (WPT) in a Fresnel area, is applied to wireless power transmission, and aims to solve the problem of lowwireless power transmission efficiency of an existing small-size antenna array. The antenna array 19 comprises a plurality of closely spaced sub-wavelength size LC (ELC) cells connected to the feed network through metal vias; a genetic algorithm optimization tool of Ansys HFSS and an ELC equivalent design model (including a Floquet port and master / slave boundary conditions) are used for optimizing LC (ELC) unit cell parameters, so that the maximum absorption (or radiation) efficiency and impedance matching are achieved on the working frequency, and the antenna array serves as a transmitting antenna 1 and a receiving antenna or antenna array 2 of a WPT system. The wireless power transfer efficiency can be very close to a continuous aperture limit value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
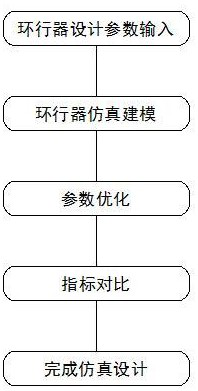
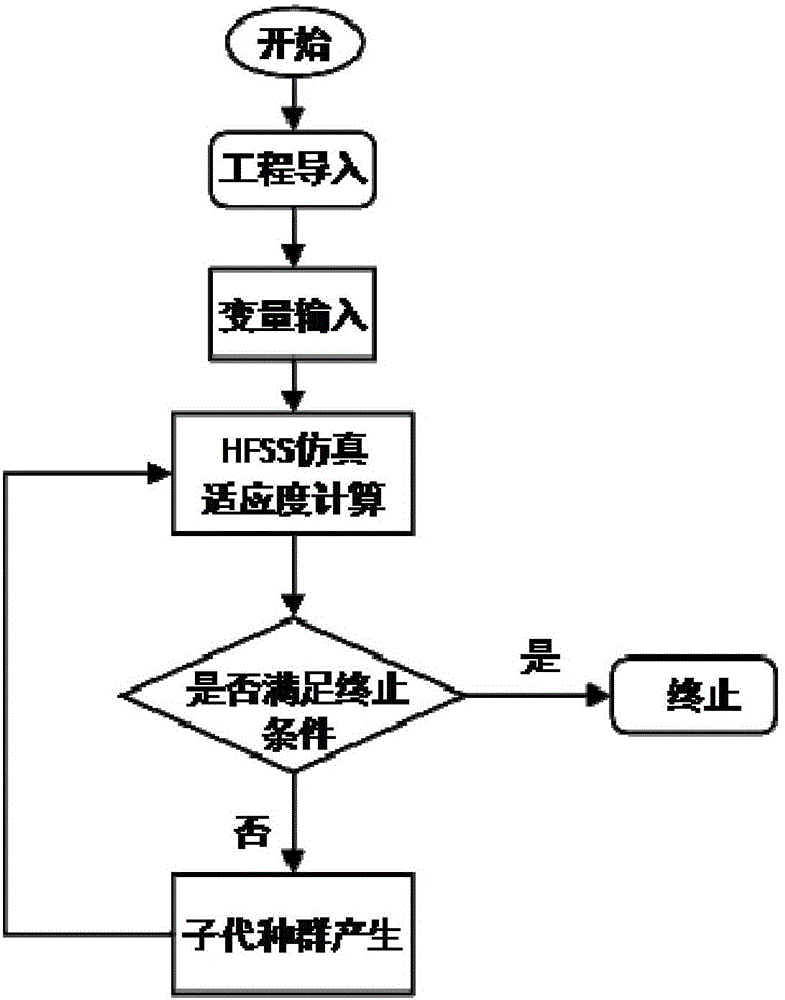
Optimization algorithm based HFSS project optimization method
ActiveCN104992015AAvoid record requirementsEliminate tedious and error-prone calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsHFSSInstability
The invention belongs to the field of HFSS project simulation design parameter optimization, and particularly relates to an optimization algorithm based HFSS project optimization method. The method comprises the following steps: a project importing step; a variable input step; an HFSS simulation fitness calculation step; and a stop condition judgment step. Therefore, the optimal fitness value of past populations is obtained and output as a result. Through the scheme, the situation of optimization program termination caused by calculation errors generated due to instability of VBScripts carrying sub HFSS project information can be effectively avoided; and the internal parameter optimization efficiency can be improved while the simulation design is simplified.
Owner:ANHUI SUN CREATE ELECTRONICS
Multi-frequency-point dielectric constant measuring device based on stepped impedance resonance structure
ActiveCN112782486ASimple structureLow costDielectric property measurementsHigh level techniquesMaterial under testHFSS
The invention relates to a multi-frequency-point dielectric constant measuring device based on a stepped impedance resonance structure. The measuring device comprises a first dielectric layer, a second dielectric layer and a third dielectric layer from top to bottom, and is characterized in that a first metal layer, a second metal layer and a third metal layer are etched on the lower surface of the first dielectric layer, a fourth metal layer is etched on the upper surface of the third dielectric layer, and a cavity filled with a tested material is arranged in the center of the second dielectric layer. According to the invention, signal lines with different widths are utilized to form microstrip lines with different impedances so as to form a stepped impedance resonance structure, the structure can generate a plurality of discrete resonance frequency points in a wide frequency band, and through electromagnetic parameters measured by a vector network analyzer and electromagnetic parameters simulated by electromagnetic simulation software HFSS, the dielectric constant of a measured material in the cavity of the measured solid or liquid or solid powder can be deduced, so that finally the multi-frequency-point dielectric constant measuring device based on the stepped impedance resonance structure is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
RFID read-write antenna design method for LCD screen
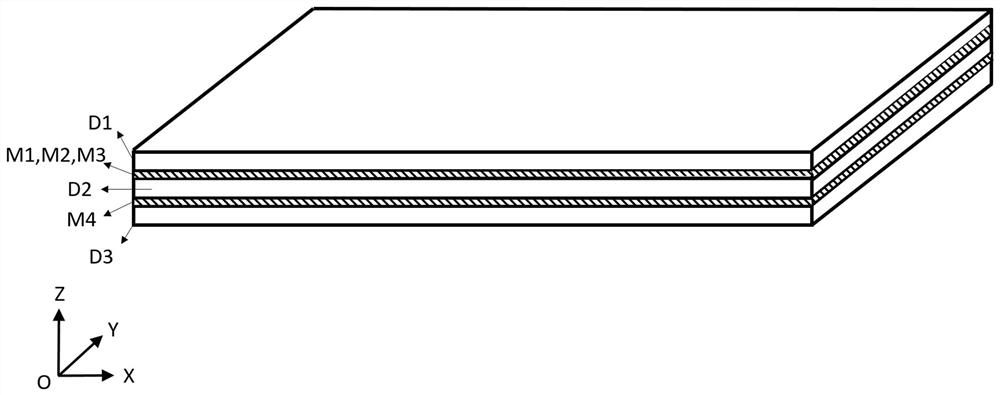
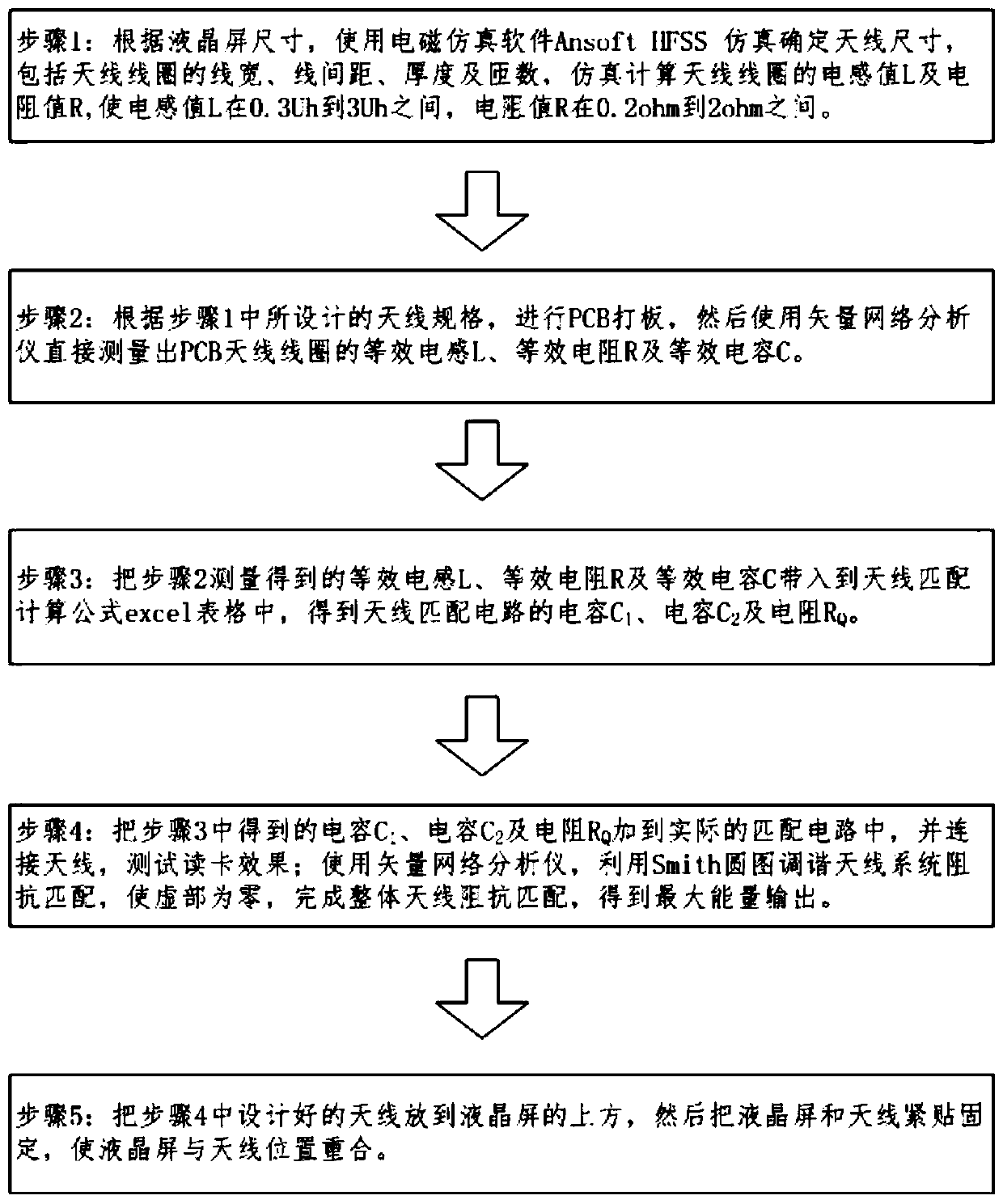
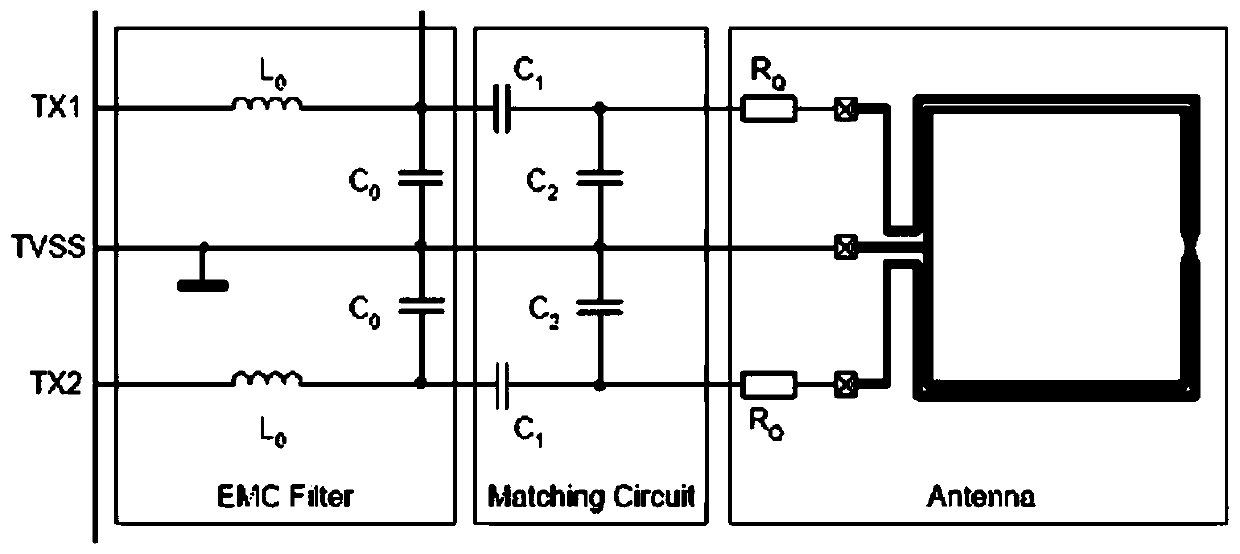
PendingCN109713450AAchieve coincidenceIncrease the usable areaNear-field transmissionAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna designCapacitance
The invention provides an RFID read-write antenna design method for an LCD screen, and the method comprises the following steps: performing simulation through electromagnetic simulation software Ansoft HFSS according to the size of the LCD screen to determine the size of an antenna; performing PCB sample proofing, and then directly measuring an equivalent inductance L, an equivalent resistance R and an equivalent capacitance C of a PCB antenna coil by using a vector network analyzer; substituting the parameters into an excel table of an antenna matching calculation formula to obtain a capacitance C1, a capacitance C2 and a resistance RQ of an antenna matching circuit. The invention relates to the RFID read-write antenna design method for the LCD screen, so that an RFID radio frequency areaand an LCD screen display area are overlapped, the limitation that a traditional card swiping area and a traditional display area cannot be the same area is broken through, the display area is the card swiping area, the use area of the vehicle-mounted consumption terminal is expanded, and the size of vehicle-mounted equipment is greatly saved.
Owner:天津渤海化学股份有限公司
A method for simulating the return wave oscillation of a traveling wave tube
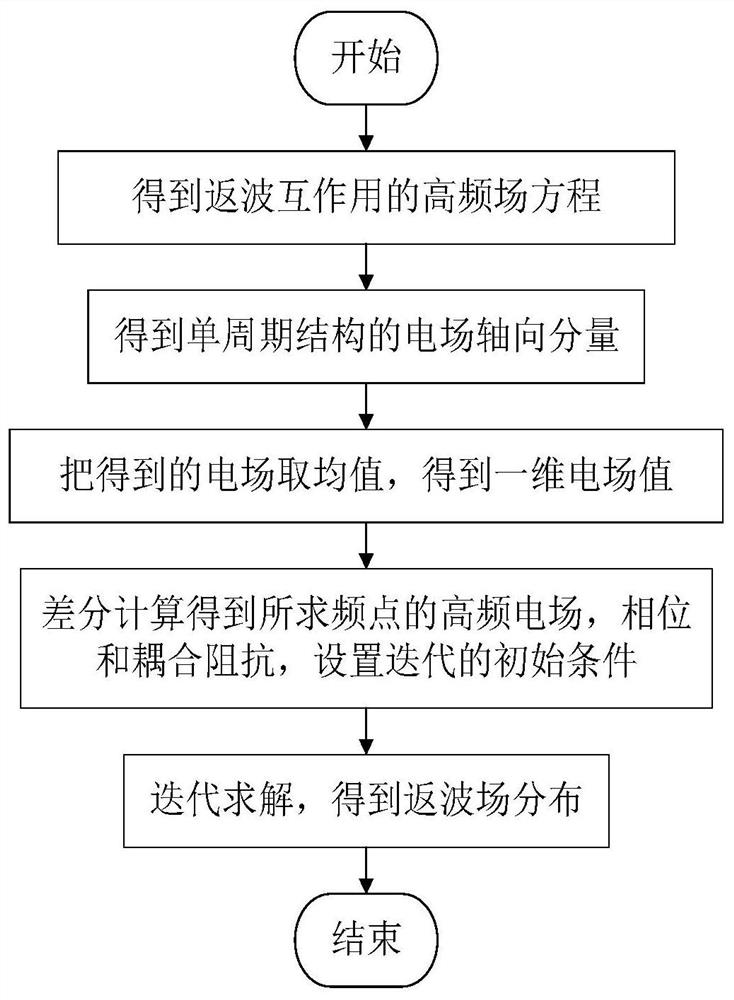
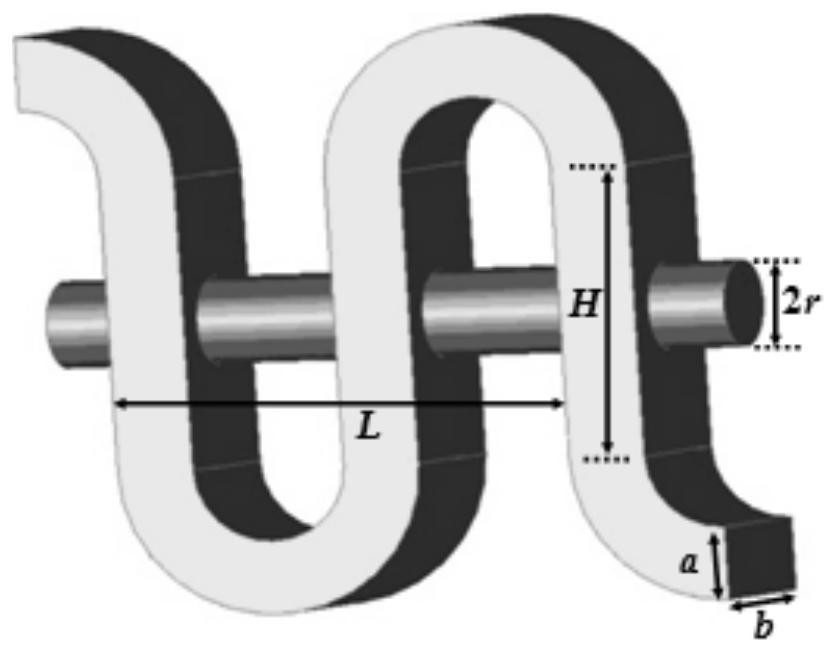
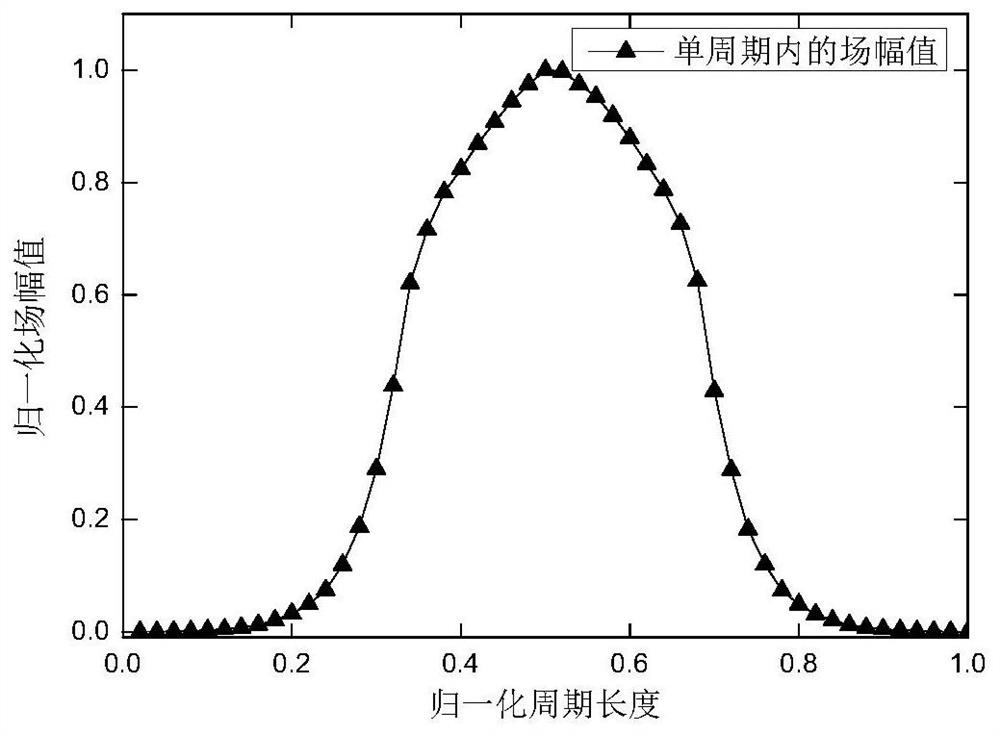
ActiveCN109033686BEase of return wave calculationTaking into account efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHFSSWave simulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of traveling wave tube return wave simulation, and in particular relates to a traveling wave tube return wave oscillation simulation method. The present invention obtains the high-frequency field distribution at any position in the periodic structure of the traveling wave tube through the high-frequency structure simulation software HFSS, and then combines the high-frequency field equation of the return wave, the electronic phase equation and the equation of motion to construct the equation group, and calculates through step-by-step iteration. The back-wave interaction result of the traveling wave tube is obtained; the method of the present invention can calculate the back-wave interaction in various periodic structures within a few minutes. Since the method of the present invention directly deals with the field distribution of a single period in the periodic structure, the present invention is not limited to a specific traveling wave tube, and can calculate the return waves of various periodic structures, which can be used for various The return wave calculation of traveling wave tube provides great convenience. The invention realizes both versatility and high efficiency in the research of the return wave oscillation of the traveling wave tube.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
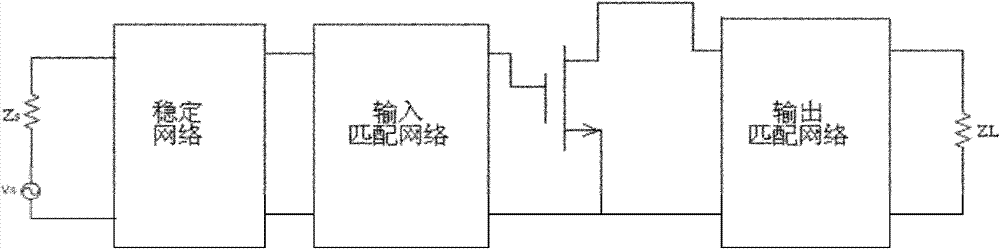
Method for manufacturing microwave hybrid integrated circuit based on Ansoft HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator)
ActiveCN102542075BAchieving Global Optimal DesignReduce performanceSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringOperability
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a microwave hybrid integrated circuit based on an Ansoft HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator). The method comprises the steps of: determining a source impedance and a leakage impedance: designing a prototype circuit of an input and output matching network; carrying out segmented optimization design by using the Ansoft HFSS; designing a prototype circuit of a stabilizing network; carrying out optimization design on an input part circuit; exporting simulation data of the output network and the input circuit to an ADS (Advanced Design System), electrically connecting with an active device, judging whether the circuit reaches the expected requirements including gain and stability, if yes, completing the design; and if not, carrying out fine control optimization on the circuit until reaching the requirement. On the premise of meeting full-frequency band stabilizing requirement, the invention realizes working frequency, gain and output power specified by the micro hybrid integrated circuit, and ensures that the microwave hybrid integrated circuit has better maneuverability.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sectional type through hole modeling method including influence of plane on resonance characteristic
ActiveCN102436516BReduce complexitySimplify the modeling processSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitancePhysical model
The invention discloses a sectional type through hole modeling method including influence of a plane on a resonance characteristic. The type through hole modeling method comprising the seven steps of: 1, decomposing a through hole structure in a center position of each flat plate; 2, extracting capacitor and inductor parameters in all parts of equivalent circuits of a through hole; 3, building an equivalent circuit map of a top microstrip line to an upper through hole vertical conversion structure and a lower through hole to a bottom microstrip line vertical conversion structure; 4, extracting a parameter impedance of the plane to a position where the center of a circle of the through hole is; 5, adding a Zpp obtained in the step 4 to an equivalent circuit model of an intermediate vertical through hole; 6, sequentially cascading all equivalent circuits of the through hole according to the upper part, the middle part and the lower part, and respectively adding a terminal port at two ends of the final equivalent circuit; and 7, building a one-order circuit model with a through hole structure in an ADS (Application Development System), establishing a physical model of the through hole in a simulation software HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator), calculating an S11 parameter and an S21 parameter, and comparing the obtained result with the result in the step 6.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Design method of X-waveband high-Q-value SIW transmission line
InactiveCN112838345ASimple designDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmHFSS
The invention relates to a microwave technology, in particular to a design method of an X-waveband high-Q-value SIW transmission line. From the perspective of the Q value, the relationship between the Q value of the X-band SIW and each parameter (d, p, a) is researched. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out gradual simulation analysis on a transmission line model by utilizing three-dimensional electromagnetic simulation software HFSS so as to obtain relatively reliable experimental data, and carrying out formula fitting by utilizing MATLAB so as to obtain a relation curve of a Q value, d and p and a corresponding fitting formula; then, obtaining the optimal combination between the high Q value of the substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) and various parameters through the obtained fitting formula. The high Q value design of the X-waveband SIW transmission line is realized on the premise that other parameters are met, the range of various parameters given by a traditional design formula is narrowed, and a more accurate quantitative relation is given.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
25G DFB laser high-frequency interconnection method
ActiveCN113626977AReduce high frequency return lossImprove yieldLaser optical resonator constructionDesign optimisation/simulationHFSSEngineering
The invention discloses a 25G DFB laser high-frequency interconnection method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) designing one or more of the shape and size of a ceramic substrate microstrip line, a mounting position of a DFB laser diode chip, a geometric shape and asize of a bonding gold wire, a driving source and an impedance value of a load terminal; and (2) establishing a high-frequency 3D structure HFSS simulation model of the DFB laser diode chip, verifying one or more designs in the step (1) through the simulation model, and then optimizing design parameters. Through verification of a simulation model, the optimized DFB laser high-frequency interconnection design has the advantages that the high-frequency return loss of the 25G DFB laser is reduced, the yield of devices and modules is improved, and the cost is reduced, and the high-frequency return loss of the optimized TO5625G TO tube DFB laser high-frequency interconnection design is restrained to be about-15dB.
Owner:南京光通光电技术有限公司
Method of Optimizing PCB Microstrip Line Structure Based on Response Surface Method and Genetic Algorithm
ActiveCN106844924BSimple designSimple calculationCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationDielectricElectromagnetic simulation
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
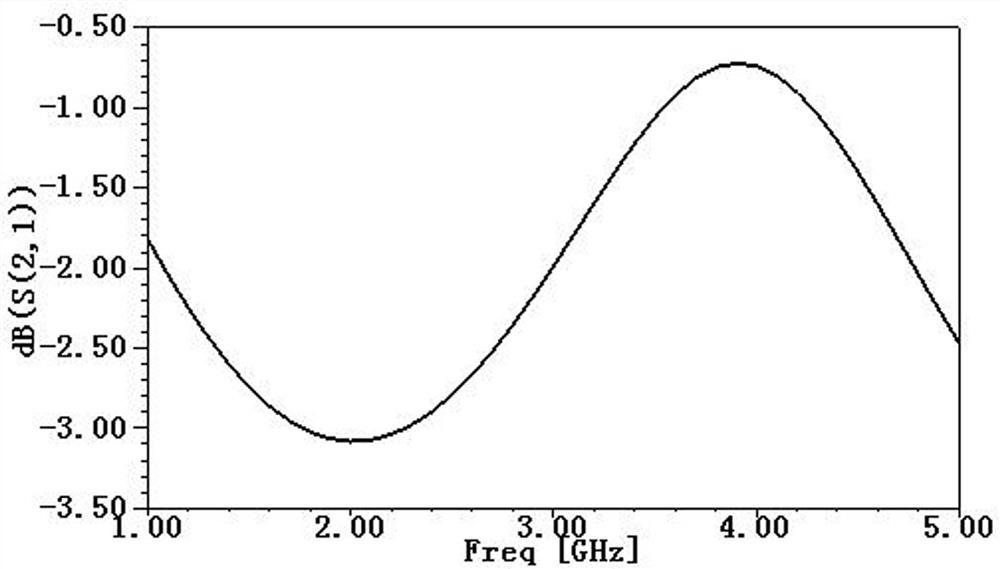
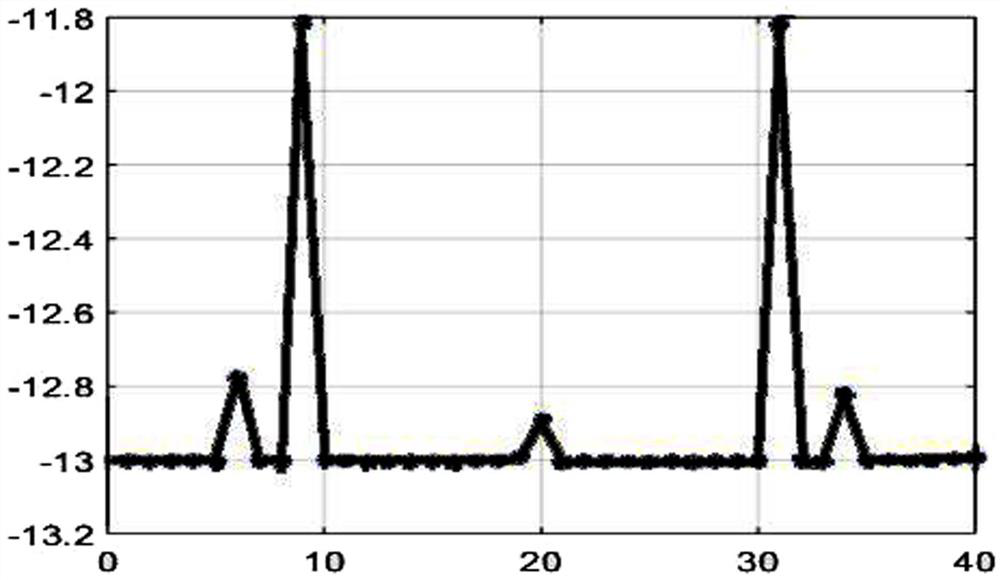
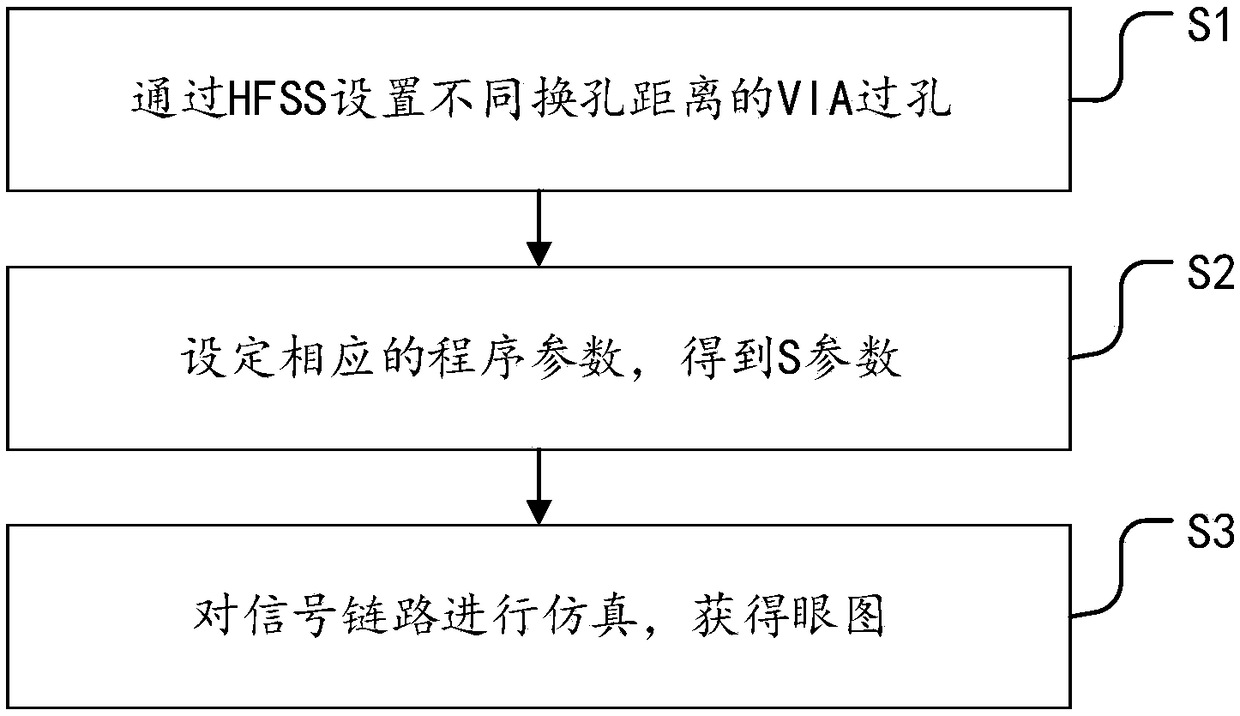
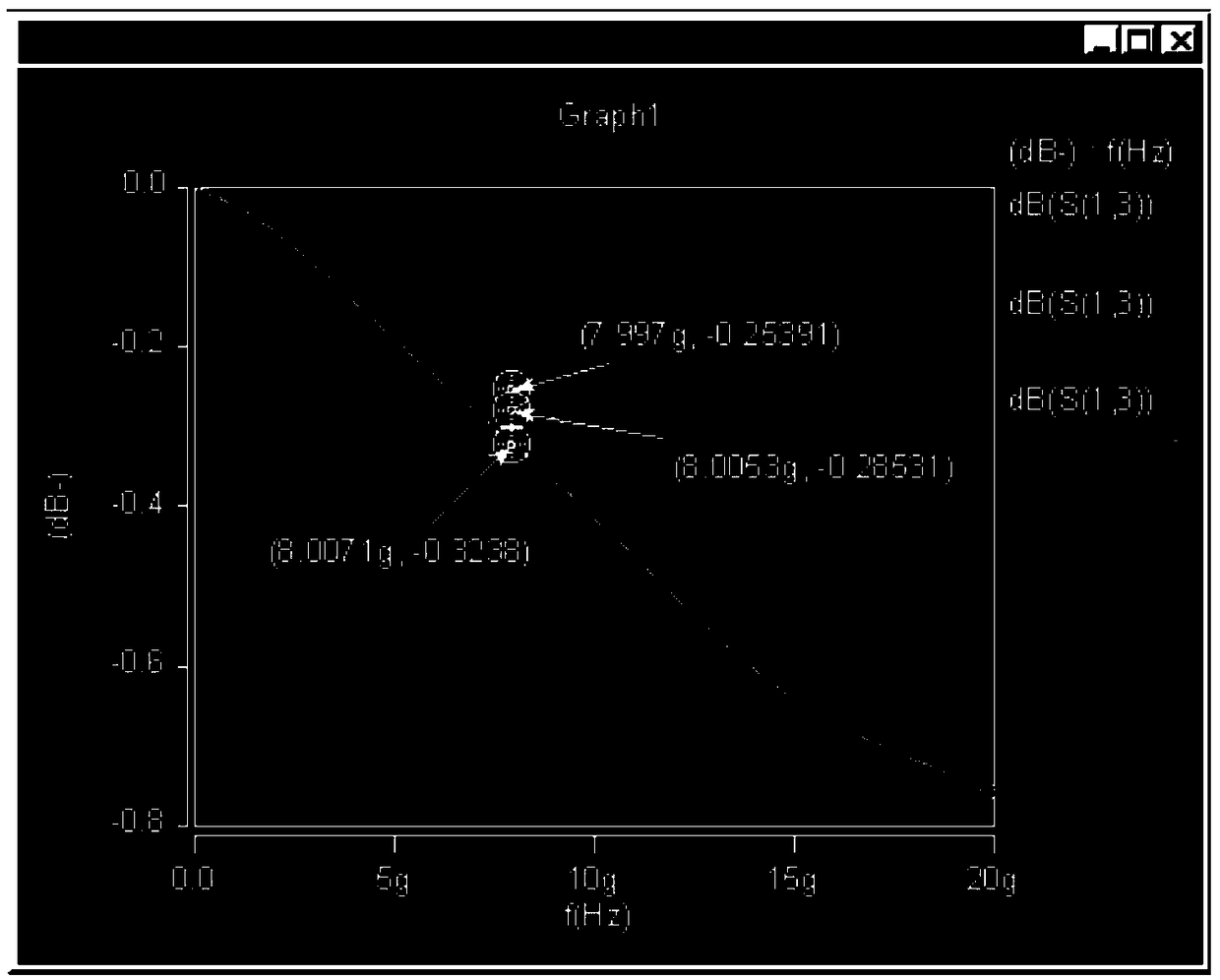
A method and system for analyzing the influence of different hole-changing distances on signal quality
InactiveCN109214096ASolve Energy ReflectionSolve quality problemsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designHFSSAnalysis method
The invention provides a method and a system for analyzing the influence of different hole changing distances on signal quality, comprising the following steps: S1, VIA vias with different hole changing distances are arranged through HFSS; S2, setting corresponding program parameters to obtain S parameters; S3, simulating the signal link and obtaining the eye diagram. The invention provides a specific S value for different hole changing distances of a high-speed line through analysis, and expresses the influence of the via distance on the high-speed signal. And the signal link topology is simulated to compare the eye diagrams of different hole-changing distances by signal simulation, which makes the effect of hole-changing distances on the signal more intuitionistic and visible. The invention solves the problem that the circuit board via hole can cause energy reflection and weaken the signal quality in the prior art, obtains the influence of the hole changing distance on the signal quality, and realizes the reduction of the signal loss and the improvement of the signal quality by setting the optimum via hole distance.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Airborne electric small short-wave antenna impedance characteristic optimization method and broadband short-wave antenna
ActiveCN111313159AAchieve resonanceReduce section heightAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsAntenna impedanceHFSS
The invention belongs to an airborne short-wave communication antenna, and provides an airborne electric small short-wave antenna impedance characteristic optimization method and a broadband short-wave antenna, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, designing a conventional airborne electric small short-wave antenna A through employing electromagnetic simulation software HFSS; S2, adjusting the size of the antenna A to enable the working frequency band of the airborne electric small short-wave antenna to be within 2-30MHz; S3, taking the airborne electric small short-wave antenna Adesigned in the step S1 as a center, and adding eight electric small short-wave antennas as parasitic units to form a 3*3 array form; S4, designing a parasitic unit, enabling the structure of the parasitic unit to be the same as the structure of the airborne electric small short-wave antenna A, and deleting the feed port; S5, setting the distance between the eight parasitic units and the centers of two adjacent units of the airborne electric small short-wave antenna A to be d; and S6, adjusting the coupling between the parasitic unit and the airborne electric small short-wave antenna A by adjusting the size of d, and enabling the impedance of the port of the antenna A to reach a state of being easy to match 50 ohms in a broadband range.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Method for improving transmission characteristics of fixed-length bonding wires
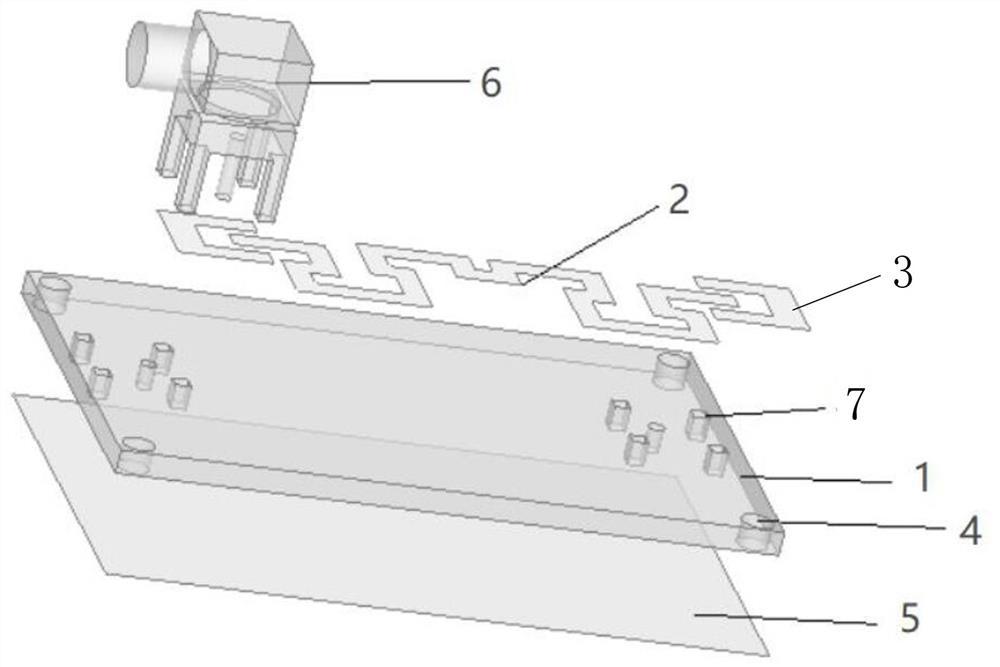
InactiveCN111626012AImprove transmission characteristicsMultiple-port networksCAD circuit designModel extractionLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a method for improving transmission characteristics of a fixed-length bonding wire. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a bonding wire simulation model, extracting model distribution parameters, fusing the extracted distribution parameters into a five-order Chebyshev low-pass filter prototype; and completing the design of the microstrip line filter by using the ADS according to the prototype parameters of the filter, performing optimization design through an ADS optimization control until the design requirement is met, and importing the design resultinto the HFSS to perform simulation design by using a bonding wire model to obtain a final simulation result. When the length of the bonding wire is fixed, the transmission characteristic of the bonding wire interconnection circuit can be remarkably improved, and the bonding wire interconnection circuit has the advantages of being simple in design thought, easy to implement, wide in frequency bandwidth and capable of being applied to any bonding wire.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A Planar Microwave Resonant Antenna with Dual Frequency Points and High Radiation Efficiency
ActiveCN110797653BSimple structureSimple materialSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMetal foilDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a novel dual-frequency / high-radiation-efficiency planar microwave resonant antenna, which includes a rectangular dielectric substrate, the bottom surface of which is a ground radiation patch, and a right-angled fold line symmetrical concave metal foil placed on the upper surface of the dielectric substrate. Chip feeder. Solder the inner core directly to the feeder using the SMA connector, and connect the ground radiation patch. The invention uses the electromagnetic simulation software ANSYS HFSS for simulation design, real-time simulation by changing the shape and size of the feeding antenna, and joint calculation of multi-parameter simulation data and simulation diagrams to optimize the structure, material and process of the antenna, confirm The reliability of the simulation results. Increase the effective radiation resistance of the antenna, reduce the generation of high-order modes, improve the radiation efficiency of the antenna, improve the overall effect of the antenna system, and realize the requirements of dual frequency points and high radiation efficiency on the same substrate and the same plane, and achieve dual frequency points Applications.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
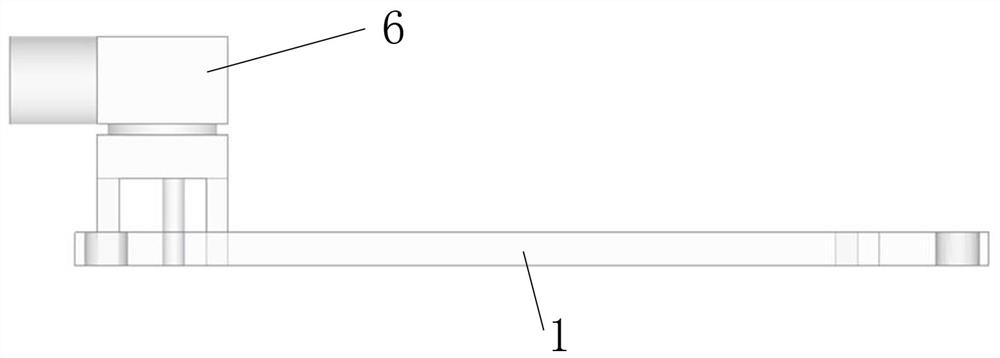
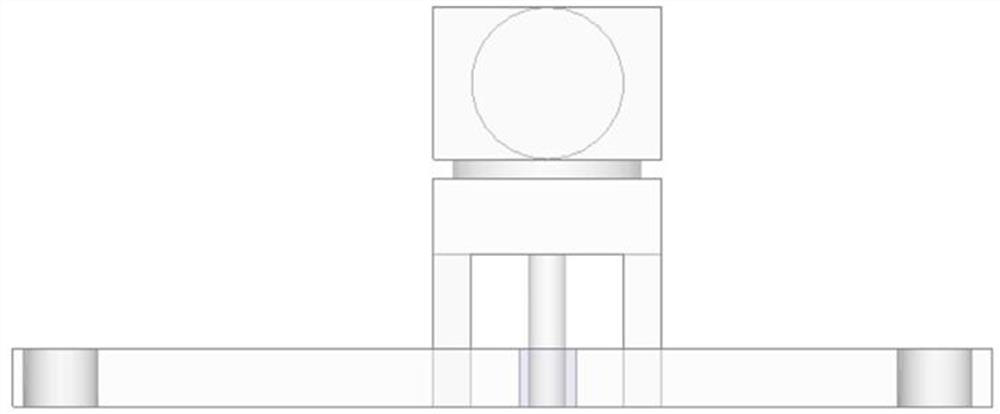
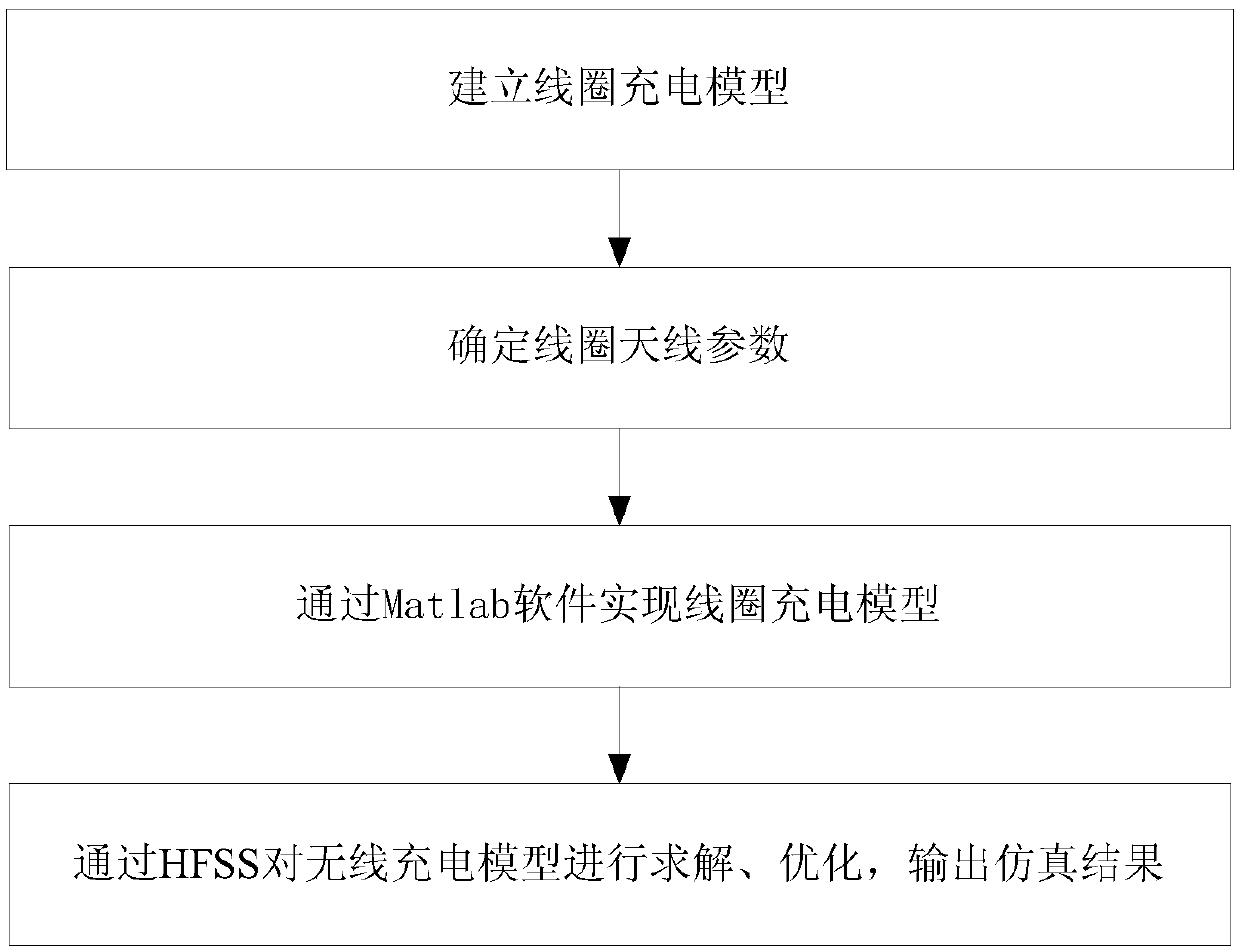
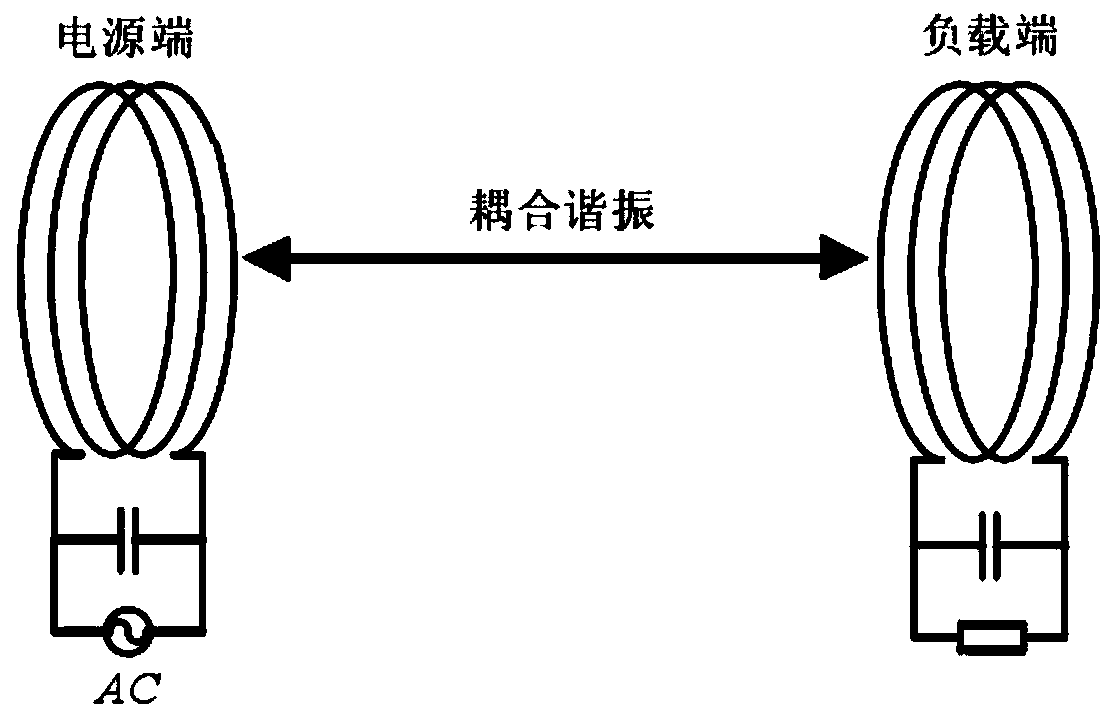
A wireless charging simulation method combining matlab and hfss software
ActiveCN106250657BOvercoming the Shortcomings of Scientific ComputingSpecial data processing applicationsCoupled mode theoryMathematical model
The invention discloses a wireless charging simulation method capable of combining MATLAB (Matrix Laboratory) software with HFSS (High Frequency Structure Simulator) software. Firstly, on the basis of a coupled-mode theory, a wireless charging model of a coil antenna is established; then, according to a circuit model theory and analysis for a resonant mode wireless charging mathematical model, the parameter of the coil antenna is determined; according to the parameter of the coil antenna and the resonant mode wireless charging mathematical model, the practical device parameter and the theoretical model parameter of the coil antenna are obtained; through the MATLAB software, the wireless charging model of the coil antenna is realized; and through the HFSS software, the wireless charging model of the coil antenna is solved, optimized and simulated, and a simulation result is output, wherein the simulation result comprises a coil antenna parameter, charging efficiency and an electromagnetic field distribution diagram. By use of the method, in virtue of he powerful numerical value calculation and modeling functions of the MATLAB, the HFSS is adopted to carry out accurate simulation on the resonant mode wireless charging mathematical model, wireless charging simulation is effectively optimized, and a foundation is laid for the market requirements of resonant mode wireless charging.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Height-adjustable reconfigurable reflective array antenna structure and design method
The invention discloses a height-adjustable reconfigurable reflective array antenna structure and a design method. The height-adjustable reconfigurable reflective array antenna structure comprises an array surface (2), and the array surface (2) is composed of more than one radiation unit (9); each radiation unit (9) is connected with a screw rod (4) of a stepping motor (8) through a supporting rod (3); the stepping motor (8) is fixed in the supporting structure (7); the design method comprises the following steps: designing the radiation unit of the reconfigurable reflective array antenna; simulating the radiation unit in Hfss, and obtaining a reflection amplitude and phase curve by using a master-slave boundary condition and a Floquet port simulation unit structure; determining the ratio of the focal length to the aperture of the reflective array antenna; acquiring the phase distribution of the antenna array through calculation in Matlab; generating a reconfigurable reflective array by using an Hfss script interface and a Matlab script tool; therefore, the technical problems that a reconfigurable reflective array antenna in the prior art is narrow in bandwidth, large in loss, complex in unit design and the like are solved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Passive Intermodulation Suppression Method for Communication Circulator
The invention discloses a passive intermodulation suppression method for a circulator used in communication, including (1) determining the frequency band of the circulator to be processed, the power index, and the expected PIM value under the power index; (2) HFSS simulation The simulation model of the circulator is established in the software, and under the power index, it is obtained in (2 f 1 - f 2 ),(2 f 2 - f 1 ) of the maximum field strengths A and B; (3) Calculate the PIM value of the simulation model according to A and B, and mark it as the simulated PIM value; (4) Compare the simulated PIM value and the expected PIM value, and use the HFSS simulation software to The structure of the simulation model is adjusted until the condition is met. The invention determines the determinant factor causing the passive intermodulation of the circulator, and proposes a method for quantitatively analyzing the passive intermodulation index of the circulator by using the determinant factor, which is also applicable to other third-order passive components based on gyromagnetic ferrite materials. Microwave passive devices that require source intermodulation suppression.
Owner:中国电子科技集团公司第九研究所
Optimal Design Method of Circularly Polarized Triangular Microstrip Antenna Based on Eigenmode Theory
ActiveCN103311664BEasy to handleSimple structureRadiating elements structural formsAdaptive controlEngineeringAntenna feed
The invention discloses an optimum design method of a circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna based on a characteristic module theory. The optimum design method includes steps of 1 obtaining the optimum side length a of a triangular patch; 2 optimally designing the gap size of the patch; and 3 optimally designing the feed position. The single feed point circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna is simple in structure and easy to process and has satisfactory impedance and axial ratio bandwidth. The optimum design method can explain the working principle of the circular polarization triangular micro-strip antenna in the aspect of the physical concept, designs the determined antenna feed position and working frequency, and greatly improves the efficiency compared with manual antenna parameter adjustment processing by aid of High Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) simulation software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method of simulating the absorption of plane waves using FEM software tools
InactiveUS9759693B2Component separationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsValidation methodsImpedance matching
A novel and useful method of visualization by detection of EM radiation being irradiated or reflected from objects in the imager's field of view using Finite Element Method (FEM) simulation software tools. The methodology provides a verification method of antenna operation from an electrical point of view since bolometer performance cannot be estimated using regular antenna parameters such as directivity, gain, impedance matching, etc. as the bolometer does not behave as an antenna but rather behaves as an absorber. An incident wave is triggered on the absorber and the absorption of the bolometer structure is estimated using commercially available Finite Element Method (FEM) software (e.g., ANSYS® HFSS software, CST MICROWAVE STUDIO®, etc.). How much of the energy is reflected is subsequently measured. The energy which is not reflected is considered to be absorbed by the absorber.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com