Compositions and methods of RNA analysis
A technology of groups and substitutes, applied in the field of composition at the level of existence and expression, can solve problems such as inhibiting the extraction of important information, reducing RNA quality, and lagging gene expression profiles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Example 1: Development of in situ ligation hybridization sequencing (LISH-seq)
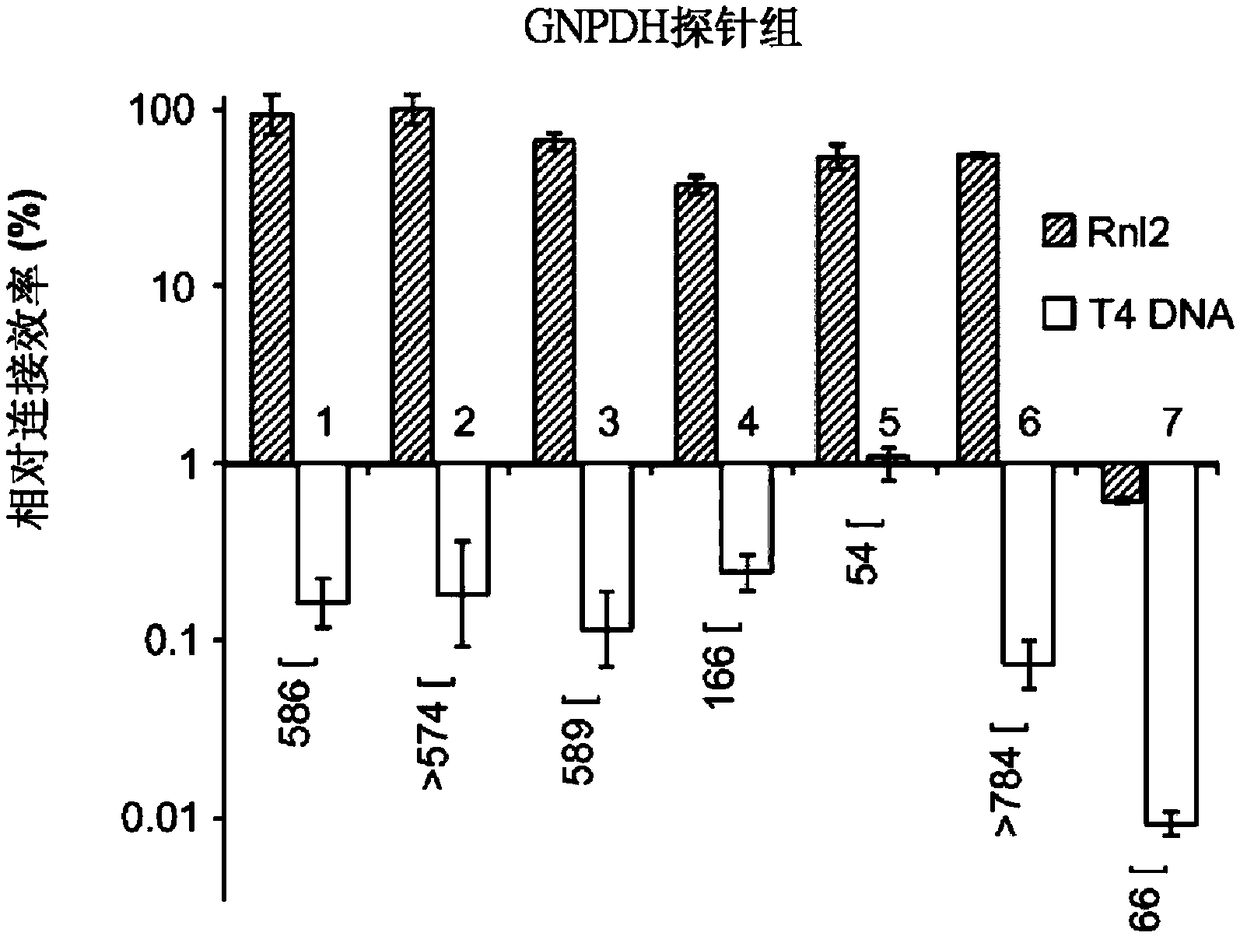
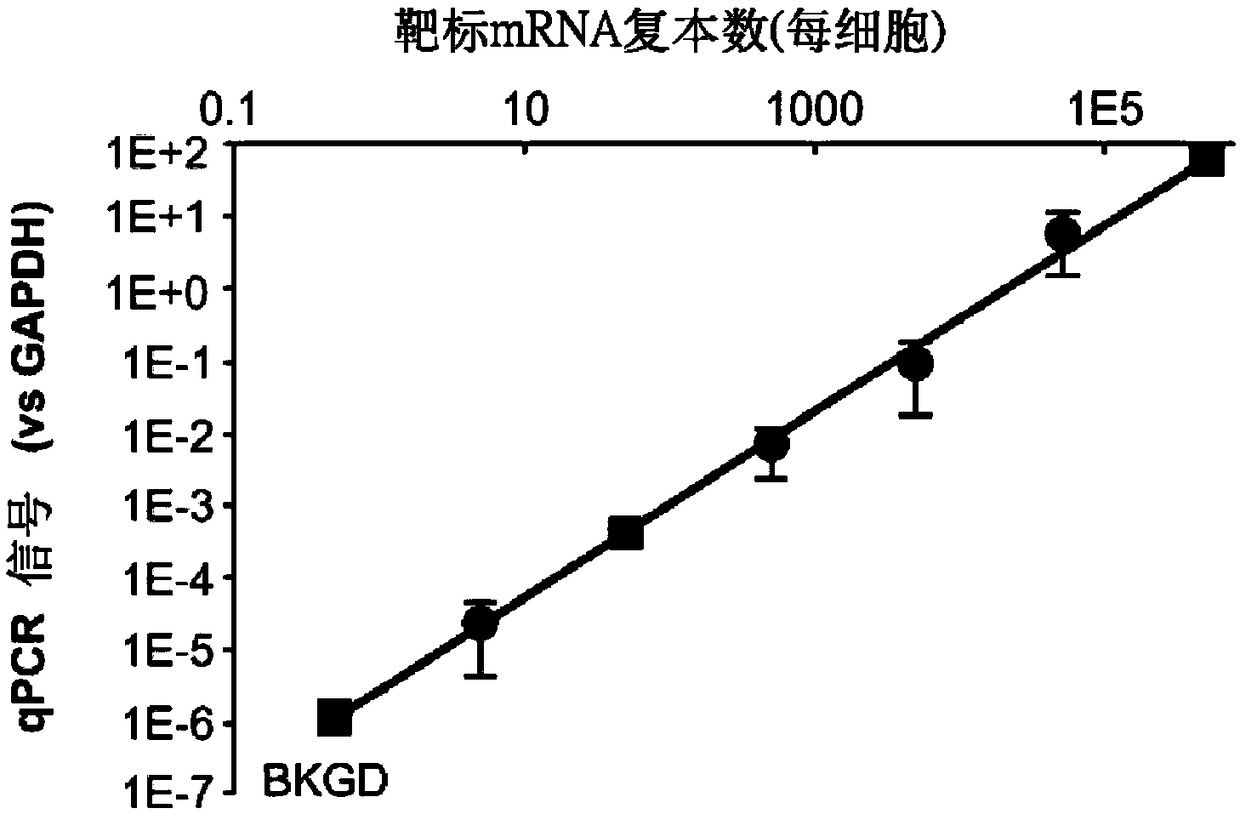
[0112] The optimal protocol to efficiently generate probe ligation products in FFPE sections was identified. A housekeeping gene probe set was used to explore the impact of various protocol differences on the signal (on-target probe ligation) and interference (off-target probe ligation) of the assay after a decade. The efficacy of LISH was assessed by direct comparison with RT-qPCR. High-throughput DNA sequencing of pooled LISH products ("LISH-seq") demonstrates the degree of multiplexing (eg, hundreds to thousands of transcripts per tissue section) afforded by this system. A batch of long-term stored specimens was analyzed by LISH-seq. This dataset demonstrates the extent to which LISH-seq unlocks archived large patient tumor specimens for highly multiplexed mRNA analysis. A strategy exists that uses LISH-seq to overcome limitations previously associated with the analysis of RNA extract...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2: Maintaining spatial resolution of amplified LISH products: LISH-imprinting
[0140] If this spatial distribution of transcript levels is preserved, the value of multiplex gene expression analysis can be greatly enhanced. The technique is particularly useful for characterizing the complex interactions between tumor tissue and cells of the immune system. A platform capable of highly multiplexed, spatially resolved analysis of gene expression in FFPE tissue sections is transformable for cancer researchers and pathologists.
[0141]The utility of LISH is extended to methods to imprint LISH products on target surfaces and amplify to preserve spatial information ("LISH-imprinting"). This attempt is based on the imprinting of DNA molecules on replica high-density DNA microarrays. To locally amplify imprinted LISH products, bridge PCR is used, which has been revealed in the literature and is the basis of Illumina high-throughput DNA sequencing technology. After de...
Embodiment 3
[0162] Example 3: Measurement of RNA-Seq in FFPE
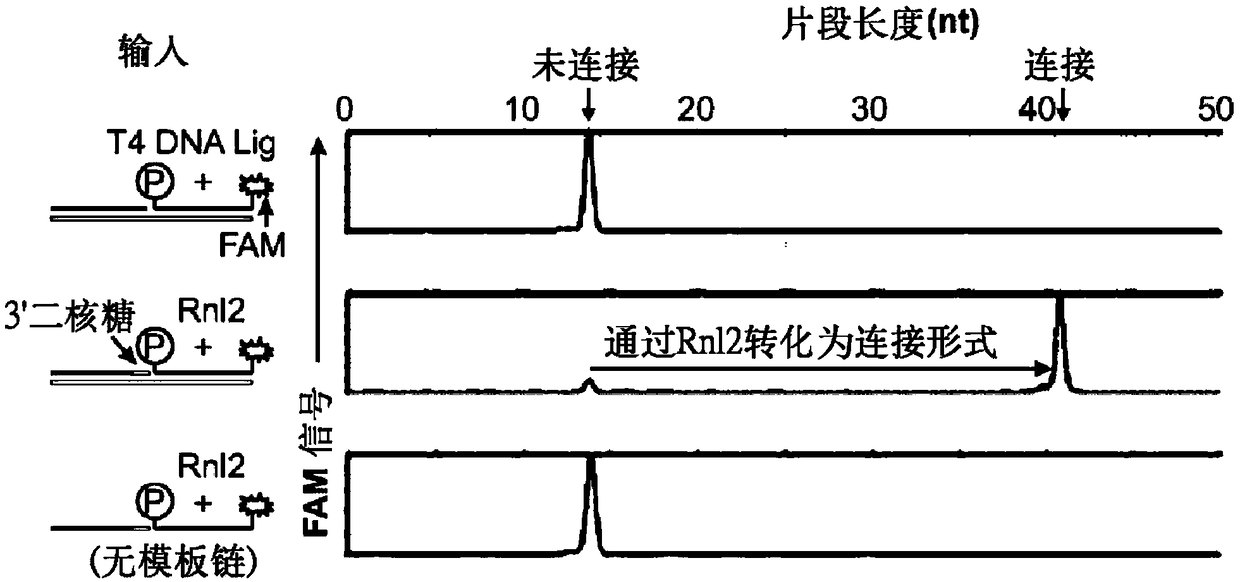
[0163] Reports in recent years have shown that RNA-templated probe ligation chemistry is sensitive, specific, and appropriate for large-scale multiplexing (Larman, H.B., et al. Nucleic acids Research 42, 9146-9157 (2014), incorporated herein by reference in its entirety). This pathway employs T4 RNA ligase 2 (Rnl2), an enzyme that ligates sets of adjacently annealed sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes to RNA "splints." In this context, Rn12 requires that the acceptor oligonucleotide be 3'-terminated by two ribonucleotides (herein referred to as "3'-diriboprobe"). In some examples, the acceptor oligonucleotide can have a 3' end cap of at least two RNA bases. Phosphorylated donor probes (referred to herein as "5'-phosphate probes") can be entirely DNA ( Figure 5A ). Thus, the linked 3'-diriboprobe set and 5'-phosphate probe set are DNA molecules containing internal diribonucleotide sequences.
[0164] No known DNA lig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com