Single-phase ground fault detection method based on line equivalent impedance value
A single-phase ground fault, equivalent impedance technology, applied to the fault location, fault detection according to the conductor type, measurement of electricity and other directions, can solve the problems of pedestrian life threats, large calculation errors, high step voltage, etc., to improve sensitivity , easy engineering implementation, and good applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
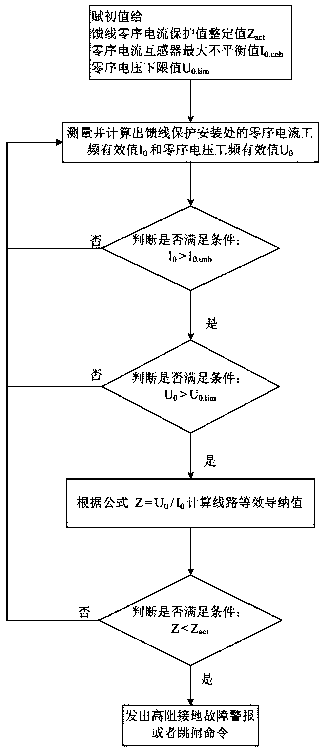
[0032] Such as figure 1 Shown is the first embodiment of the single-phase ground fault detection method based on the line equivalent impedance value, including the following steps:
[0033] S1. Assign the initial value to the protection action setting value Z act , Zero-sequence current maximum unbalance value I 0.unb And the zero sequence voltage lower limit value U 0.lim ;
[0034] S2. Collect and calculate the power frequency effective value I of the feeder zero-sequence current 0 And the power frequency effective value U of the zero-sequence voltage of the busbar 0 ;
[0035] S3. Compare and judge whether I is satisfied 0 > I 0.unb , if satisfied, go to step S4; if not, return to step S2;
[0036] S4. Compare and judge whether U is satisfied 0 >U 0.lim , if satisfied, go to step S5; if not, return to step S2;
[0037] S5. According to the formula Z=I 0 / U 0 ×10 3 Calculate the equivalent admittance value of the feeder;
[0038] S6. Compare and judge whether ...
Embodiment 2
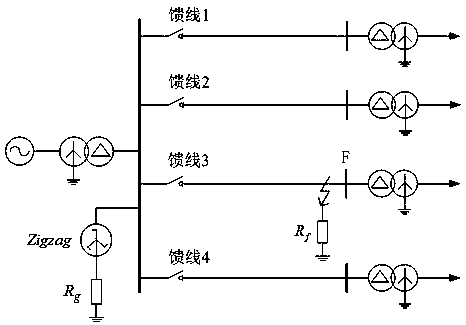
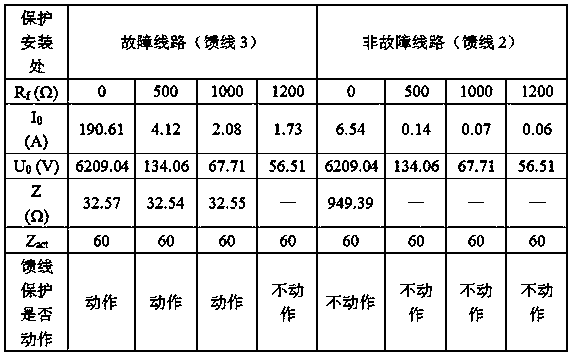
[0043] This embodiment is an application embodiment of the method described in Embodiment 1, and a substation with a 10kV neutral point as a small resistance grounding method is used as a model, such as figure 2 As shown, the small grounding resistance of this embodiment and the zero-sequence impedance of the transformer are 10Ω, and the lengths of feeder 1, feeder 2, feeder 3, and feeder 4 are 6km, 9km, 12km, and 15km respectively, and each feeder uses a cable line. Both are YJV 22 ‐3*300, the positive sequence parameters are: R1=0.500Ω / km, L1=0.318mH / km, C1=0.376μF / km, the zero sequence parameters are: R0=0.500Ω / km, L0=6.398mH / km , C0=0.370μF / km. The load rate of the distribution transformer is 60%, and the power factor is cosθ=0.9. In this embodiment, a single-phase transition resistance grounding fault point F is set at the head end, midpoint and end of the feeder 3 respectively, and the protection actions of the faulty line feeder 3 and the non-faulty line feeder 4 are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com