Linear array image sleeper positioning and counting method based on multi-region gray projection
A technology of grayscale projection and line array image, which is applied in image data processing, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., and can solve problems such as low precision and poor reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
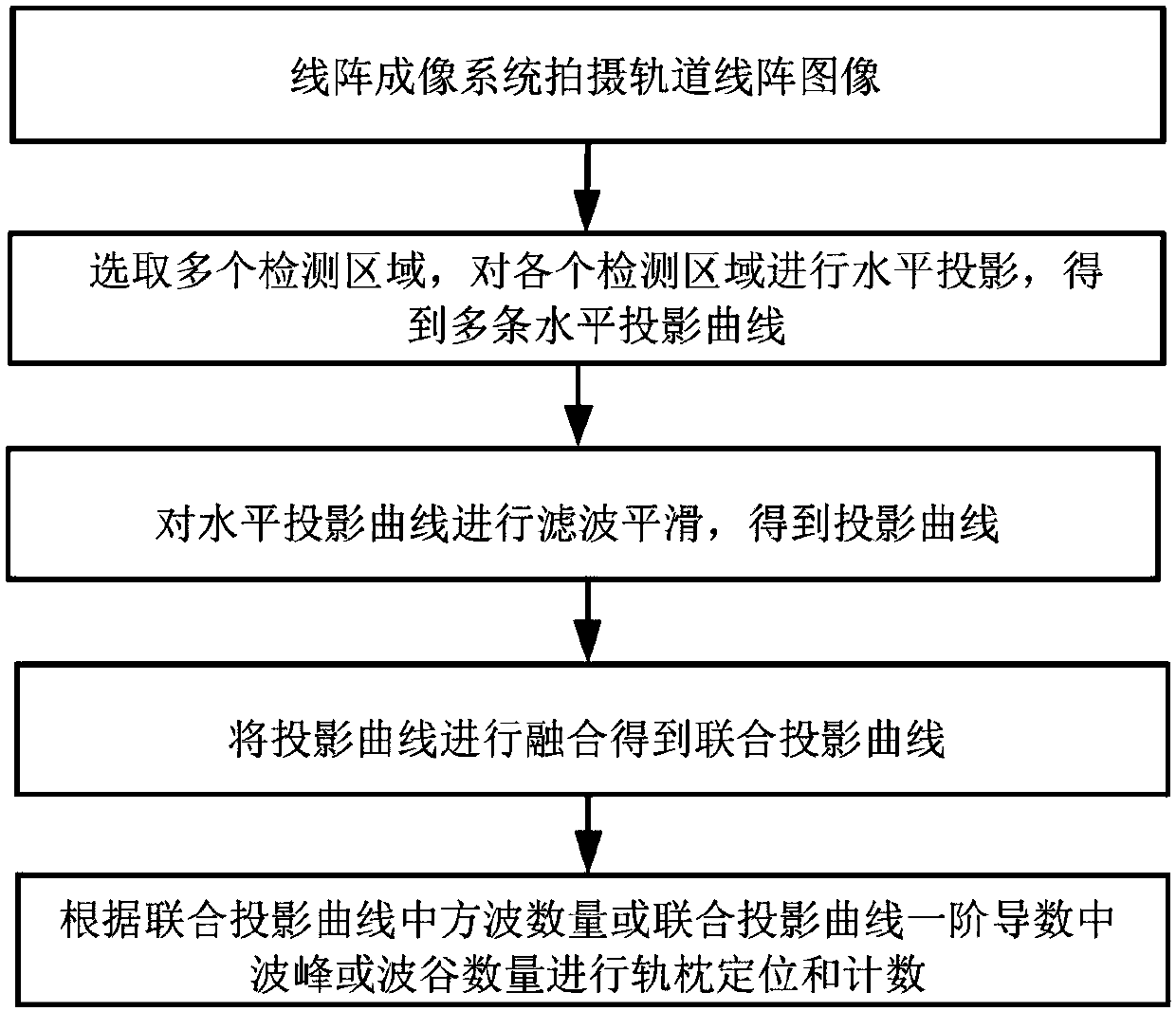
[0069] Embodiment 1: use the number of square waves in the joint projection curve to count sleepers.
[0070] Step 1: Take the qth track two-dimensional image I, and select K detection areas {R 1 ...R K}, the value range of K is 1~10, in the specific implementation process, take K=3, such as Figure 6 As shown, respectively for K detection areas {R 1 ...R K} to perform horizontal projection on the pixel values to obtain K horizontal projection curves {S 1 ... S K}, detection area R 2 The corresponding horizontal projection curve S 2 Such as Figure 7 shown. The heights of the K detection areas are equal, and only sleepers are included in the detection area, fasteners and rails are not included;
[0071] Step 2: For K horizontal projection curves {S 1 ... S K} for fusion to obtain the joint projection curve S′;
[0072] Step 3: Use the adaptive threshold method to binarize the joint projection curve S′ to obtain the binarized curve B, such as Figure 10 shown;
...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment 2: counting sleepers by using the number of crests or troughs in the first derivative of the joint projection curve.
[0082] Utilize the linear array imaging system to acquire Q two-dimensional images of tracks containing sleepers, and sequentially perform the following processing on the Q two-dimensional images of tracks:
[0083] Step 1: Take the qth track two-dimensional image I, and select K detection areas {R 1 ... R K}, K ranges from 1 to 100, in the actual implementation process, K = 3, respectively for K detection areas {R 1 ... R K} to perform horizontal projection on the pixel values to obtain K horizontal projection curves {S 1 ... S K}. The heights of the K detection areas are equal, and only sleepers are included in the detection area, fasteners and rails are not included;
[0084] Step 2: For K projection curves {S 1 ... S K} for fusion to obtain the joint projection curve S′;
[0085] Step 3: Perform first-order differential filteri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com