Method and system for reducing interference caused by phase noise in radar system
A phase noise, radar system technology, applied in the radio wave measurement system, the use of re-radiation, the reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, etc., can solve the problems of reducing accuracy and range, interference, and high computational cost, achieving low computational cost, Influence of suppression, effect of suppression of phase noise/phase noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
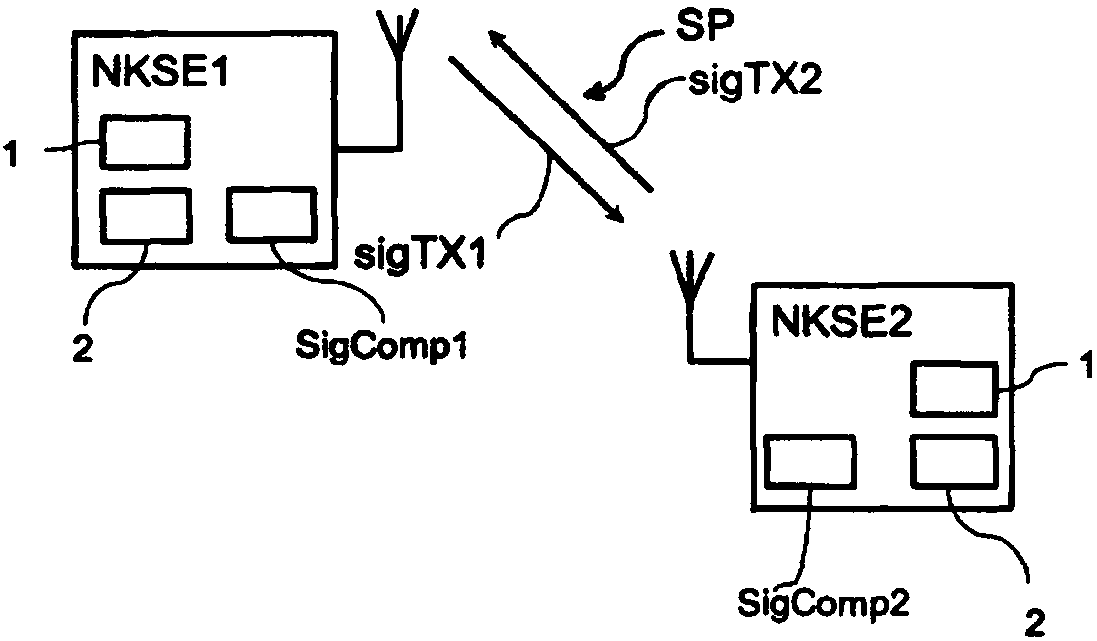
[0048] as from figure 1 It can be seen that the two sending and receiving units NKSE1 , NKSE2 communicate with each other via the radio interface. Here, the first or second signal sigTX1, sigTX2 is transmitted. The transmitting and receiving units NKSE1, NKSE2 each have a signal source 1, a unit 2 for clock matching or comparison signal modulation and a transmitting comparison unit (SigComp1, SigComp2).
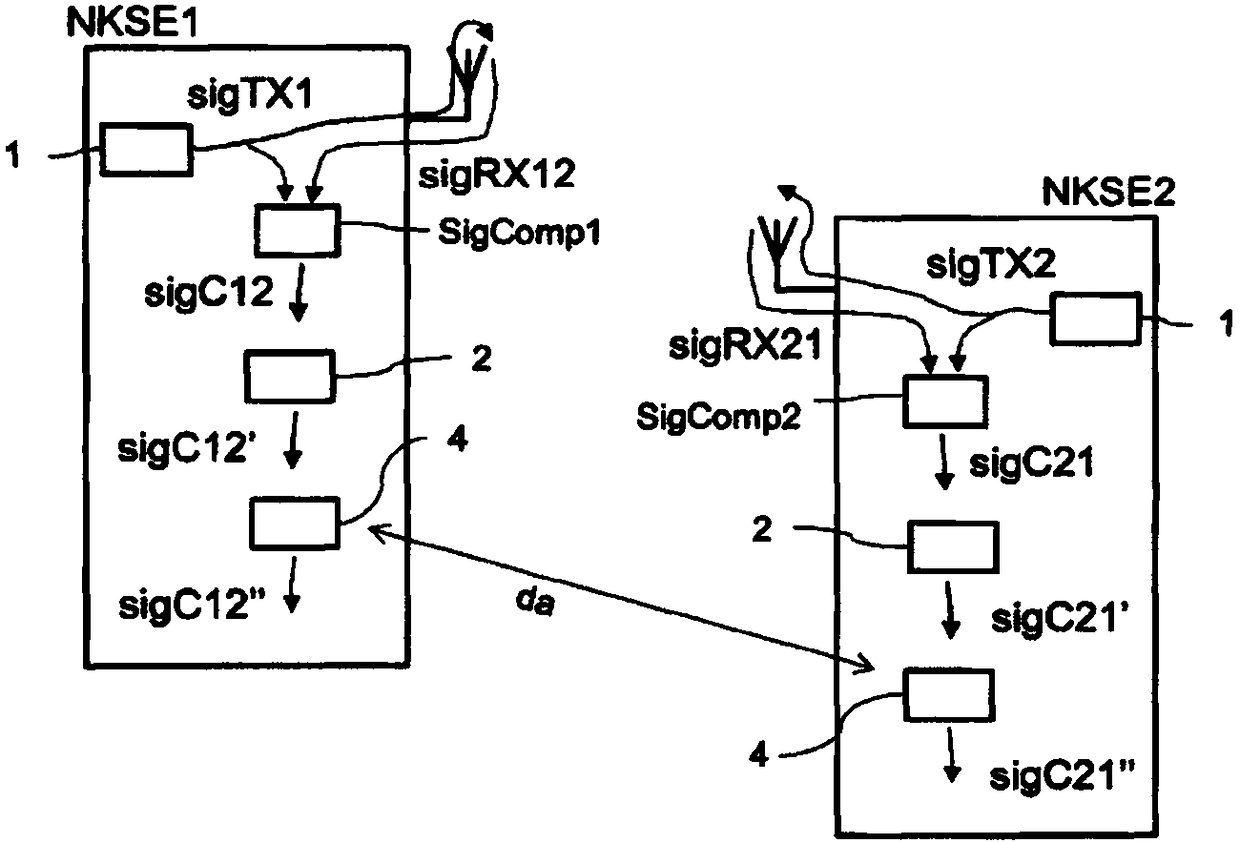
[0049] figure 2 In addition, units for phase modulation 4 are shown in each case. Data exchange takes place between the two units for phase modulation 4 .
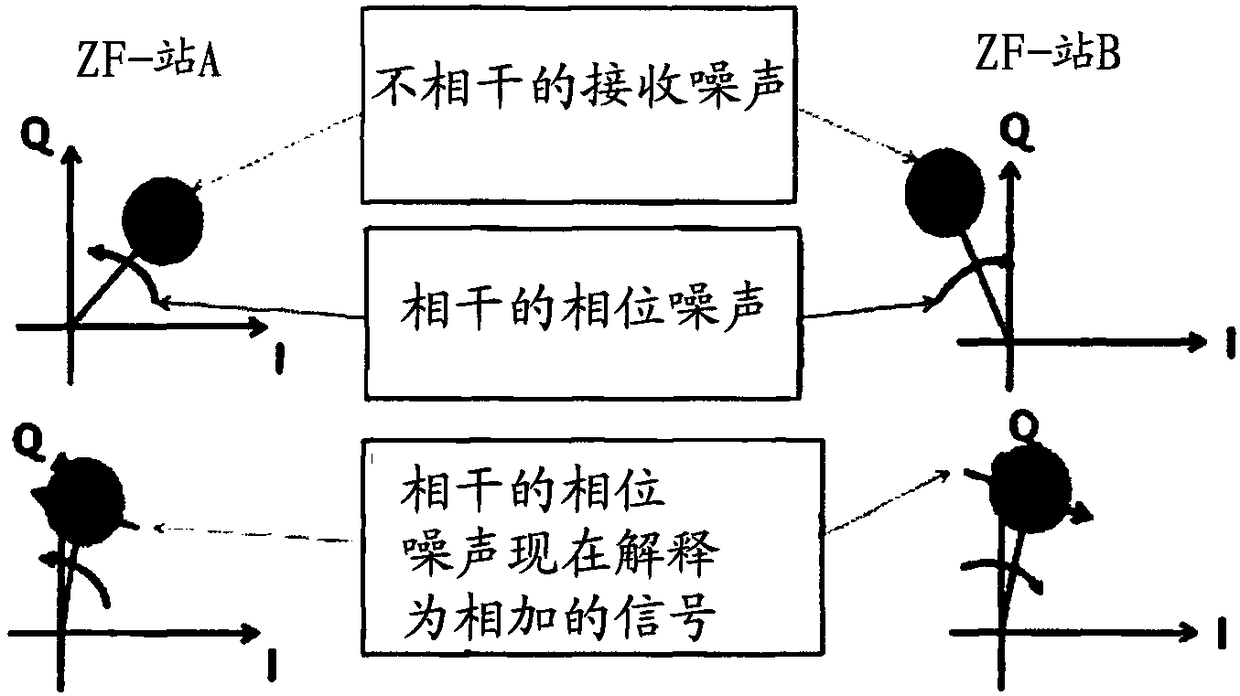
[0050] Next, a precise mathematical derivation according to the invention is carried out. In a first non-coherent transmit and receive unit (NKSE1), a first signal (sigTX1) is generated and transmitted, in particular transmitted, via a path (SP). In a further transmission and reception unit, in particular a second non-coherent transmission and reception unit (NKSE2), a second signal (sigTX2) is generated and sent, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com