Multi-agent cognitive planning algorithm based on heuristic search
A heuristic search and multi-agent technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as insufficient expression ability, poor scalability, and limited depth of belief nesting, and achieve good versatility and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
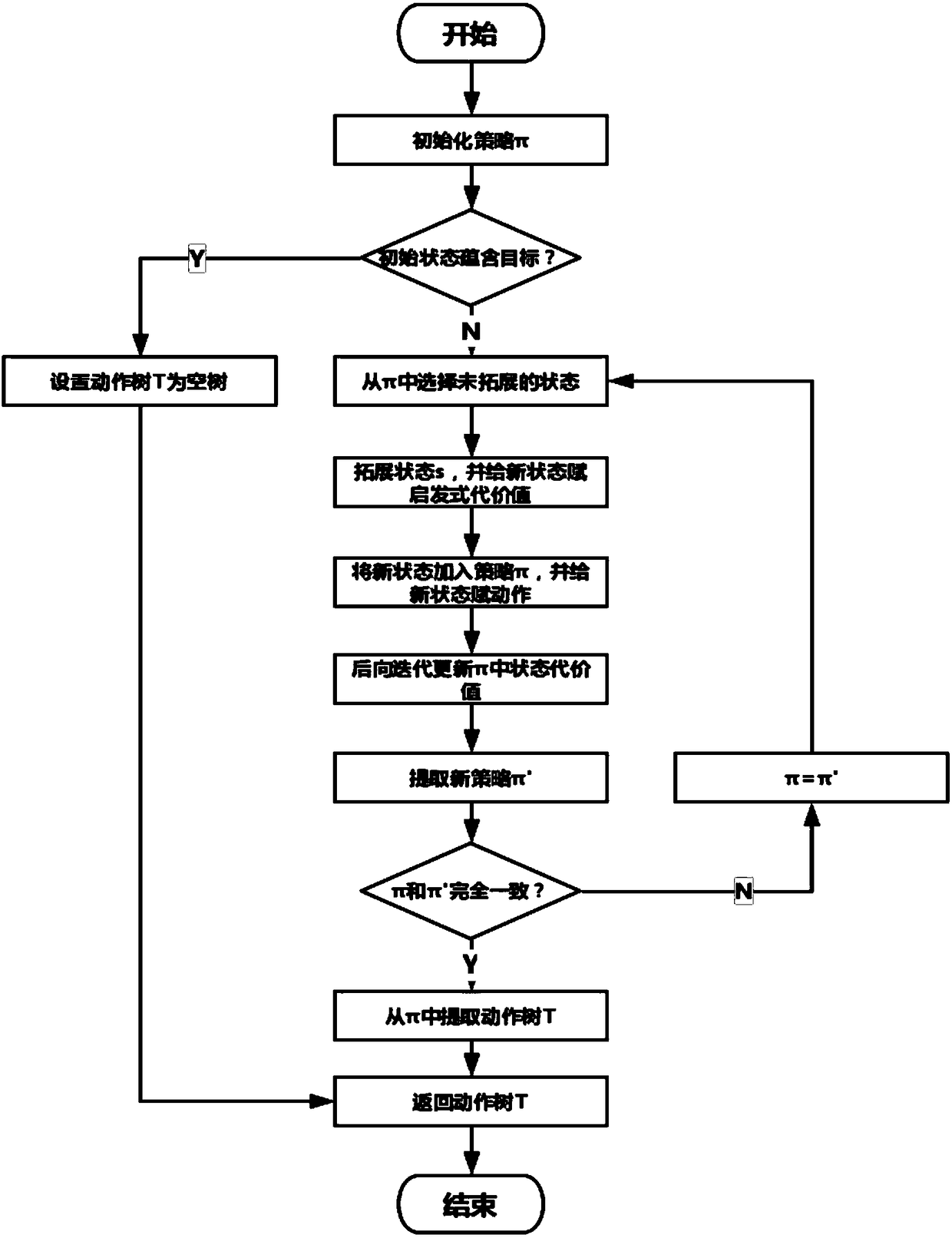
[0067] In this embodiment, there are three objects a, b, and c. It is known that one or two of them carry materials on their bodies. The three objects can check whether other objects carry materials on their bodies, but they cannot check themselves, and they can ask other objects Whether they are aware of their own situation, and the person being asked will answer honestly. The initial state is that a does not know whether he has materials on his body, and the goal is that a knows whether he has materials or not. The steps are as follows figure 1 As shown, the problem is modeled according to the multi-agent cognitive planning framework proposed in Huang's literature, and the initial state I, goal G, constraint γ, perceptual action set S, and deterministic action set D are obtained.
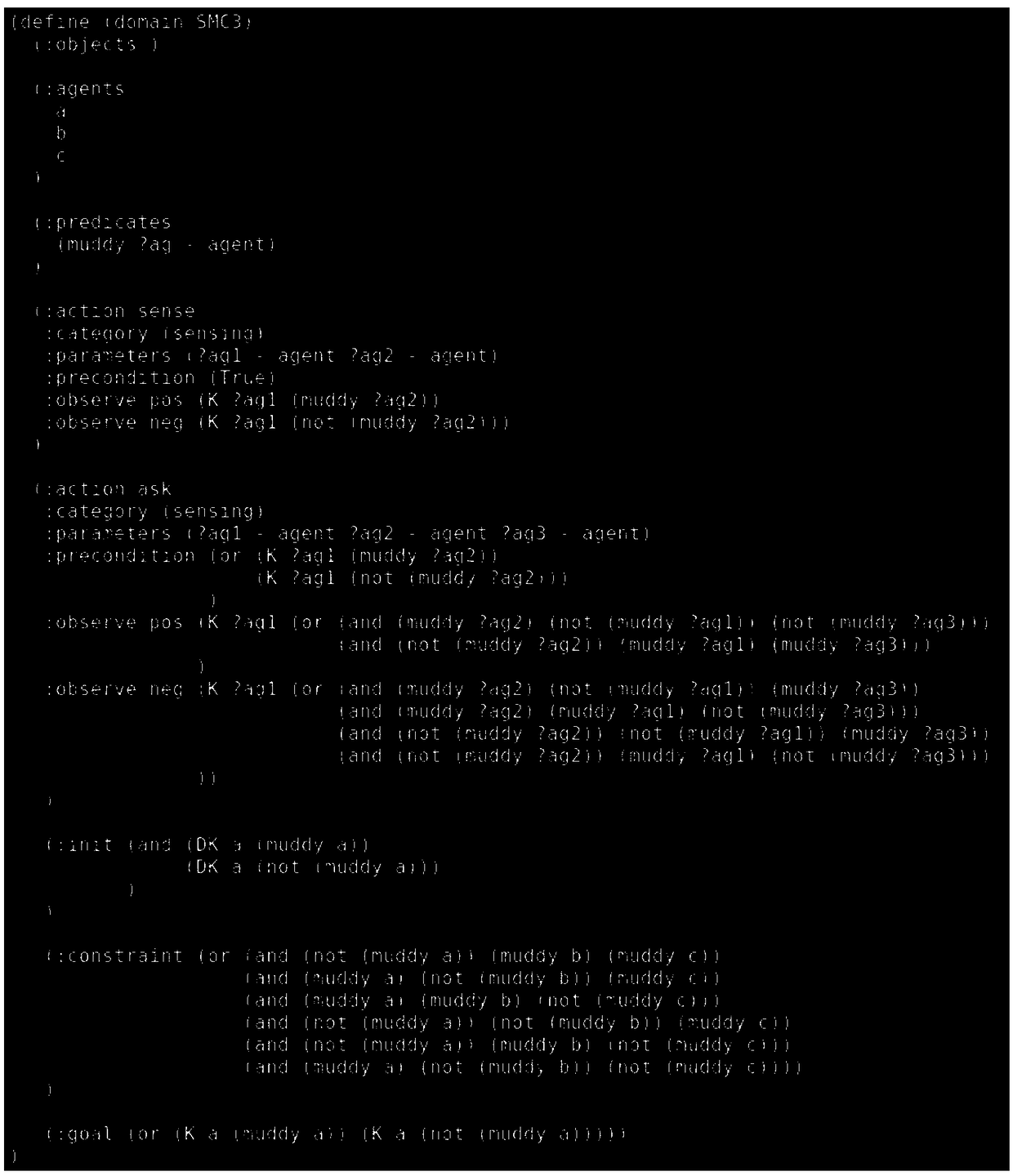
[0068] Input: initial state I, goal G, constraint γ, perceptual action set S, deterministic action set D, where figure 2 for the input document.
[0069] Output: The solution corresponding to th...
Embodiment 2
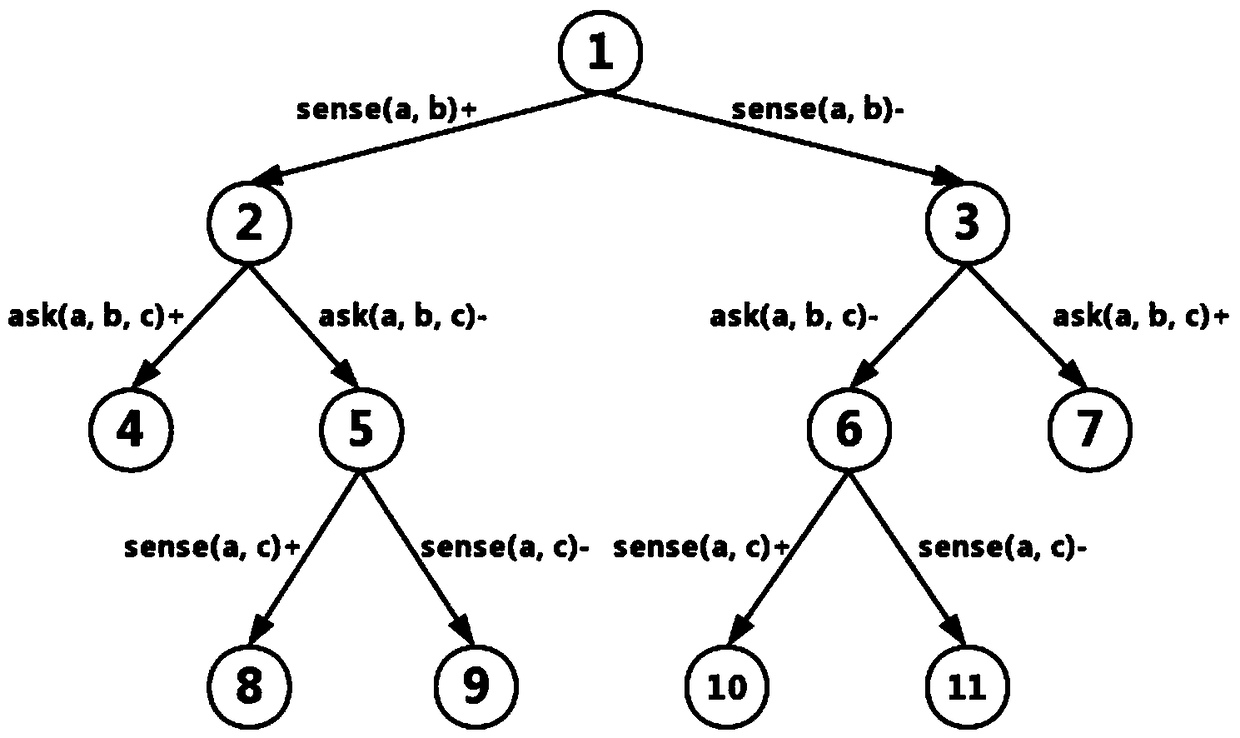
[0095] The input of the multi-agent cognitive planner MEPL based on our algorithm is the problem description document, which is written in EPDDL language, and the output is the solution corresponding to the multi-agent cognitive planning problem, that is, the action tree. Such as image 3 Shown is the input document for Example 1, such as Figure 4 Shown is a solution of Example 1 obtained by MEPL
[0096] The experimental comparison data of the planner MEPL realized based on the algorithm of the present invention and the existing multi-agent cognitive planner MEPK, such as Figure 4 As shown, the first column is the name of the test set, and all the test cases are from the literature of Huang et al., the second column is the number of agents, the third column is the depth of belief formula, the fourth and fifth columns are MEPK and The experimental data of MEPL, where A-B(X / Y) means, A is the total time required (in seconds), B is the time used for the search (in seconds), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com