Method of cleanly recovering and reutilizing glyphosate after inactivation with activated carbon catalyst
An activated carbon and catalyst technology is applied in the field of clean recycling and reuse of activated carbon catalysts for glyphosate after deactivation, which can solve problems such as non-compliance with the concept of clean recycling of resources, secondary pollution, etc. Effects of Solid Hazardous Waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
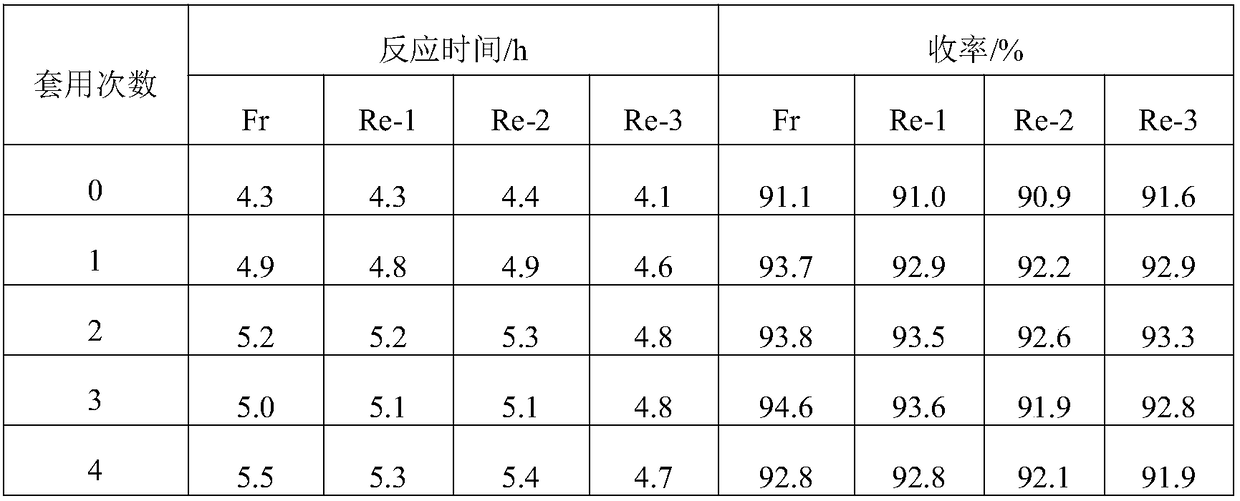
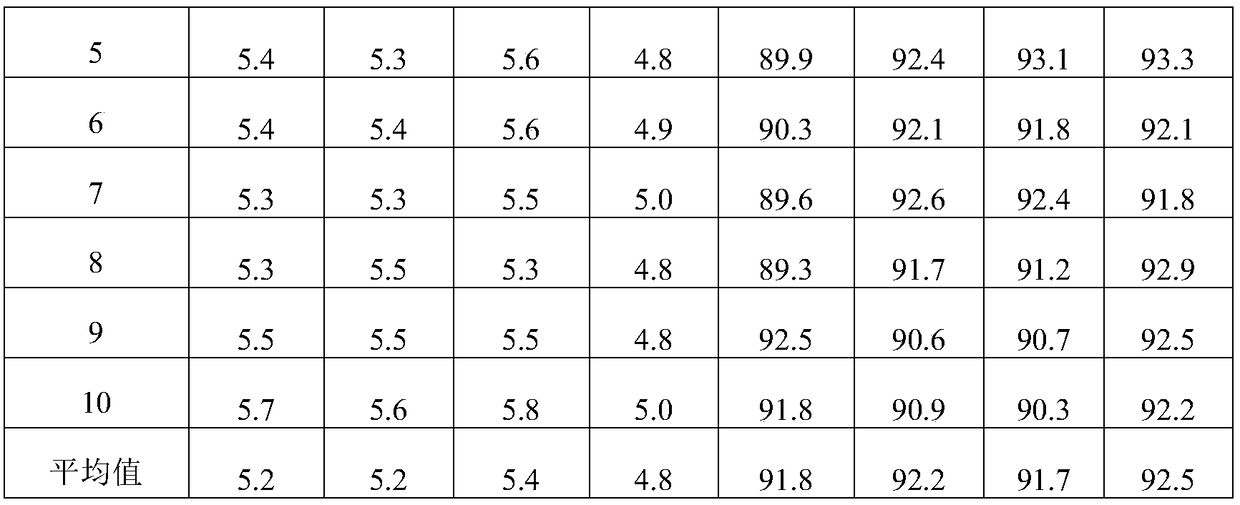
[0051] A method for cleaning and reusing glyphosate after being deactivated by an activated carbon catalyst, comprising the steps of:
[0052] 1) Oxidation treatment: put 2 kg of deactivated activated carbon catalyst into the roasting furnace, under 4.75L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 300°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and then oxygen was introduced at a rate of 0.25L / min, and oxidized and roasted for 6h;
[0053] 2) Reduction heat treatment: After the oxidation treatment is completed, stop feeding oxygen, at 4.75L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 700°C at a rate of 5°C / min, kept for 0.5h, and then 0.2L / min of H 2 , 700 ℃ constant temperature roasting 6h, after cooling down to room temperature to obtain regenerated activated carbon Re-1.
Embodiment 2
[0055] A method for cleaning and reusing glyphosate after being deactivated by an activated carbon catalyst, comprising the steps of:
[0056] 1) Oxidation treatment: put 2 kg of deactivated activated carbon catalyst into the roasting furnace, under 4.75L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 350°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and then oxygen was introduced at a rate of 0.25L / min, and oxidized and roasted for 4h;
[0057] 2) Reduction heat treatment: After the oxidation treatment is completed, stop feeding oxygen, at 4.75L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 600°C at a rate of 5°C / min, kept for 0.5h, and then 0.2L / min of H 2 , 600 ℃ constant temperature roasting 8h, after cooling down to room temperature to obtain regenerated activated carbon Re-2.
Embodiment 3
[0059] A method for cleaning and reusing glyphosate after being deactivated by an activated carbon catalyst, comprising the steps of:
[0060] 1) Oxidation treatment: Put 2kg of deactivated activated carbon catalyst into the roasting furnace, under 4.5L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 350°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and then oxygen was introduced at a rate of 0.5L / min, and oxidized and roasted for 6h;
[0061] 2) Reduction heat treatment: After the oxidation treatment is completed, stop feeding oxygen, at 4.5L / min N 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 800°C at a rate of 5°C / min, kept for 0.5h, and then 0.3L / min of H 2 , 700 ℃ constant temperature roasting 8h, after cooling down to room temperature to obtain regenerated activated carbon Re-3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com