Synchronous calibration device and method for strain and temperature of distributed sensor fiber (cable)
A technology of sensing optical fiber and calibration method, applied in measurement devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in distinguishing strain and temperature cross effects, large calibration result errors, inconsistent displacement of optical fiber cores, etc., and achieves a simple and easy test process. It is easy to operate, reduce the difficulty of calibration, and has a good performance-price ratio.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
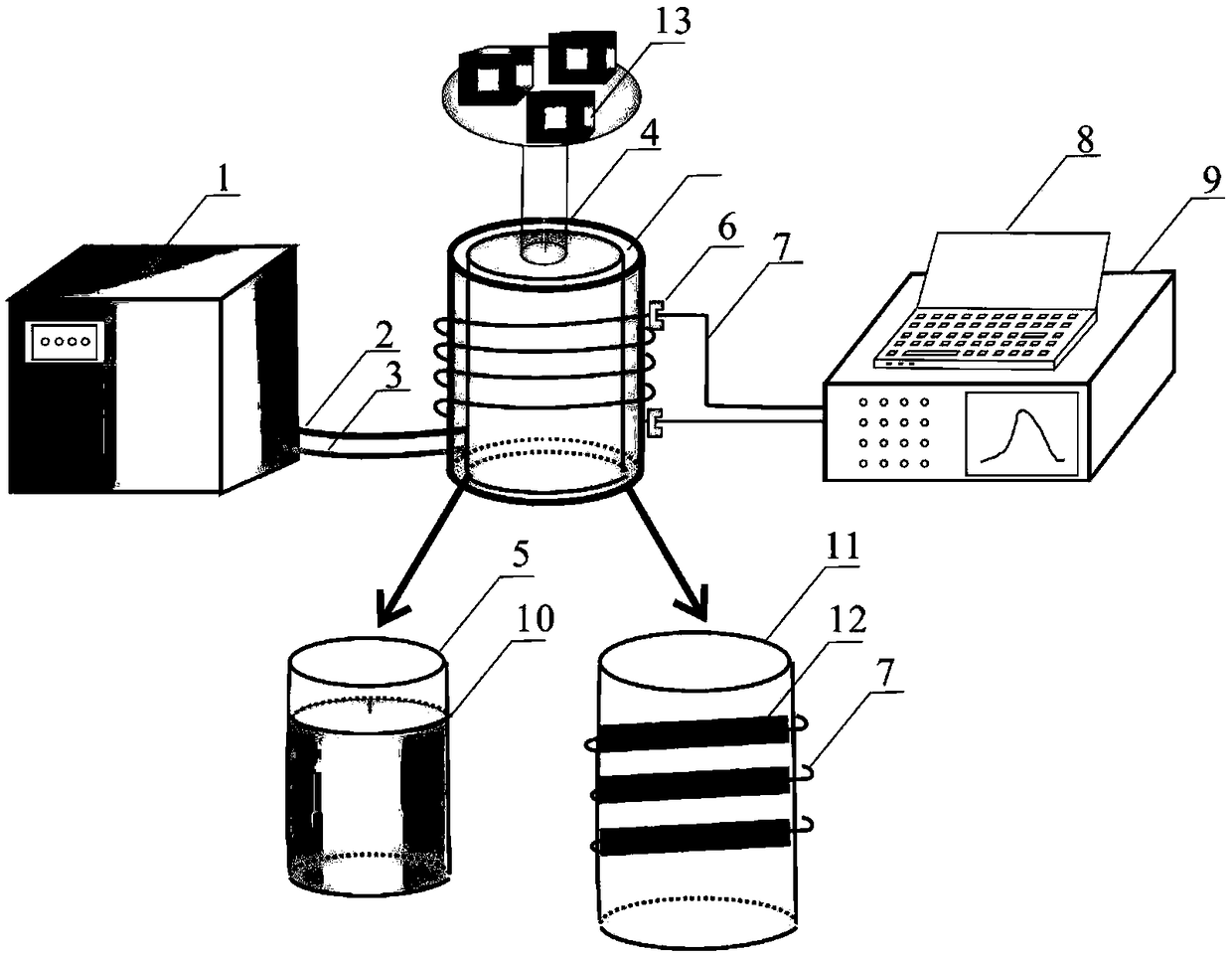
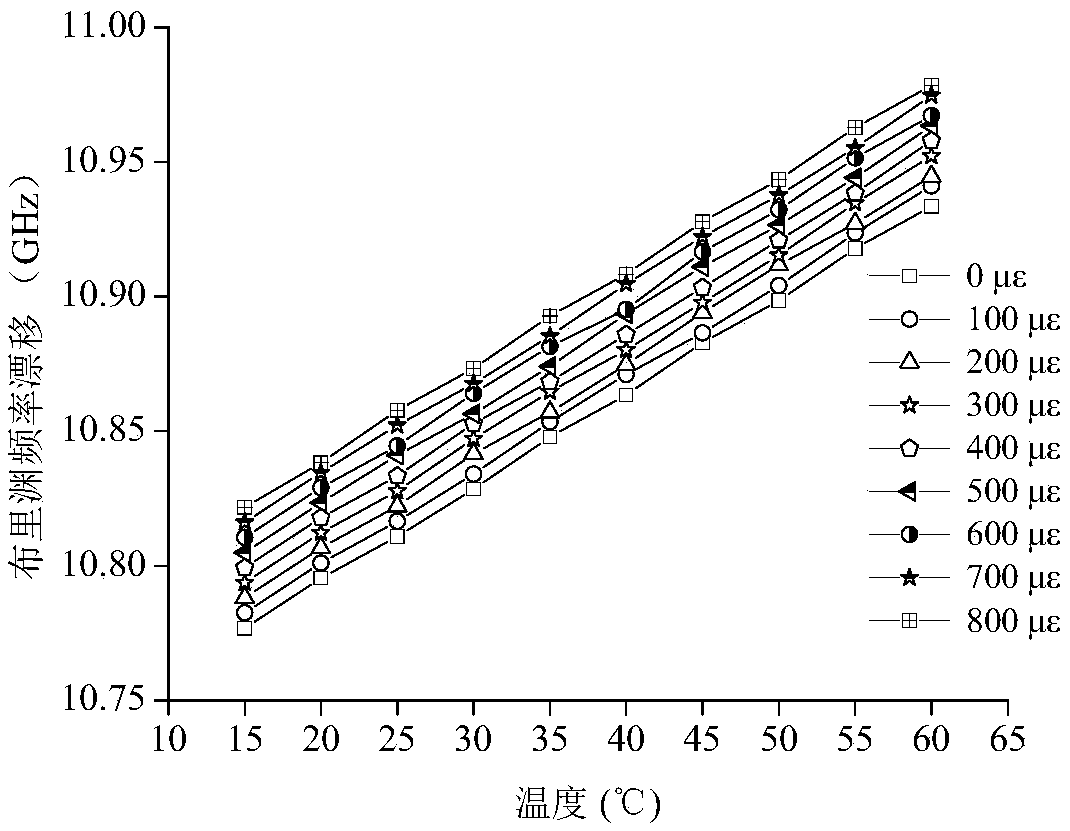
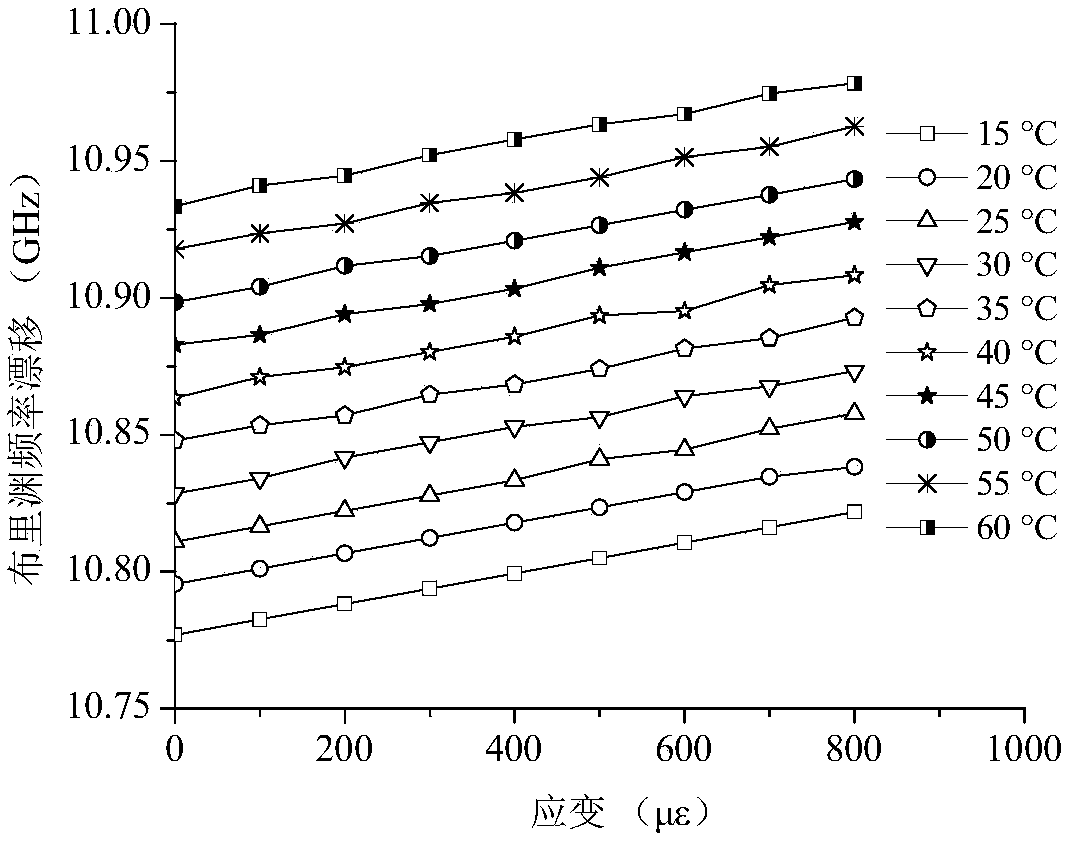
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, a distributed sensing optical fiber (cable) gauge coefficient and temperature coefficient calibration device includes: 1. Temperature control box, 2. Insulated liquid inlet pipe, 3. Temperature control device, 4. Weight connecting rod, 5. Inside of the calibration barrel, 6. Optical fiber fixture, 7. Calibration optical fiber, 8. Data processor, 9. Distributed optical fiber demodulator, 10. Liquid level, 11. Outer wall of the calibration barrel, 12. Outer wall groove, 13. Weight . The distributed optical fiber interrogator is a Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry Optical Fiber Strain / Temperature Measuring Instrument (BOTDR), the model of which is AV6419. The height of the calibration barrel is 20cm, the radius of the bottom surface is 6cm, and the barrel volume is small, which is easy to carry and test; the calibration column is hollow, and the preferred groove depth of the thread on its side surface is 2mm, and the interval is 5mm; t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com