A mathematical model method for multi-scale and multi-field coupling seepage flow of carbon dioxide replacement shale gas
A carbon dioxide, multi-scale technology, applied in complex mathematical operations, electrical digital data processing, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as huge differences in hole and seam systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0116] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following:
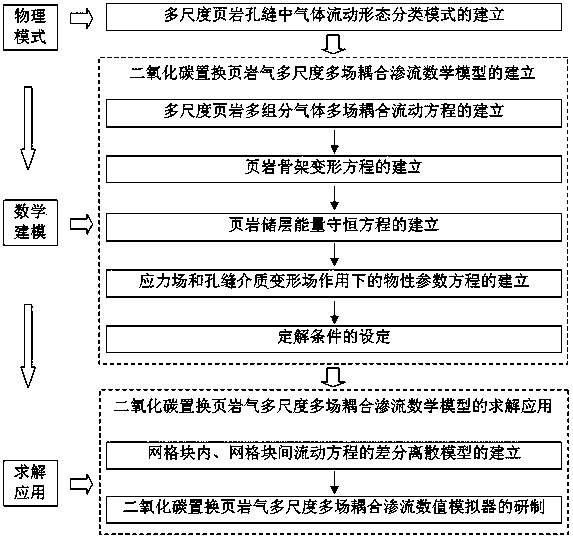
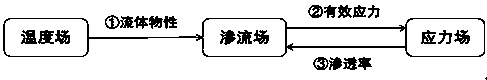
[0117] Such as figure 1 As shown, a carbon dioxide replacement shale gas multi-scale multi-field coupling seepage mathematical modeling method, which includes the following steps:
[0118] S1. Establish a multi-scale gas flow classification model in shale pores and fractures, specifically including the following steps:
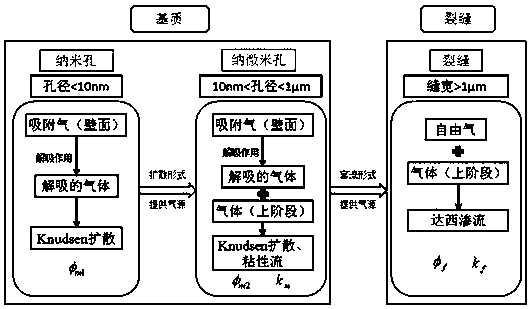
[0119] S11. Establish a one-to-one correspondence between the Knudsen number (Kn) and the shale pore size. As shown in Table 1, the main matrix nanopores with a pore size 1 μm, just correspond to Kn > 0.1, 0.001 < Kn < 0.1 and Kn < 0.001, respectively.
[0120] Table 1. Three-scale pores and fractures in shale, Knudsen number (Kn) and gas flow regime division scheme
[0121]
[0122] Therefore, matrix nanopores (referred to as "nanopores", the same below), matrix nano-micropore...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com