Method for establishing in-vitro detection model of chemical-induced human esophageal cancer
A technology for in vitro detection and establishment of methods, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, measurement/testing of microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of lack of efficient and accurate in vitro experimental methods, difficulties in observing complex effect end points, etc., and achieve the detection process Efficient and accurate, satisfying high-throughput detection, and the effect of cumbersome detection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
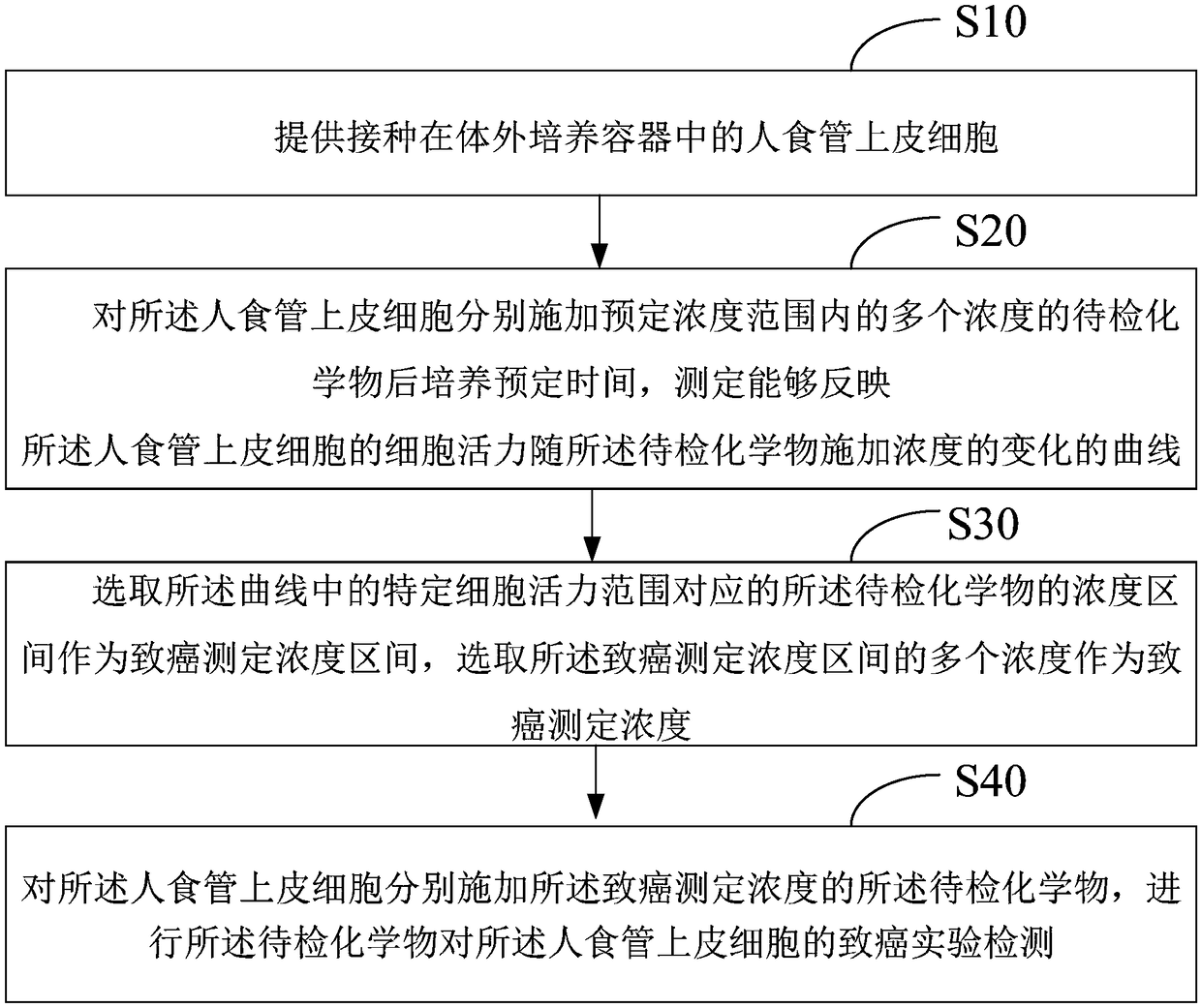
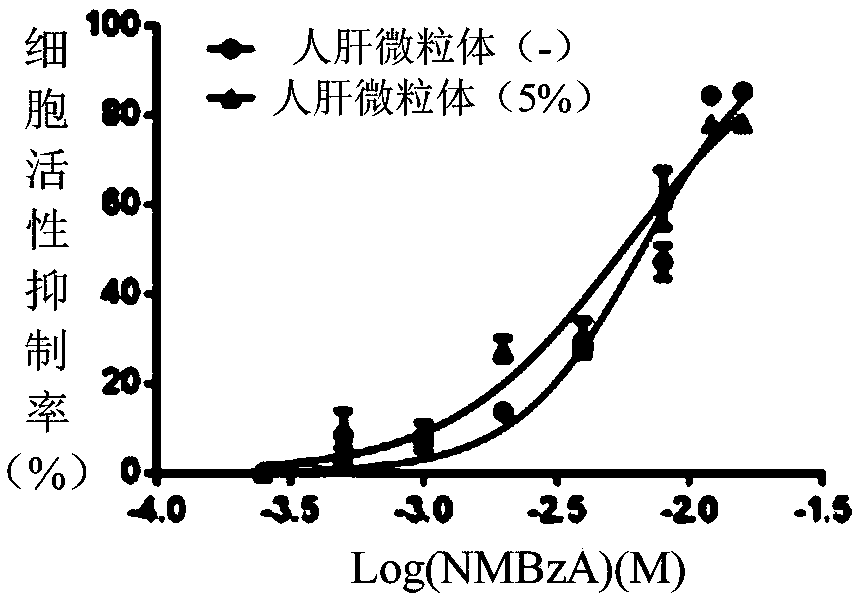
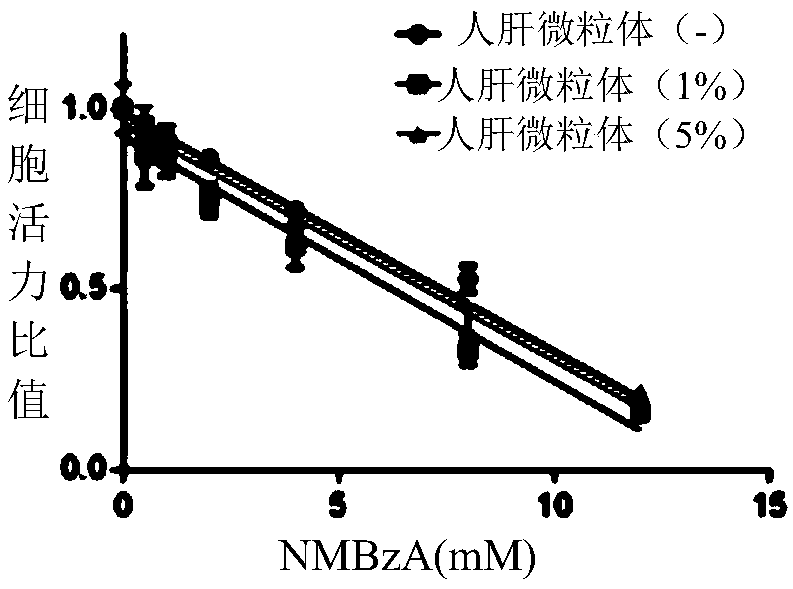
[0064] (1) Cell culture of human esophageal epithelial cells
[0065] Human normal esophageal cell line Het-1A (ATCC) was cultured in Bronchial epithelial cell basalmedium (BEGM) medium. Culture vessel: 25cm 2 Culture flask, use after coating with 0.1% gelatin. Culture conditions: 95% air, 5% carbon dioxide, 37C. During the cell culture period, the culture medium was changed every 3 days, and the cells were subcultured when the cells grew to cover 80% of the area of the culture bottle. When the cells are subcultured, wash the cells twice with PBS, digest with trypsin until the cells become round, collect the cells after the BEGM medium terminates the reaction, centrifuge at 500g for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, and add new culture medium for subculture at a ratio of 1:3. . When the cells are cryopreserved, select the cells with good growth status and vigorous growth, wash the cells twice with PBS, digest with trypsin until the cells become round, stop the reaction...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com