Production system and method of nano biomedical material
A technology for biomedical materials and production systems, applied in chemical instruments and methods, feeding devices, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost and low purity, and achieve simple production methods, simple production systems, The effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
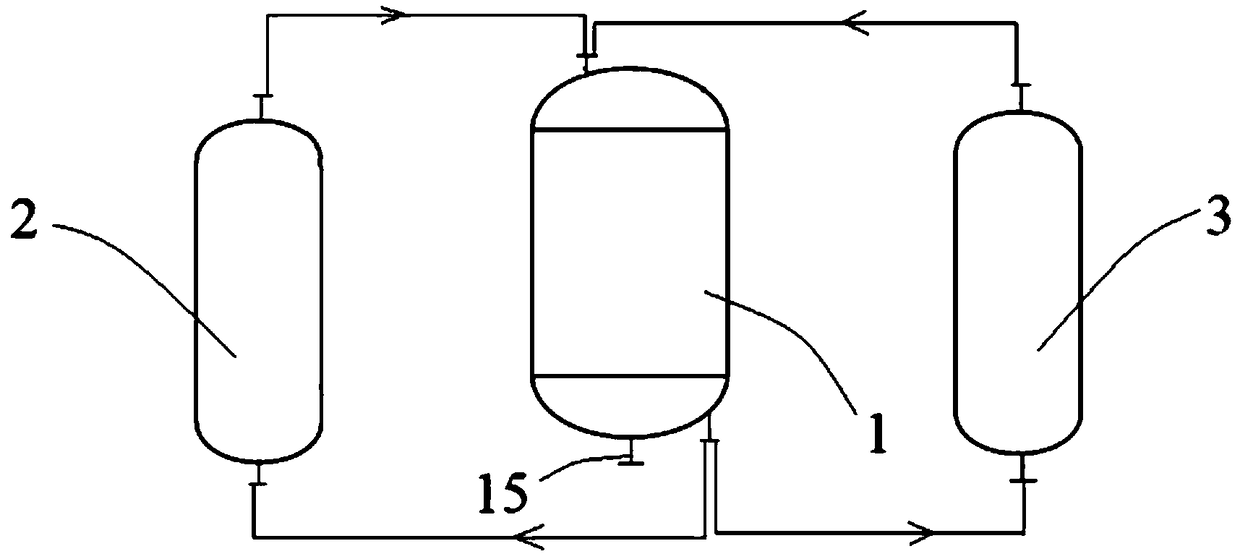
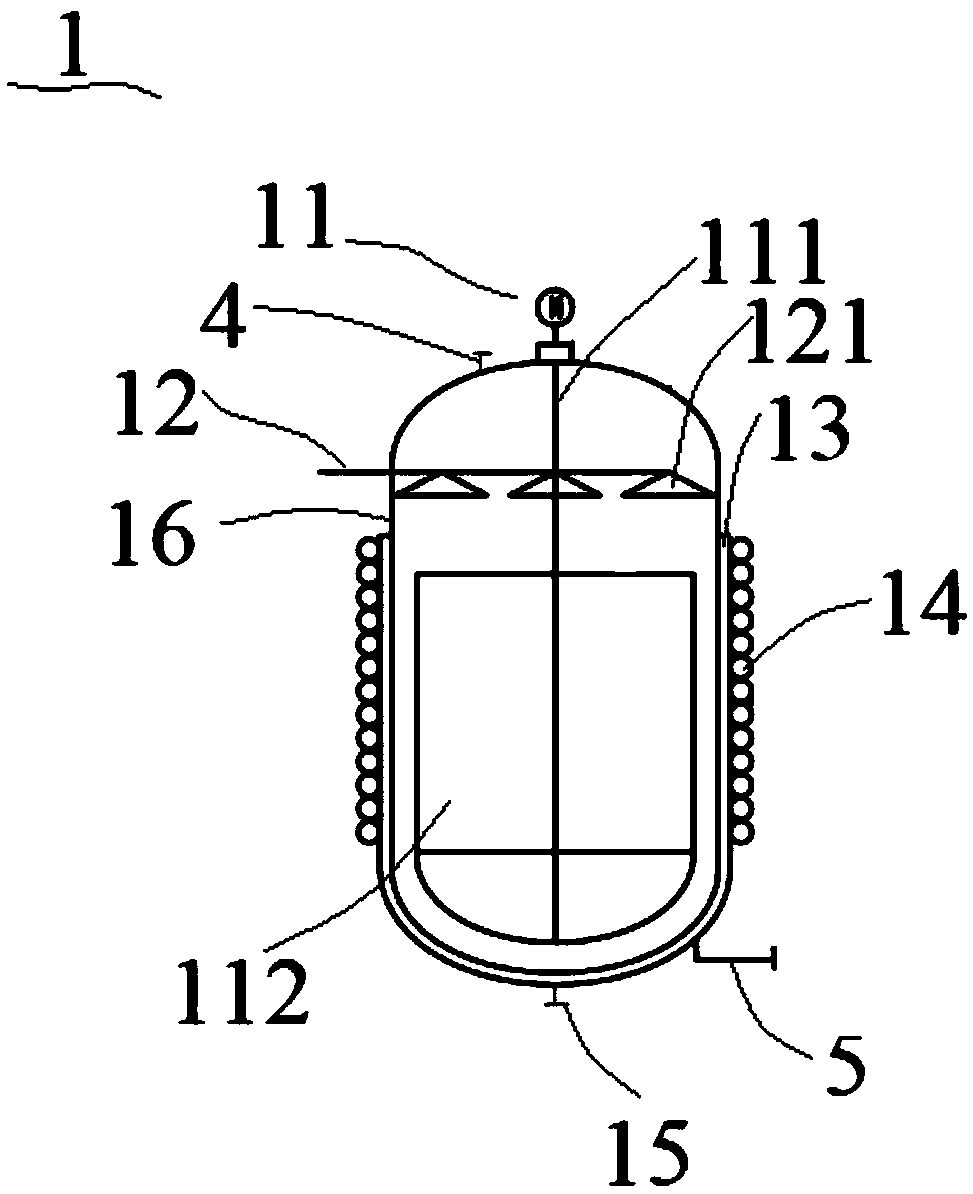
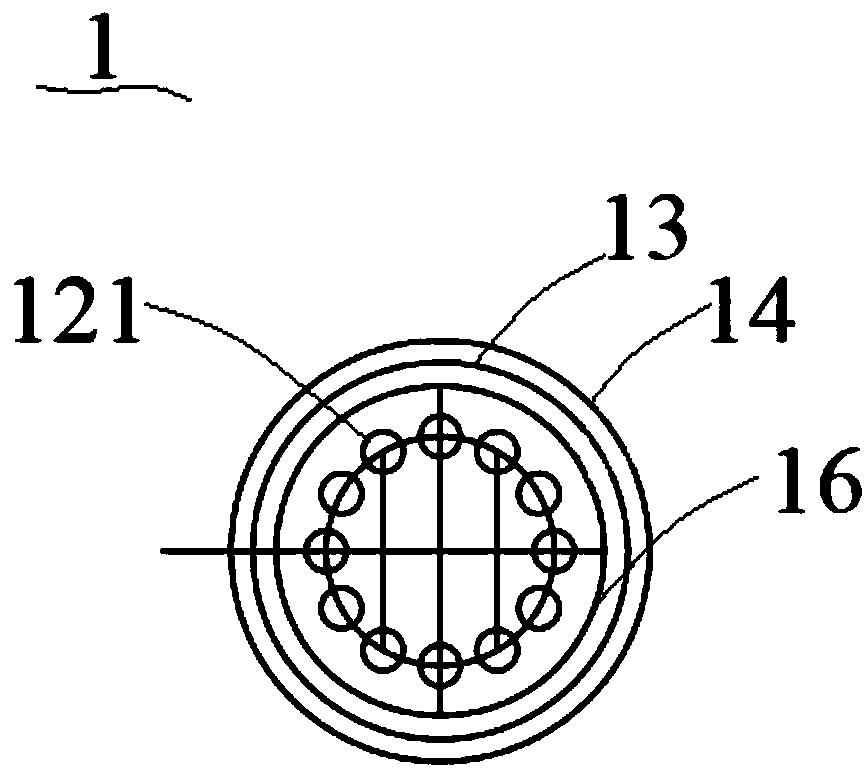
[0048] combine Figure 1-3 As shown, a production system for nano-biomedical materials, including:
[0049] Reactor 1, react raw materials to generate initial magnetic particle reaction solution, separate the magnetic particles in the initial magnetic particle reaction solution and wash the magnetic particles, refine the washed magnetic particles and remove the particles that do not meet the particle size requirements The magnetic particles that meet the molecular weight requirements after refined treatment are coated with organic polymers, and the reaction solution of magnetic particles that meet the molecular weight requirements after organic coating with polymers is concentrated;
[0050] The first membrane separator 2 removes particles that do not meet the particle size requirements and molecular weight requirements after the refinement treatment;
[0051] The second membrane separator 3 removes particles that do not meet the molecular weight requirements after the polyme...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The process of producing nano-biomedical materials using the above-mentioned production system of nano-bio-medical materials includes:
[0060] S1. Put the raw materials used for preparing nano biomedical materials into the reactor 1 from the feed port of the reactor 1, and the reactor 1 is stirred at a stirring speed of 500-2000 rpm for 30 minutes under normal pressure and a constant temperature of room temperature to 80°C. ~360min, to obtain the initial magnetic particle reaction solution;
[0061] S2. Adsorb the magnetic particles in the initial magnetic particle reaction liquid in the reactor 1 on the inner wall of the reactor 1, and discharge the remaining reaction liquid out of the reactor 1 through the discharge port of the reactor 1, wherein the magnetic particles are reacted during the adsorption process The magnetic field strength of the reactor 1 is 2000 gauss to 10000 gauss, setting the magnetic field strength of the reactor 1 within this range can reduce th...
Embodiment 3
[0075] combine Figure 4 Shown, a kind of production method of nanometer biomedical material comprises:
[0076] S1. Mix the raw materials used to prepare nano-biomedical materials, stir and react under normal pressure and constant temperature conditions to obtain the initial magnetic particle reaction liquid, wherein the stirring speed of stirring is 500-2000rpm, and the stirring time is 30-360min ;The temperature of constant temperature is from room temperature to 80°C;
[0077]S2. Separating the magnetic particles in the initial magnetic particle reaction solution, and discharging the remaining reaction liquid. The magnetic particle separation is carried out by magnetic adsorption. The magnetic field strength during the magnetic adsorption process is 2000 Gauss to 10000 Gauss. Set the magnetic field strength to Within this range, the magnetic particles can be effectively separated from the initial magnetic particle reaction solution while reducing the cost;
[0078] S3. W...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com