A method for predicting the fatigue life of a bonding layer of a bonding structure under high-temperature and low-temperature cold and hot circulation conditions
A prediction method and fatigue life technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, time-consuming, and difficult to directly apply fatigue life testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
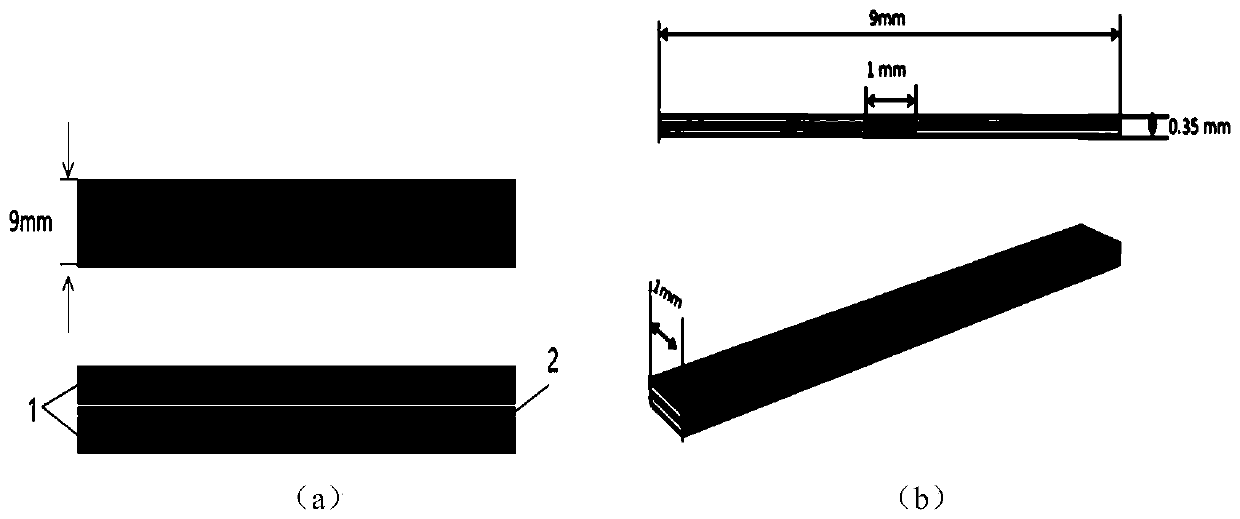
[0033] This embodiment is an aluminum / epoxy adhesive / aluminum bonded structure ( figure 1 a).
[0034] 1. Finite element simulation. According to the above-mentioned implementation mode, the test piece model of the bonded structure is established and a representative volume unit is selected for finite element thermal analysis model, numbered as Model A( figure 1 b). The upper and lower surfaces of the model are aluminum plates, and the middle layer is epoxy adhesive. The dark color in the middle area of the model indicates that the grid is dense, which is the main research area. The parameters of the finite element model are shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1 finite element model parameters
[0036] model number
Length, width and height (mm 3 )
Adhesive thickness (μm)
Model A
9*1*0.315
150
[0037] The material parameter input and result output are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.
[0038] Table 2 Input material paramete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com