Technological method of using high-phosphorus molten iron to produce ultralow-phosphorus steel
A process method, the technology of ultra-low phosphorus steel, applied in the field of iron and steel smelting, can solve the problems of deterioration of steel impact toughness, cold brittleness, and increase of steel ductile-brittle transition temperature, so as to reduce phosphorus content, reduce production costs, and optimize steelmaking process The effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
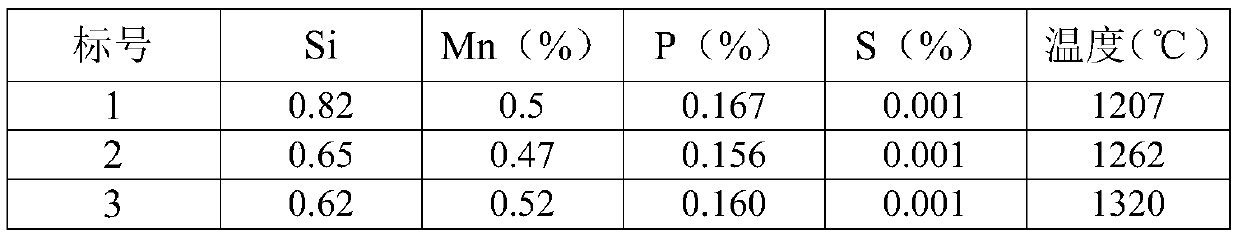
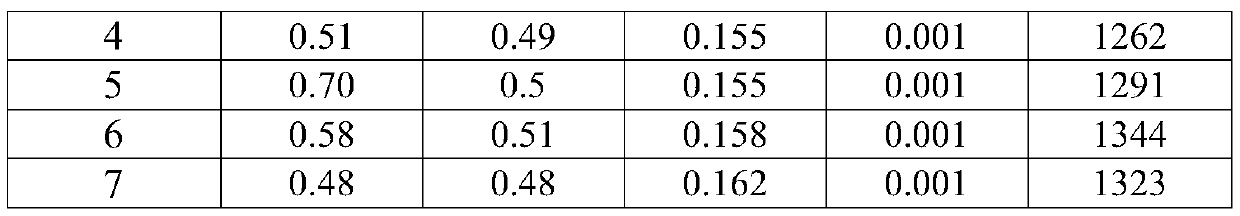
[0039] 1. Pretreatment of KR molten iron: The labels of the 7 furnaces of molten steel produced by continuous smelting are 1 to 7 in sequence. %.
[0040] Table 1 Situation of molten iron after KR desulfurization treatment (%)
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] 2. Converter smelting: control the final slag alkalinity, the blowing temperature at the end point; block the slag and tap the steel, blow the argon gas at the bottom of the ladle before tapping and stir for 1-2 minutes, and blow the argon gas at the bottom of the ladle to stir during the tapping process, and do not add molten steel for deoxidation agent and slag deoxidizer; the end temperature of converter smelting, the basicity of final slag and the composition of tapping molten steel are listed in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the P content of the steel is 0.0065-0.0123%, and the average dephosphorization rate is 94.1%. Furthermore, by controlling the end point temperature at 1600-1620°C, the P content ca...
Embodiment 2
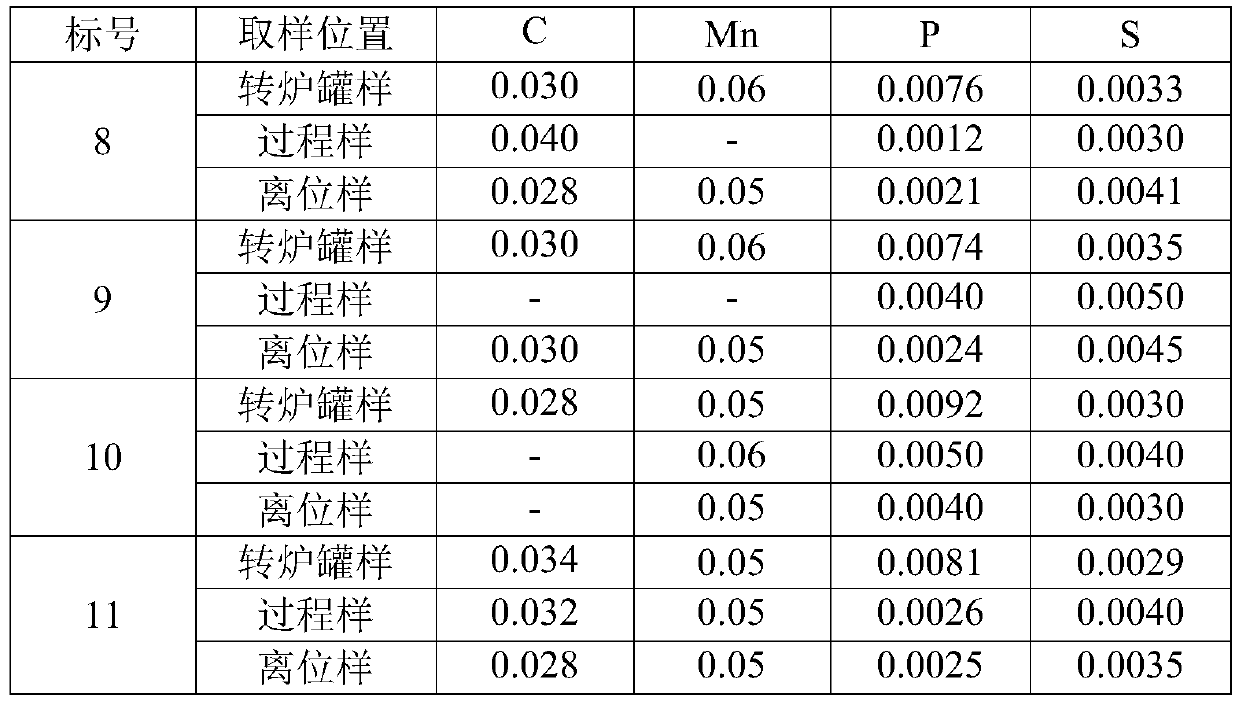
[0054] 1. Pretreatment of KR molten iron: the grades of the 4 furnaces of molten steel produced by continuous smelting are 8-11 in sequence. %.
[0055] Table 5 Situation of molten iron after KR desulfurization treatment
[0056] label
[0057] 2. Converter smelting: control the final slag alkalinity, the blowing temperature at the end point; block the slag and tap the steel, blow the argon gas at the bottom of the ladle before tapping and stir for 1-2 minutes, and blow the argon gas at the bottom of the ladle to stir during the tapping process, and do not add molten steel for deoxidation agent and slag deoxidizer; converter smelting end temperature, final slag basicity and tapping molten steel composition are listed in Table 6. It can be seen from Table 2 that the content of P in the steel is 0.010-0.012%.
[0058] Table 6 Composition of tapping at the end of converter (%) and end temperature of blowing (℃)
[0059] label
[0060] 3. LF refining: during...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com