Nucleic acid sample content determining method for genome next generation sequencing
A technology of next-generation sequencing and determination methods, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate quantitative results, improve quantitative accuracy, reduce the amount of standard substances, and reduce quantitative costs. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
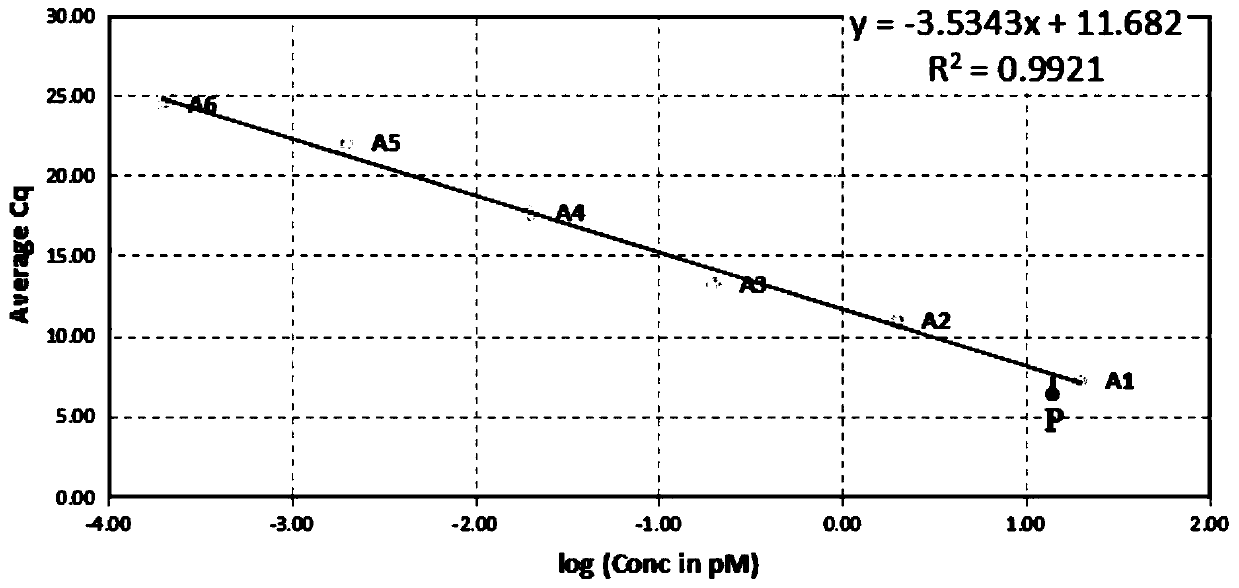
[0066] A method for determining the content of a nucleic acid sample for next-generation sequencing of a genome, comprising the following steps: performing a fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Qpcr) on a standard substance with a concentration of 20 pM and three nucleic acid samples to be tested to obtain a given fluorescence intensity The number of cycles of the next standard and the nucleic acid sample to be tested; the results are as follows:
[0067]
[0068] (2) According to the number of cycles of the standard substance obtained in step (1), select an applicable standard curve from the standard curve series;
[0069] Described standard curve embodies the linear relationship between the logarithm of initial concentration and the number of cycles; the point that embodies the given concentration logarithm value of standard substance and the number of cycles thereof in step (1) is as follows: figure 1 The point P shown in , according to condition 1, selec...
Embodiment 2
[0084] A method for determining the content of a nucleic acid sample for next-generation sequencing of a genome, comprising the following steps:
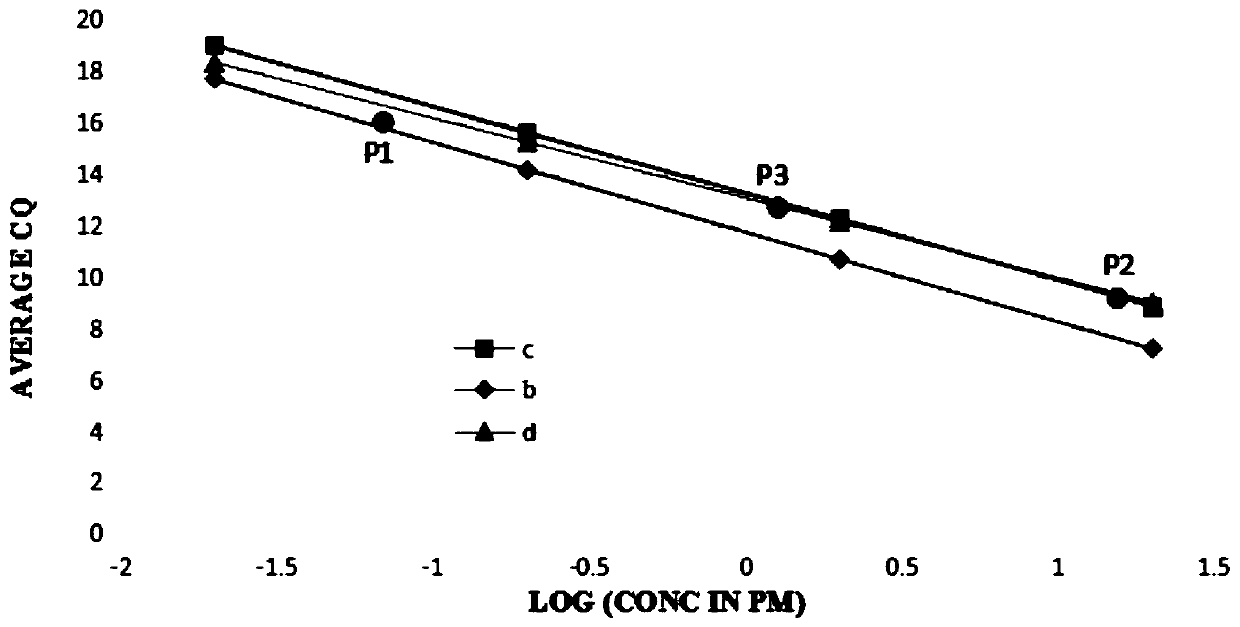
[0085] (1) Perform fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Qpcr) on 4 standard substances with concentrations of 20pM, 2pM, 0.2pM, 0.02pM and 3 nucleic acid samples to be tested to obtain the standard substance and nucleic acid samples to be tested at a given fluorescence intensity The number of cycles; the results are as follows:
[0086]
[0087] (2) According to the number of cycles of the standard substance obtained in step (1), select an applicable standard curve from the standard curve series;
[0088] The standard curve embodies the linear relationship between the logarithm of the initial concentration and the number of cycles;
[0089] The points that reflect the logarithmic value of the given concentration of the standard in step (1) and its cycle times are as follows: figure 2 Point P shown in 1 ,P 2 ,P ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] A method for determining the content of a nucleic acid sample for next-generation sequencing of a genome, comprising the following steps:
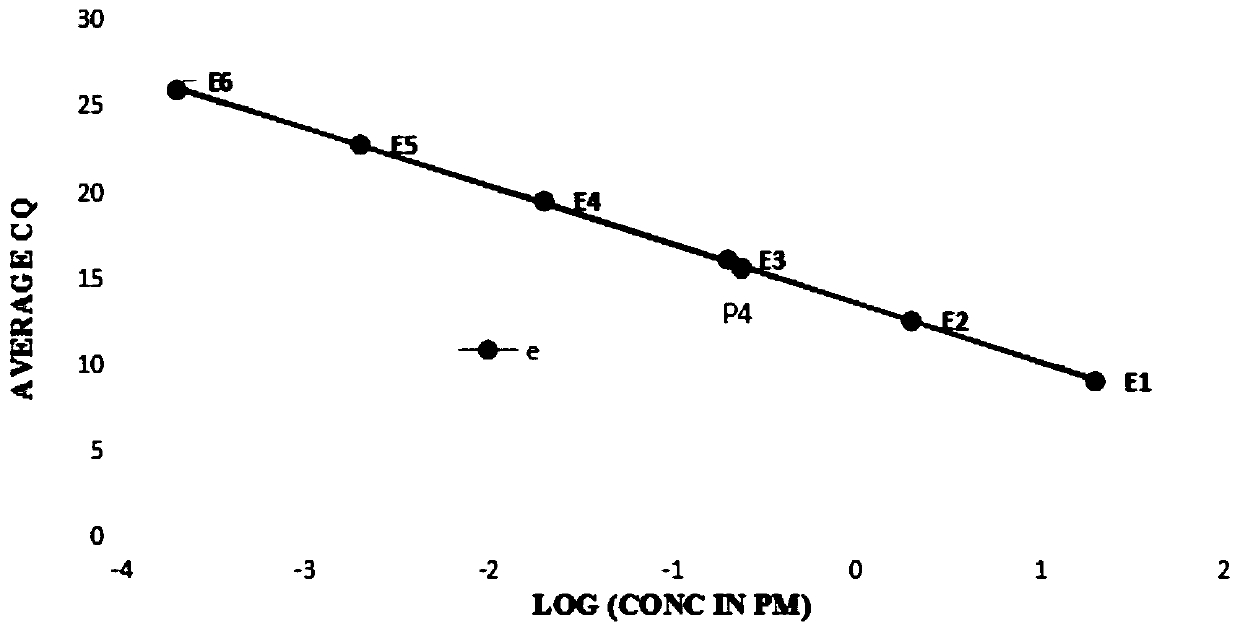
[0098] (1) Perform fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Qpcr) on a standard substance with a concentration of 20pM, 7 nucleic acid samples to be tested, and a quantitative reference substance to obtain the circulation of the standard substance and the nucleic acid sample to be tested at a given fluorescence intensity times; the results are as follows:
[0099]
[0100] (2) According to the number of cycles of the standard substance obtained in step (1), select an applicable standard curve from the standard curve series;
[0101] The standard curve embodies the linear relationship between the logarithm of the initial concentration and the number of cycles;
[0102] The points that reflect the logarithmic value of the given concentration of the standard in step (1) and its cycle times are as follows: image 3 Poin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com