A strain of Brevibacterium flavum producing l-valine and its application
A technology of Brevibacterium flavum and valine, which is applied in the field of bioengineering and can solve problems such as the inability to produce L-valine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Obtaining of Brevibacterium flavum FMME447
[0026] Screening liquid medium: valine 100g, glucose 5g, beef extract 5g, yeast powder 5g, peptone 10g, sodium chloride 5g, distilled water to 1L, pH 7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 30min.
[0027] Screening solid medium: valine 100g, glucose 5g, beef extract 5g, yeast powder 5g, peptone 10g, sodium chloride 5g, agar 20g, distilled water to 1L, pH7.0~7.2, sterilized at 121℃ for 30min .
[0028] A strain of Brevibacterium flavum was obtained by selection and breeding, which can grow normally on the screening liquid medium with a L-valine concentration of 100g / L and the screening solid medium with a L-valine concentration of 100g / L. Named Brevibacterium flavum FMME447.
[0029] Brevibacterium flavum FMME447, named Brevibacterium flavum FMME447 taxonomically, was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on January 17, 2019, with the deposit number CCTCCNO:M2019053, and the deposit address is Wuhan ...
Embodiment 2
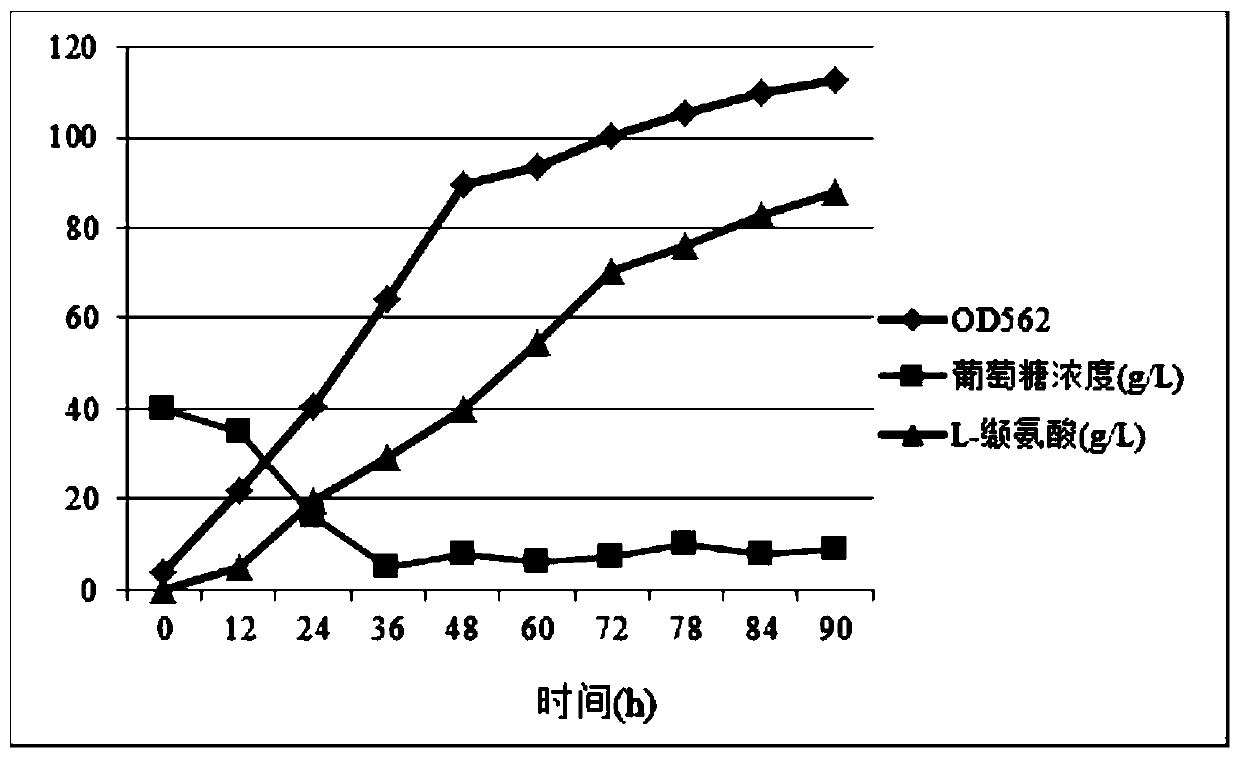
[0030] Example 2: Fermentation of Brevibacterium flavum FMME447 to produce L-valine
[0031] Solid plate medium: glucose 5g, beef extract 5g, yeast extract 10g, peptone 5g, sodium chloride 5g, agar 20g, dilute to 1L with distilled water, pH 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 30min.
[0032] Slant medium: 5g glucose, 5g beef extract, 10g yeast extract, 5g peptone, 5g sodium chloride, 20g agar, dilute to 1L with distilled water, pH 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 30min.
[0033] Seed medium: glucose 20g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g, magnesium sulfate 0.5g, corn steep liquor 20g, ammonium sulfate 3g, biotin 100μg, V B1 100μg, dilute to 1L with distilled water, adjust the pH to 7.0 with sodium hydroxide solution, and sterilize at 121°C for 30min.
[0034] Fermentation medium: initial glucose concentration 40g, corn steep liquor 10g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g, V H 200 μg, V B1 200μg, dilute to 1L with distilled water, adjust the pH to ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Fermentation of Brevibacterium flavum FMME447 to produce L-valine
[0040] The same as the fermentation process of Example 2, the only difference is that the fermentation medium is different.
[0041] Fermentation medium: initial glucose concentration 50g, corn steep liquor 15g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.3g, V H 200 μg, V B1 200μg, dilute to 1L with distilled water, adjust the pH to 7.0 with sodium hydroxide solution, and sterilize at 121°C for 30min.
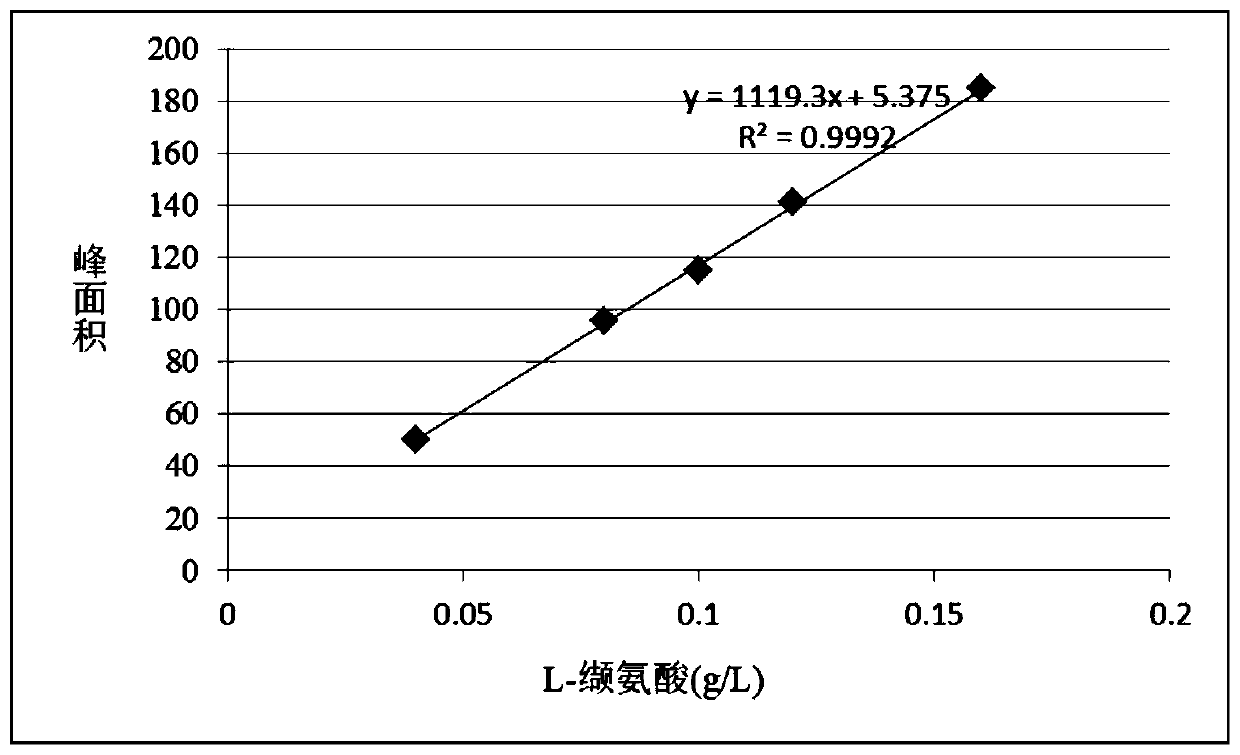
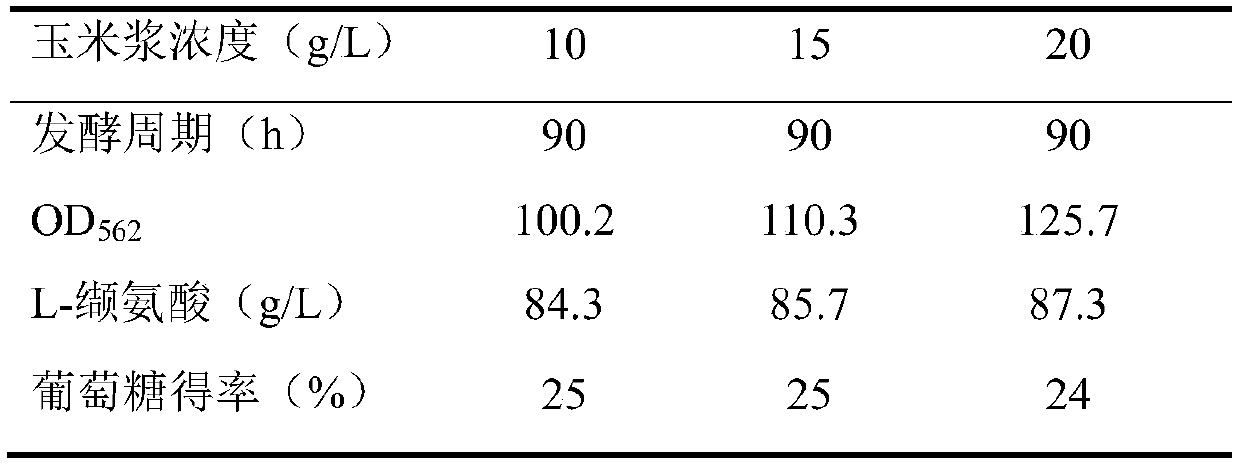
[0042] After the fermentation, the fermented liquid was collected and centrifuged, and the supernatant was collected to measure the content of L-valine in the fermented liquid by high performance liquid chromatography to be 85.7 g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com