Lead-cooled fast reactor afterheat discharging system and method
A waste heat removal system and waste heat removal technology are applied to reactors, cooling devices, and reduction of greenhouse gases. It can solve problems such as inability to exchange heat in the core, loss of heat release function of the secondary circuit, and potential safety hazards, so as to avoid common mode failures, The effect of enhancing intrinsic safety and increasing flow rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
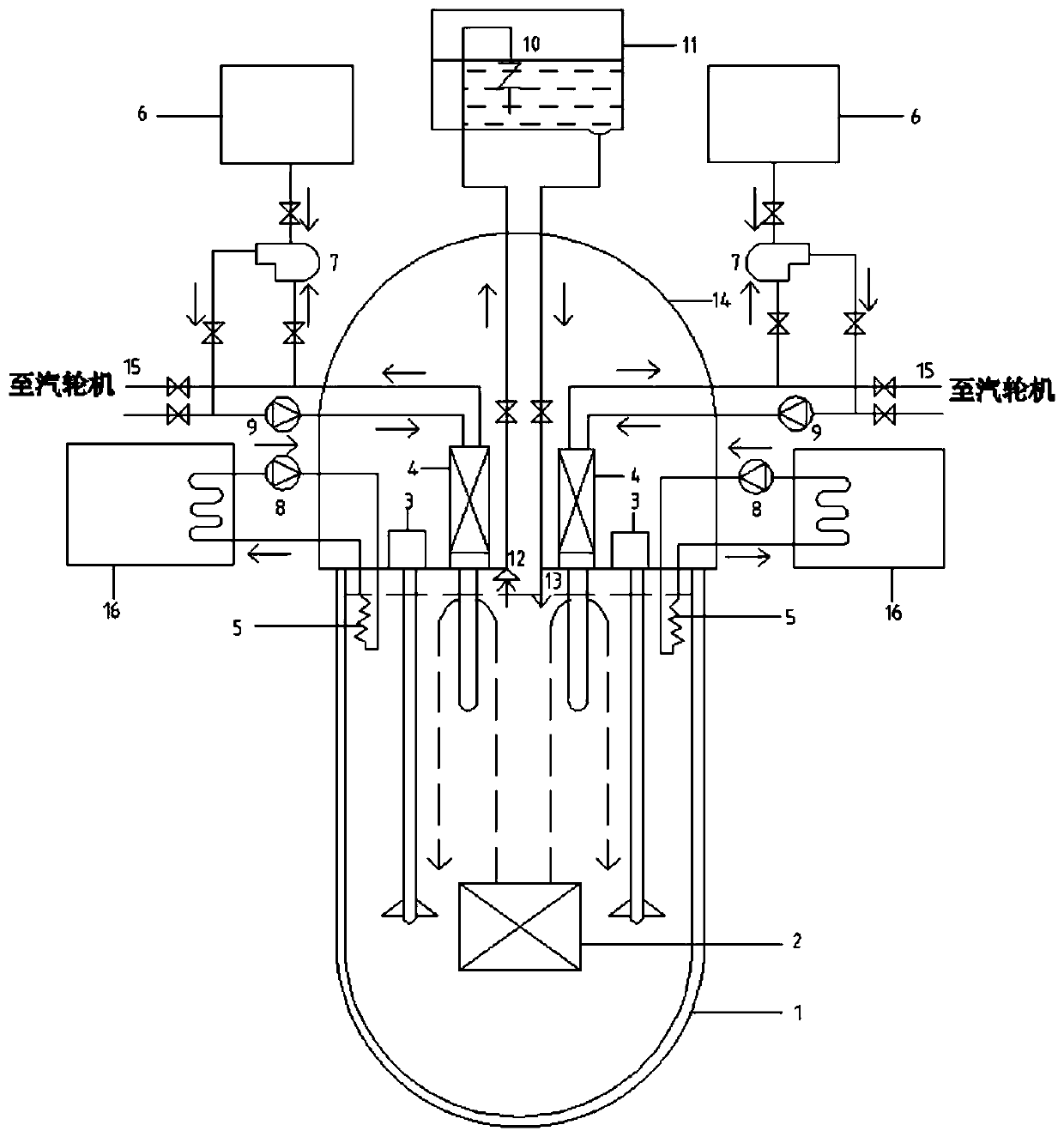
[0043] see Figure 1-5 , a waste heat removal system for a lead-cooled fast reactor, comprising a reactor pressure vessel 1 including a reactor core 2, and a containment vessel 14, a passive waste heat removal system is arranged above the containment vessel 14, and an upper portion of the containment vessel 14 is also Equipped with independent working magnetic heat exchanger active waste heat removal system and waste heat driven passive core 2 cooling system,
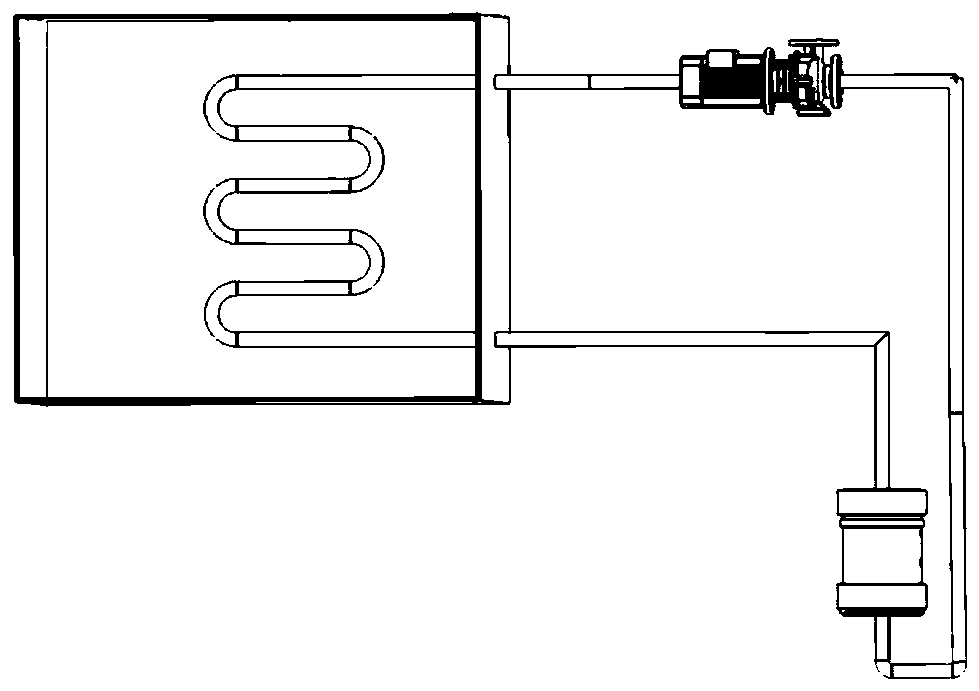
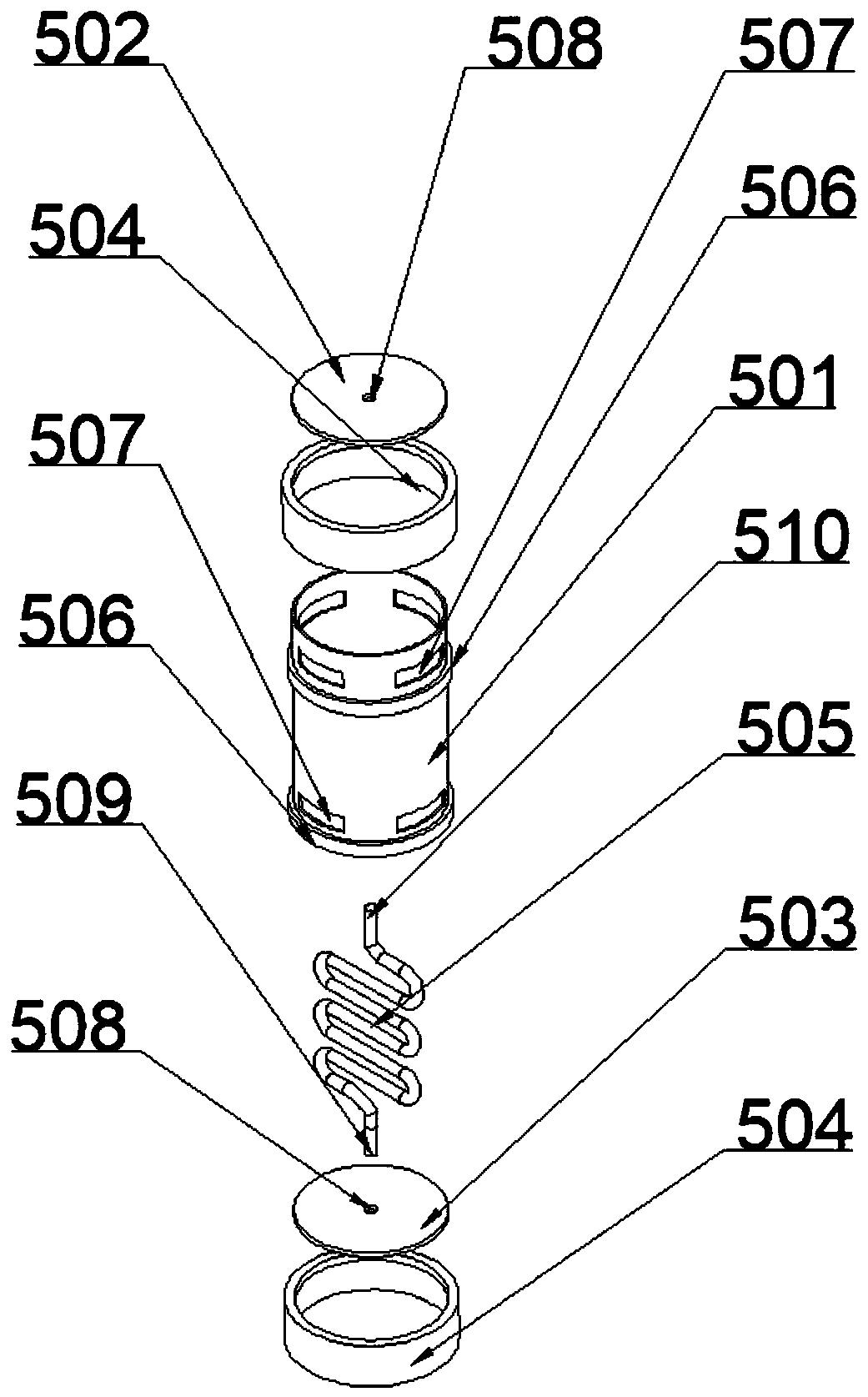
[0044] The magnetic heat exchanger active waste heat removal system includes a circulation loop composed of a water tank 16, a waste heat discharge pump 8 and a magnetic heat exchanger 5; the magnetic heat exchanger 5 is located in the reactor pressure vessel 1 internal;
[0045] The waste heat-driven passive core cooling system includes a circuit composed of pipelines connecting the main feedwater pump 9, the steam generator 4, the heating pipe and the steam turbine, and the heating pipe is located inside the reactor pr...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This embodiment provides a lead-cooled fast reactor waste heat discharge system. On the basis of Embodiment 1, the waste heat-driven passive core cooling system also includes a water supply tank 6, The pneumatic pump 7, the steam generator 4, and the heating pipe are connected to form a secondary circuit; the water inlet end of the steam generator 4 is connected with the main feed water pump 9 and the pneumatic pump 7 in parallel.
[0065] When the power failure occurs in the core 2, in step S4, while the magnetic heat exchanger 5 and the passive waste heat removal system discharge the waste heat from the core 2, the valve of the pneumatic pump 7 is opened The waste heat is discharged from the core 2, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0066] The heated lead-bismuth alloy coolant exchanges heat with the heating pipe of the passive core 2 cooling system driven by the waste heat, so that the water in the heat pipe enters the steam turbine 15 after being heated and e...
Embodiment 3
[0068] This embodiment provides a lead-cooled fast reactor waste heat discharge system. On the basis of Embodiment 2, two active waste heat discharge systems of the magnetic suction heat exchanger are arranged symmetrically on both sides of the passive waste heat discharge system, which can To ensure that the core 2 is under normal shutdown conditions and power-off conditions, the waste heat discharge of the core 2 can be further accelerated by setting the two active waste heat discharge systems of the magnetic suction heat exchanger to operate at the same time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com