Quantum error correction code flag bit symptom measurement method based on dynamic time slot distribution
A technology of dynamic time slot and time slot allocation, which is applied in the direction of using block code for error correction/detection, using linear code for error correction/detection, encoding, etc., which can solve the problem of long measurement time, low parallelism of measurement lines, and resource consumption Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of less measurement time, less resource consumption, and less auxiliary qubits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
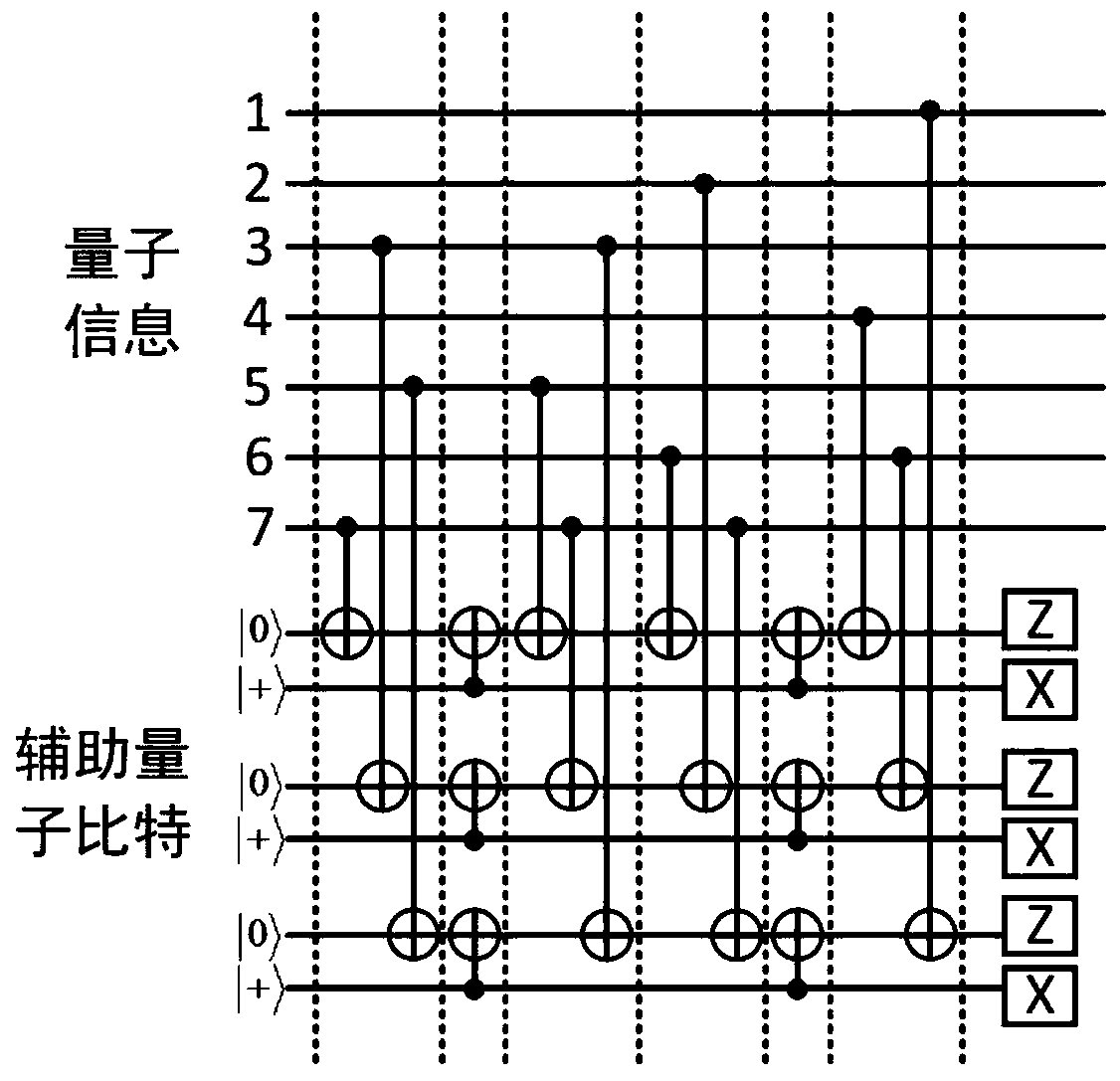
[0066] Embodiment 1 of the present invention is to use the present invention to carry out symptom measurement to quantum [[7,1,3]] code Z-type stabilizer, obtain the sign position symptom of quantum [[7,1,3]] code Z-type stabilizer Measurement wiring diagram.
[0067] Step A. Construct a matrix of qubit numbers.
[0068] The binary generator matrix of the input quantum [[7,1,3]] code is as follows, each row in the matrix represents a stabilizer, and each column represents a qubit.
[0069]
[0070] All the rows of the binary generator matrix are arranged in descending order according to the size of each stable sub-weight by using the method of elementary row transformation of the matrix. The weight of the stabilizer refers to the number of 1s contained in the row corresponding to each stabilizer in the generator matrix. The weights of the quantum [[7,1,3]] code stabilizers are all equal to 4, and the arrangement order of the rows remains unchanged.
[0071]
[0072] C...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Embodiment 2 of the present invention is to use the present invention to carry out symptom measurement to quantum [[12,2,3]] code Z-type stabilizer, obtain the sign position symptom of quantum [[12,2,3]] code Z-type stabilizer Measurement wiring diagram.
[0101] Step a. Construct a matrix of qubit numbers.
[0102] The binary generator matrix of the input quantum [[12,2,3]] code is as follows, wherein each row in the matrix represents a stabilizer, and each column represents a qubit.
[0103]
[0104] Using the matrix elementary row transformation method, arrange all the rows of the binary generator matrix of the quantum [[12,2,3]] code in descending order according to the weight of each stabilizer. Among them, the weight of the stabilizer refers to the number of 1s contained in each row corresponding to each stabilizer in the generator matrix, and the weight values of each row of the quantum [[12,2,3]] code are respectively 4, 4, 6, 4, 4, move the third row wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com