Human genetic markers associated with response to treatments that target clostridium difficile toxin b
A Clostridium difficile, treatment-responsive technology, applied in the field of genetic markers, to solve problems such as inability to eliminate CDI
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0233] Actoxumab / bezlotoxumab and belotoxumab in patients with CDI of subjects in clinical trials
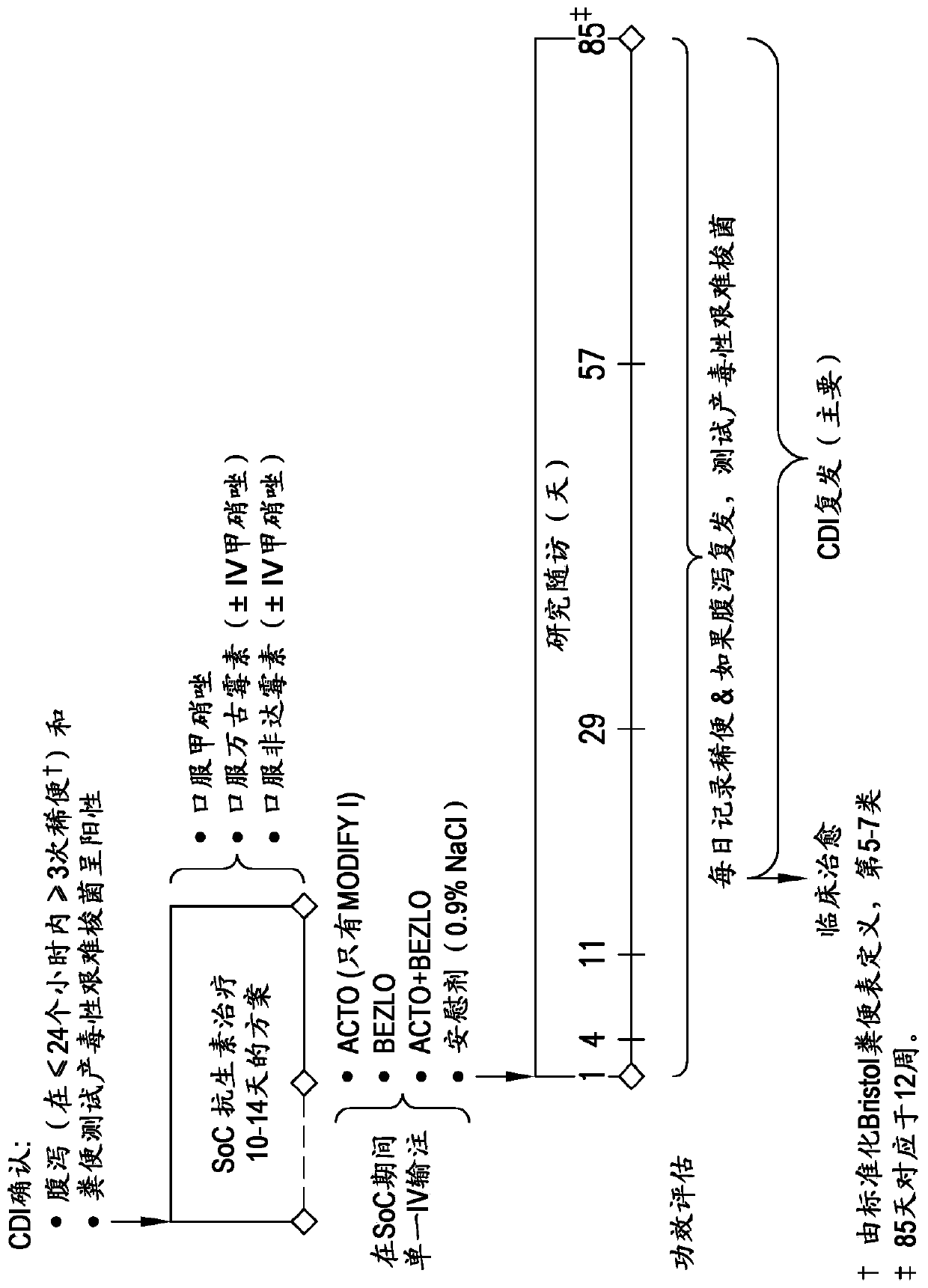
[0234] To identify genetic contributions to treatment response, the inventors performed pharmacogenetic (PGx) analysis of C. difficile-infected subjects who had undergone clinical trials employing antibodies to C. difficile toxin B to use a genome-wide association study (GWAS) method to assess whether the mean treatment difference varies in subgroups of patients defined by genetic variation. The clinical study designs of the two clinical trials called MODIFYI (PN001) and MODIFY II (PN002) are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0235] PN001 is an adaptive design phase 3 trial in which subjects diagnosed with CDI and receiving standard-of-care treatment for CDI (metronidazole, vancomycin, or fidaxomicin) were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to 4 One of the treatment groups (belotuzumab, aktokinumab, aktokinumab / belotuzumab, or placebo). In the prespecified interim analysis,...
Embodiment 2
[0241] Genome-wide association studies to identify SNPs associated with response to treatments comprising TcdB antibodies and antibiotics
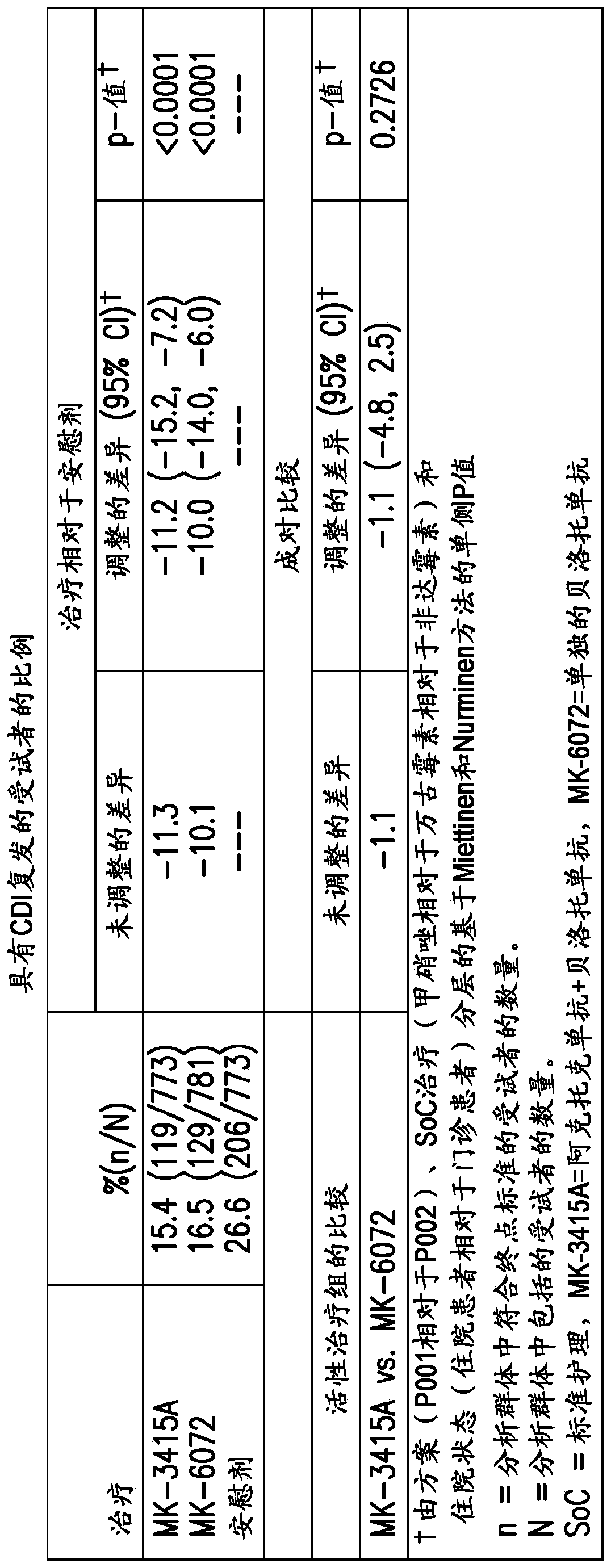
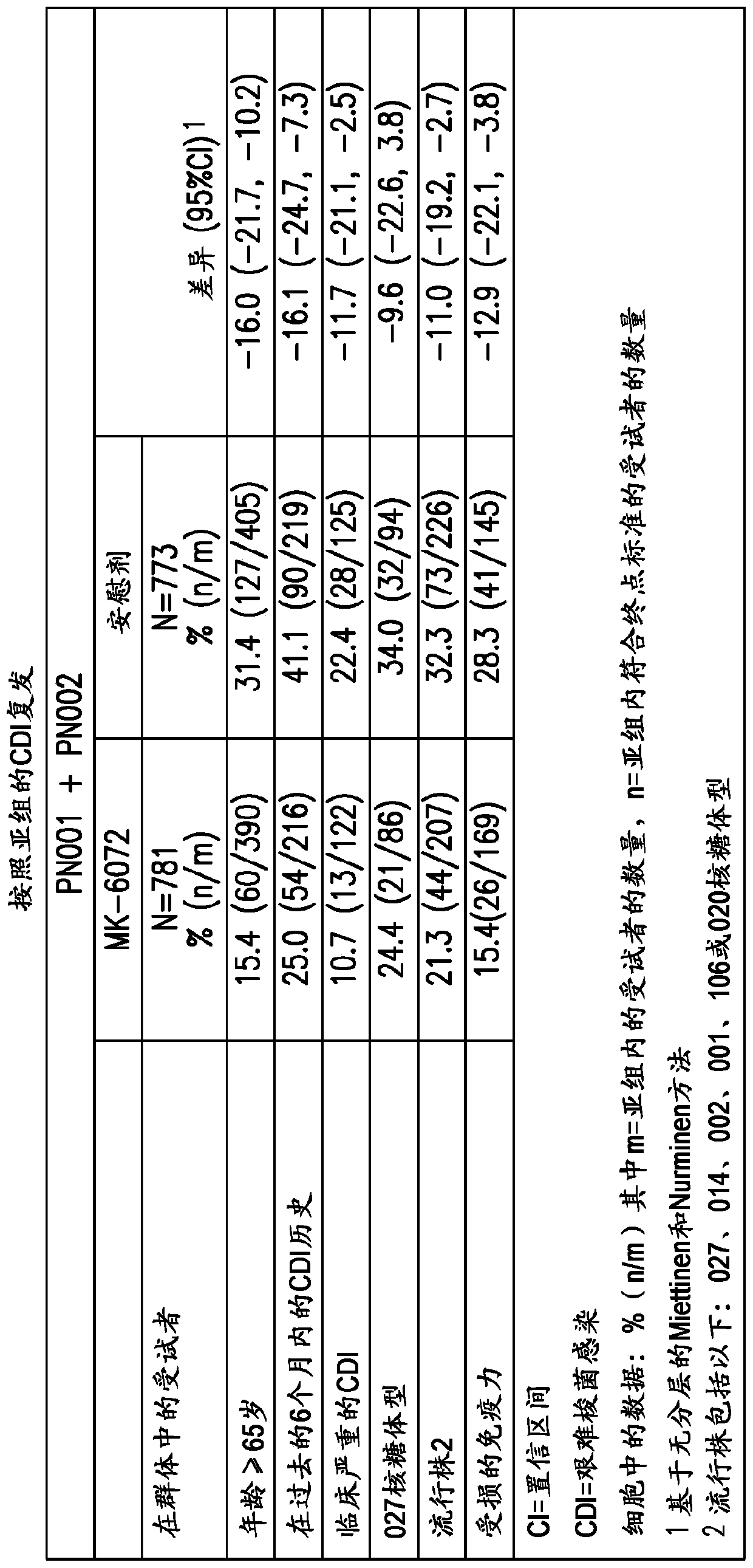
[0242] Genome-wide association studies were performed to assess whether genetic variants in the human genome were associated with differences in treatment among patients randomly assigned to different groups of the study. Because the analysis of the clinical studies confirmed that the treatment benefit was primarily derived from belotomab rather than akinetizumab, it was determined that the benefit from the belotomab-containing treatment group (belokomab alone and belokumab alone Anti + Aktoximab) subjects were pooled and compared to placebo (no mAb administered, only 0.9% NaCl). The combined dataset for GWAS analysis was based on approximately 897 patients from both MODIFY I and II (PN001 and PN002, also referred to herein as the "PGx dataset"). Subjects from the Aktoximab alone group were not used for GWAS analysis. Only subjects wit...
Embodiment 3
[0246] statistical methods
[0247] Conducting two pivotal studies, MODIFY I and II (PN001 and PN002), to evaluate beloxomab (MK-6072), aktoximab (MK-3415), belotoximab and aktoximab Combination of mAbs (MK-3415A) and placebo for prevention of Clostridium difficile relapse (rCDI) in patients receiving standard-of-care antibiotics. The primary clinical endpoint of interest was rCDI, which was defined as a new episode of diarrhea associated with a positive local or central laboratory stool test for toxigenic C. difficile following clinical cure of the initial CDI episode (3 within 24 hours or less). occurrence of one or more loose stools). The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with CDI recurrence assessed by Week 12. Initial efficacy results from two studies showed that beloxetumab was superior to placebo in reducing the rate of CDI recurrence (p<0.0001), while aktoximab alone showed no efficacy compared to placebo (p=0.3182 ).
[0248] Commercial Af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com