Indoor positioning method based on OS-ELM fusion vision and inertial information
An indoor positioning and inertial technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, surveying and mapping and navigation, etc., can solve problems such as poor results, and achieve the effect of improving positioning performance and precise positioning results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
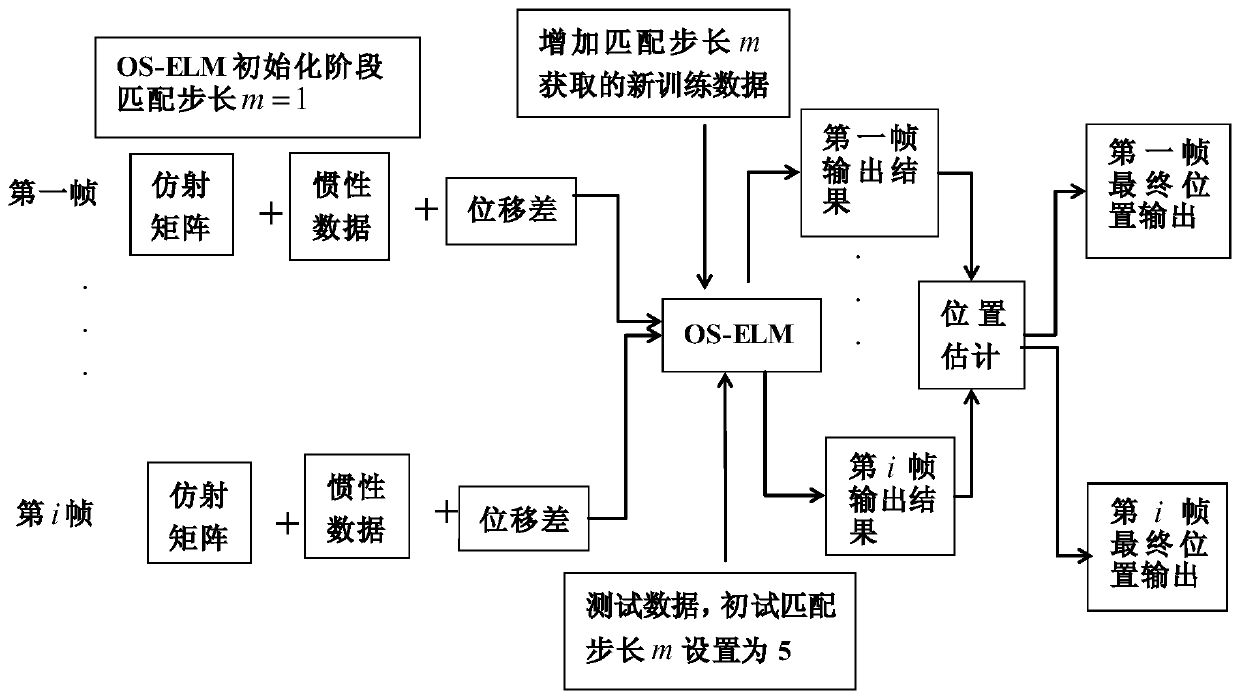
[0053] The technical solution of the present invention is further introduced below in conjunction with specific calculation formulas and accompanying drawings, see the following description for details:
[0054] Preprocess the obtained inertial and visual sensor data to generate feature vectors, and model the training data containing feature vectors and target outputs:
[0055] First, the visual information is preprocessed, and the SURF (fast robust feature) feature is extracted from each frame of training image, and the image I numbered i is i and image I numbered i+m i+m to match. Then use the two-way matching algorithm to remove the mismatching points, and keep the N with high matching degree a For matching points, calculate the affine transformation matrix P through these matching points.
[0056] Each affine transformation matrix P is calculated by the following formula:
[0057]
[0058] In the formula, r represents the rotation angle, A is the scaling vector, T ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Combine below Figure 2-Figure 4 , Table 1-Table 2, and specific examples verify the feasibility of the scheme in Example 1, see the following description for details:
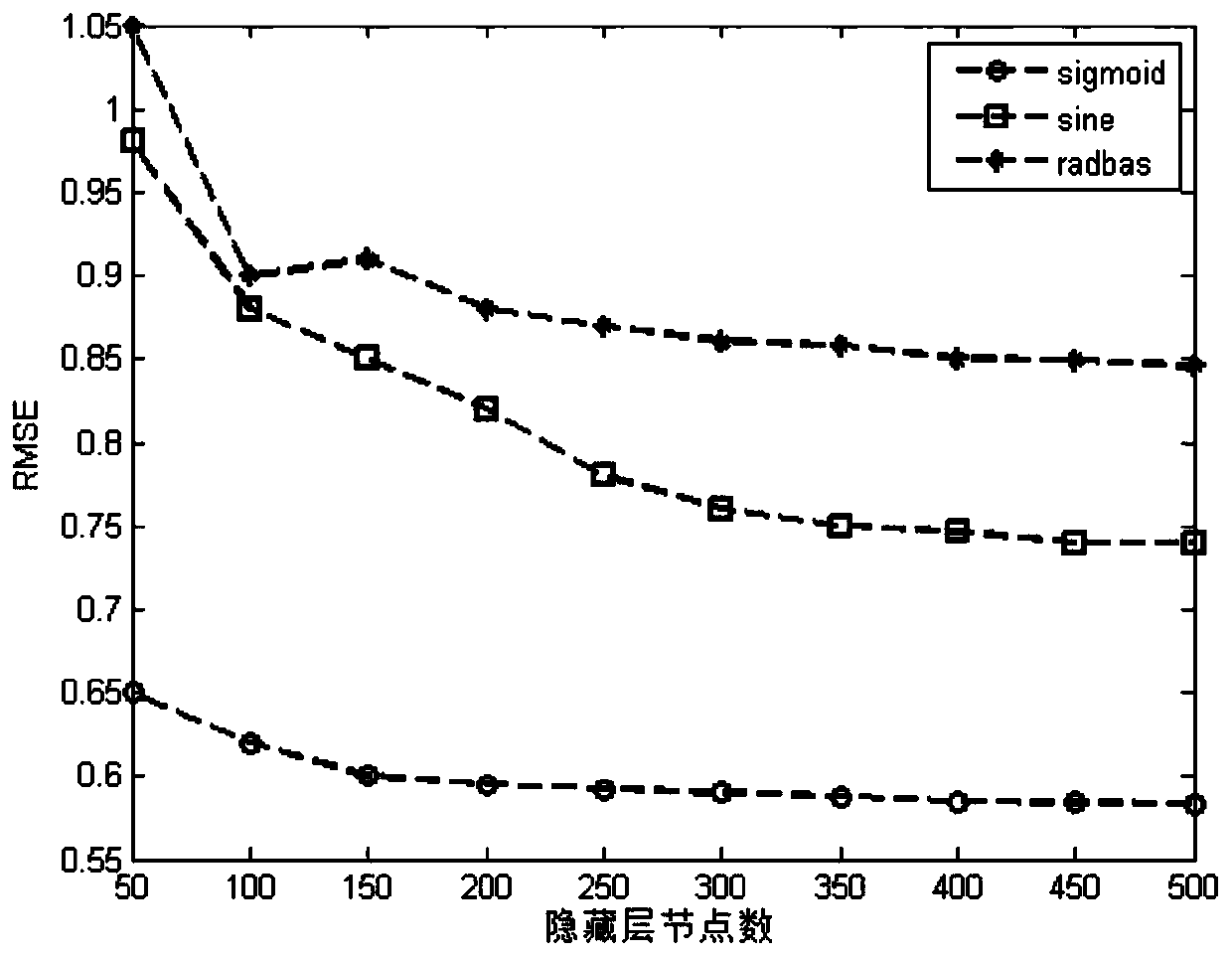
[0092] For the effect of this method, apply the algorithm steps in the above embodiment 1 to perform positioning analysis on the experiment with a total duration of 56 seconds and a displacement length of 15m. The experiment includes random entry and exit of personnel and scene mutations and other interference scenes. The parameters are set as follows: the number of hidden layer nodes is 150, the number of SURF features is 40, and the threshold of matching pairs is N a is 24, and the initial matching step in the online adaptive positioning stage is 5.
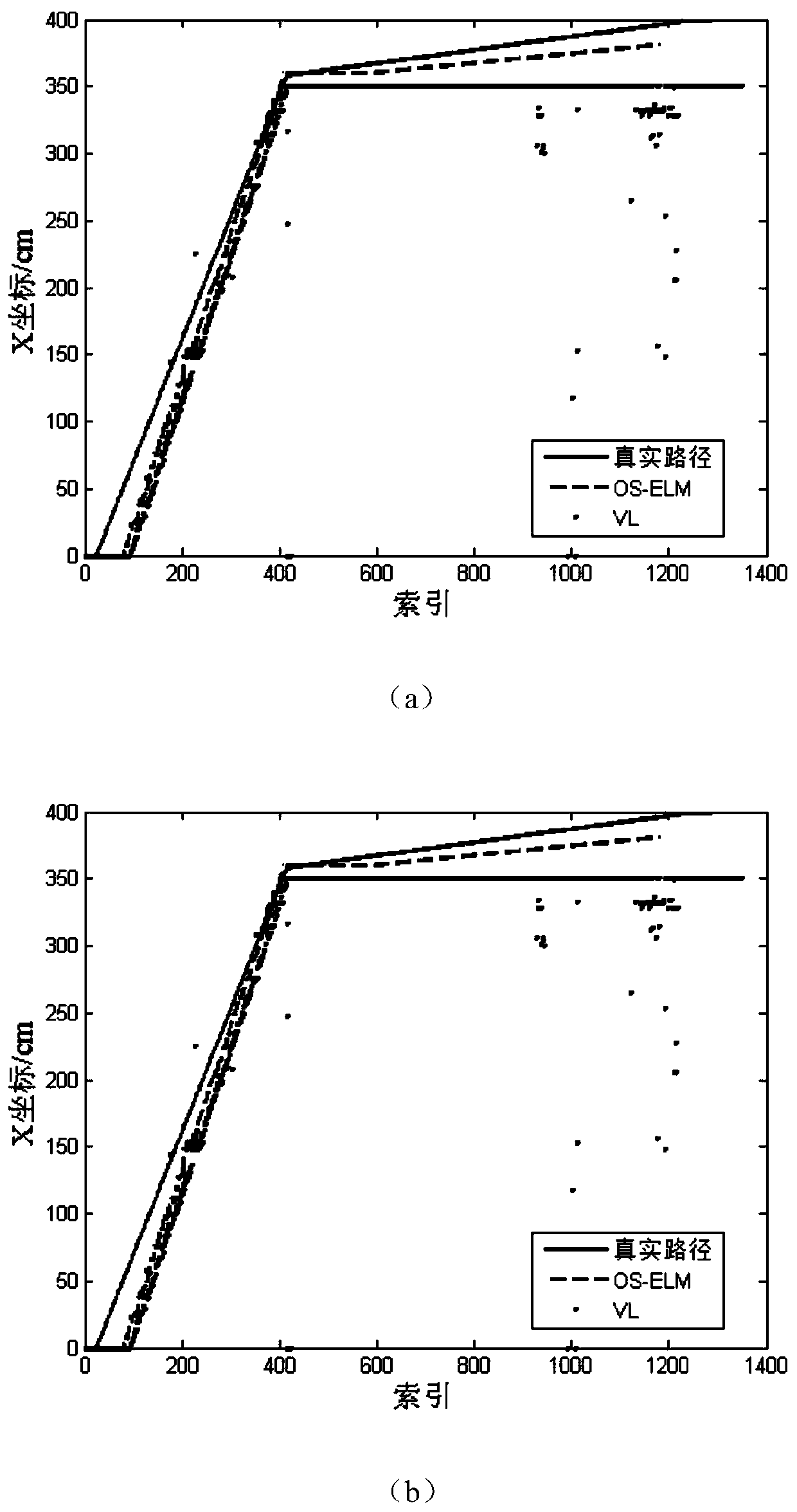
[0093] qualitative angle, figure 2 It shows the comparison of the positioning effect between this method and the positioning algorithm proposed in [4]. image 3 This is a schematic diagram of the comparison of error cumulative distribution graphs bet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com