Method and device for determining tubular tissue region of interest, equipment and medium
A region of interest, tubular technology, applied in the field of medical imaging, can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-intensive editing, and the difficulty of determining the outer wall of blood vessels, etc., to achieve the effects of time-consuming and labor-intensive, accurate measurement and size assessment, and simple determination methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
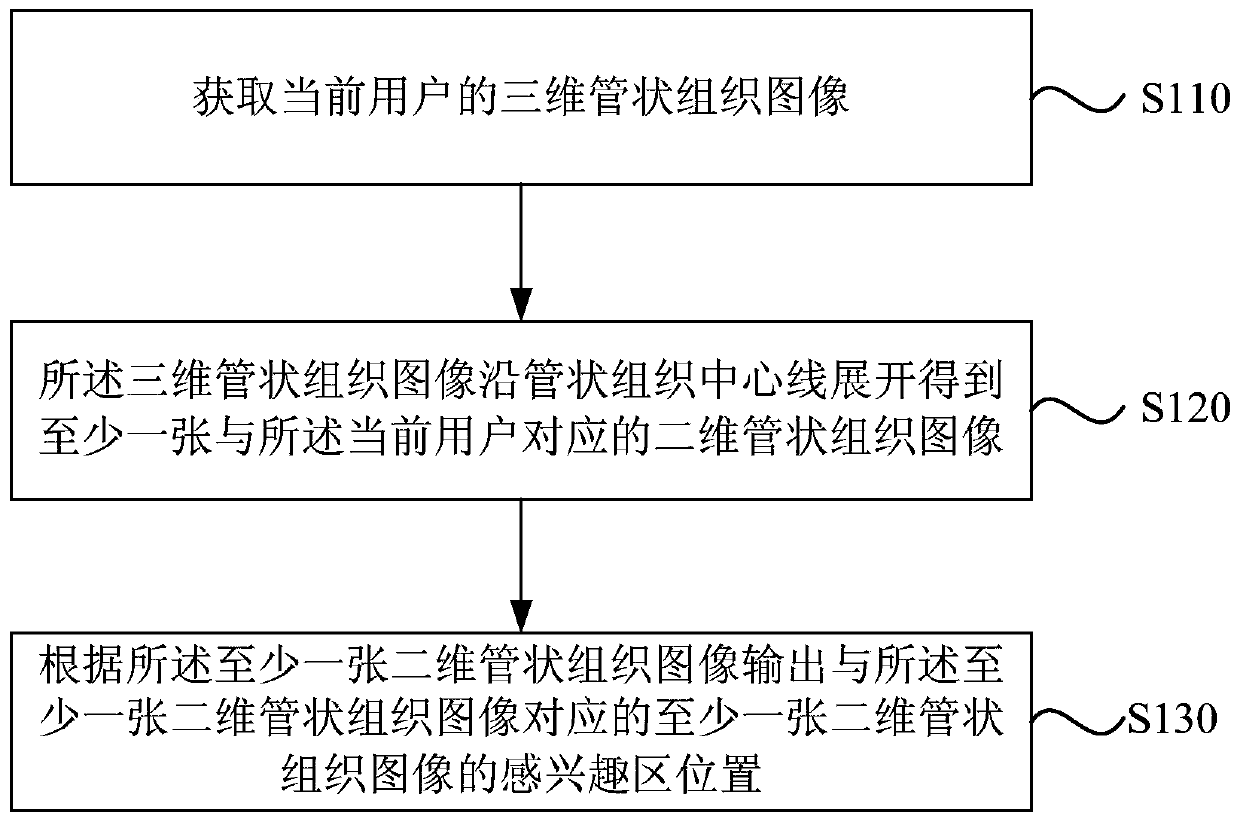
[0052] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a method for determining a region of interest in tubular tissue provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to the situation of determining a region of interest in tubular tissue. The method can be determined by determining the region of interest in tubular tissue The device is implemented, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0053] S110. Acquire a three-dimensional tubular tissue image of the current user.
[0054]Among them, tubular tissues include blood vessels and trachea. The three-dimensional tubular tissue image may include enhanced CT blood vessel images, may also include images obtained by MR blood vessel imaging such as MR angiography images or MR TOF images, and any other three-dimensional images that can image blood vessels.
[0055] S120. Expand the three-dimensional tubular tissue image along the centerline of the tubular tissue to obtain at least one two-dimensional tubula...
Embodiment 2
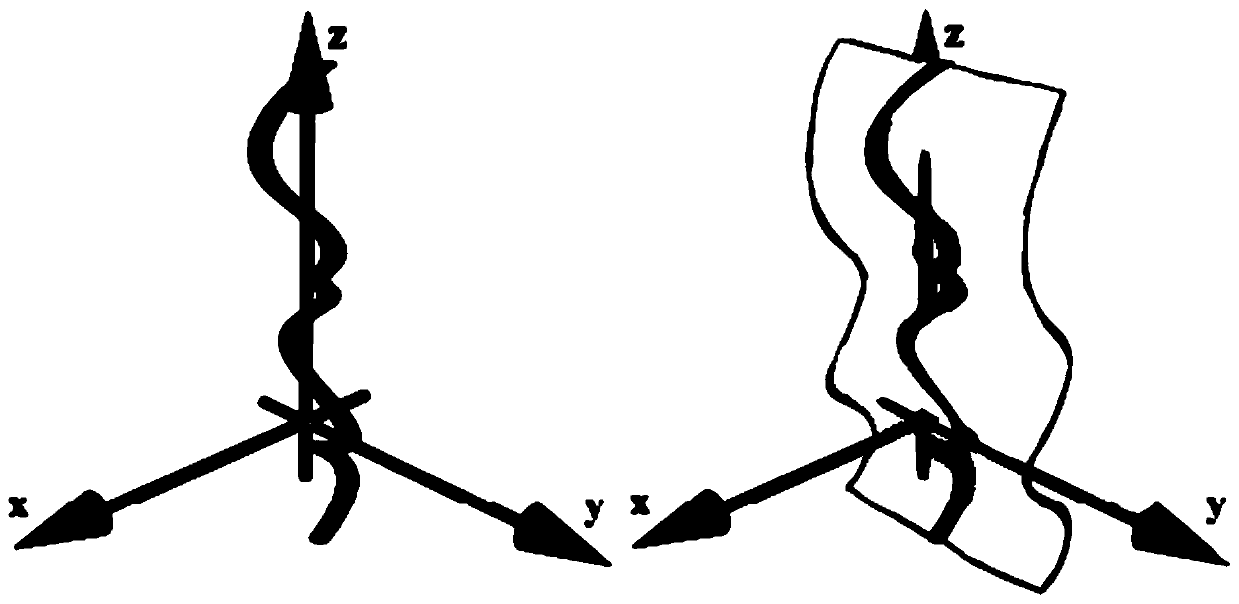
[0064] Figure 4 It is a flowchart of a method for determining a region of interest in tubular tissue provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is optimized based on the above embodiments. In this embodiment, the three-dimensional tubular tissue image described in the step is expanded along the tubular tissue centerline to obtain at least one two-dimensional tubular tissue image corresponding to the current user for further optimization. It is: unfolding the three-dimensional tubular tissue image along the centerline of the current user's tubular tissue to obtain at least one two-dimensional tubular tissue image corresponding to the current user from different angles. On this basis, the step of outputting the ROI position of the at least one two-dimensional tubular tissue image corresponding to the at least one two-dimensional tubular tissue image according to the at least one two-dimensional tubular tissue image is further optimized as follows: the at...
Embodiment 3
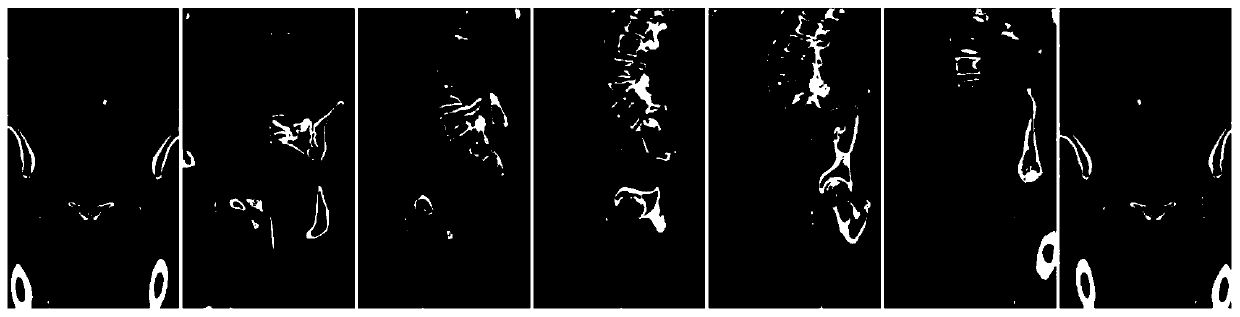
[0078] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of an optional embodiment of a method for determining a region of interest in tubular tissue provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. On the basis of the foregoing embodiments, a preferred embodiment is provided. The method for determining a region of interest in tubular tissue includes:
[0079] Acquire historical 3D tubular tissue images.
[0080] The centerline of the historical three-dimensional tubular tissue is extracted by means of automatic extraction, semi-automatic extraction or manual extraction, etc. to extract the centerline of the tubular tissue.
[0081] Expand the historical 3D tubular tissue image along the tubular tissue centerline to obtain at least one 2D tubular tissue image corresponding to the historical 3D tubular tissue image at different angles, which is convenient for intuitive observation. After unfolding, the same tubular tissue image according to different reconstruction angles can be obtained...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com