Application of SIRT1 inhibitor in prevention and treatment of radiation-induced intestinal diseases
A 1. SIRT1, inhibitor technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of lack of ideal drugs and effective treatment methods for intestinal damage, and achieve the effect of reducing epithelial cell death, promoting regeneration ability, and broad market application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
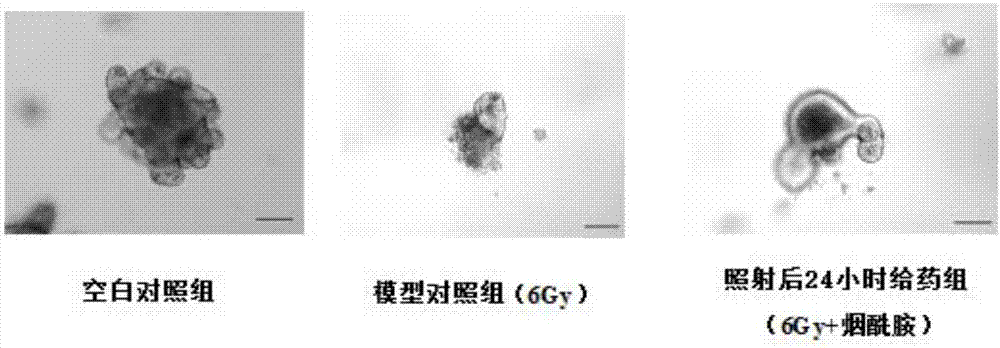
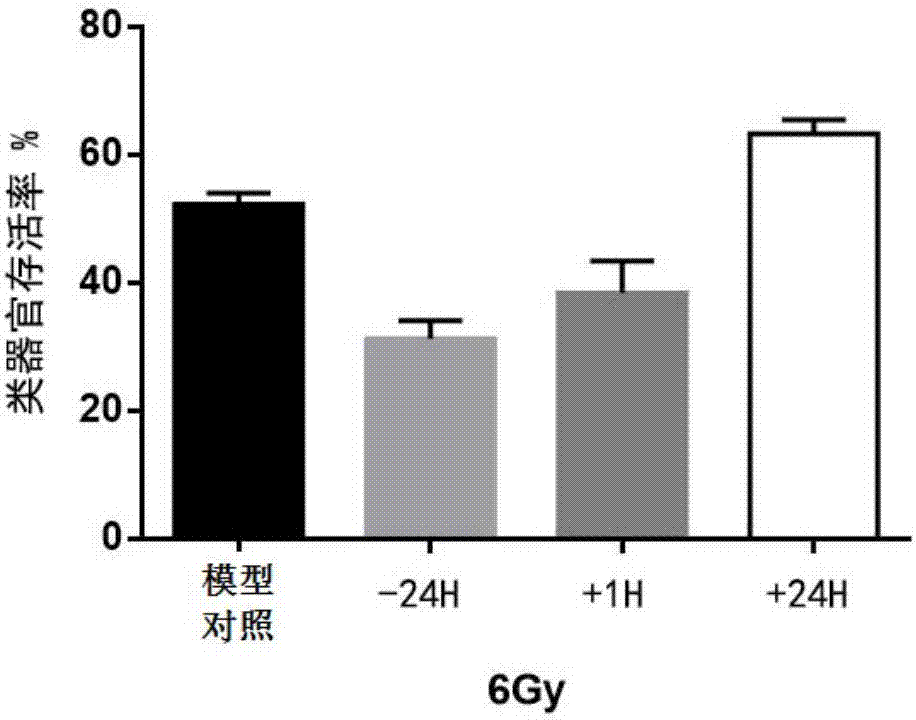
[0061] (1) To study the protective effect of nicotinamide administered at different times on intestinal damage caused by X-ray 6Gy irradiation:
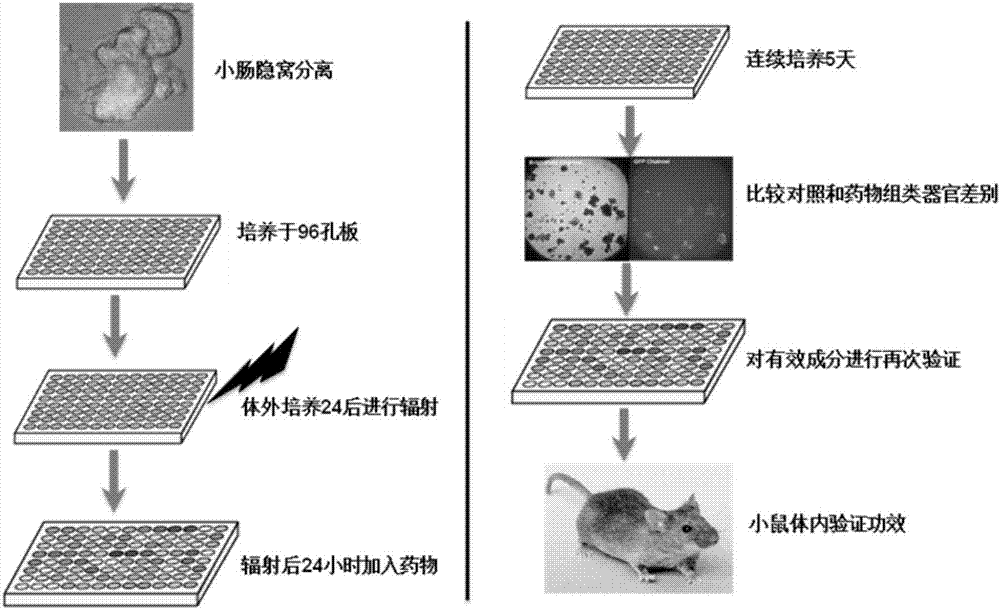
[0062] Small intestinal crypts were isolated from 8-12 week-old C57BL mice, planted in Matrigel with conditioned medium, and inoculated for 24 hours, and five groups of small intestinal organoids were taken, and they were set as blank control group (no irradiation) and model control group , the administration group 24 hours before the irradiation, the administration group 1 hour after the irradiation, and the administration group 24 hours after the irradiation. X-ray 6Gy was used to irradiate the small intestinal organoids in the model control group, the 24 hours before irradiation group, the 1 hour after irradiation group, and the 24 hours after irradiation group. The first 24 hours administration group was administered nicotinamide 10 mM before irradiation, and the administration group 1 hour after irradiation and the administratio...
Embodiment 2
[0071] To study the protective effect of EX527 on radiation-induced intestinal injury:
[0072] Small intestinal crypts were isolated from 8-12 week-old C57BL mice, planted in Matrigel with conditioned medium, and three groups of small intestinal organoids were taken 24 hours after inoculation, and were set as the model control group and the nicotinamide group 24 hours after irradiation. 24 hours after exposure to the EX527 group. X-ray (RAD-320 X-ray machine (PXI, USA)) 8Gy was used to irradiate small intestinal organoids in the model control group, the nicotinamide group 24 hours after irradiation, and the EX527 group 24 hours after irradiation. Among them, the model control group No administration, nicotinamide 10mM 24 hours after irradiation, nicotinamide 10mM for 24 hours after irradiation, EX527 (100μM) for EX527 group 24 hours after irradiation. The above three groups were cultured for 5 days and observed There were differences in organ survival rate and size between t...
Embodiment 3
[0077] To study the protective effect of Sirtinol against radiation-induced intestinal damage:
[0078] Small intestinal crypts were isolated from 8-12-week-old C57BL mice, planted in Matrigel with conditioned medium, and inoculated for 24 hours. Five groups of small intestinal organoids were taken, and they were set as model control groups, and Sirtinol ( 10 μM) group, Sirtinol (50 μM) group 24 hours after irradiation, Sirtinol (100 μM) group 24 hours after irradiation, nicotinamide (10 mM) 24 hours after irradiation. Then 8Gy was irradiated with x-ray (RAD-320 X-ray machine (PXI, USA), and different concentrations of SIRT1 inhibitor Sirtinol (10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM) were added 24 hours after irradiation, and DMSO control and nicotinamide control were set. Culture 5 Days later, the difference in organoid survival rate between the treatment group and the control group was observed.
[0079] result: Figure 10 It shows the model control group, the Sirtinol (10μM) group given 24...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com