MMC direct current transmission line fault identification method based on SOD transformation
A DC transmission line, fault identification technology, applied in the fault location, detection of faults by conductor type, etc., can solve problems such as damage to the transmission system, and achieve good application prospects, good quickness, and noise elimination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
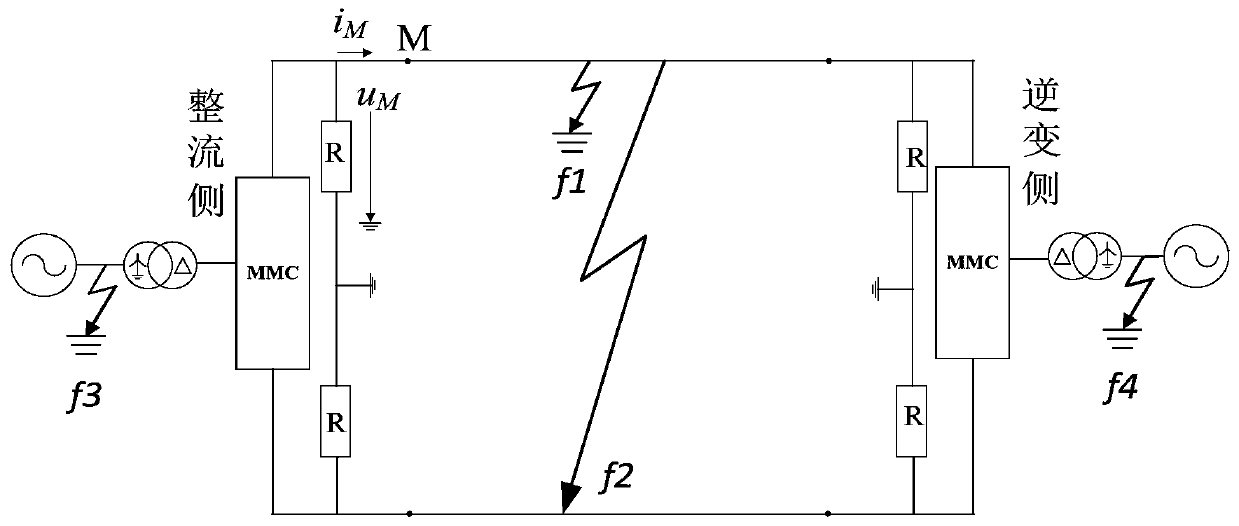
[0031] Example 1: Establish as attached figure 1 The MMC HVDC transmission system shown is used as a simulation model. The winding on the valve side of the connecting transformer adopts a delta connection without a neutral point, and the AC side of the connecting transformer adopts a star connection, and its neutral point is directly grounded. The DC side is grounded through the clamping resistor, which has a large resistance value. Its main function is to clamp the two-pole voltage and provide a potential reference point for the DC system during normal operation. The DC voltage is ±320kV, the transmission line is 400km, and M is the measurement terminal.
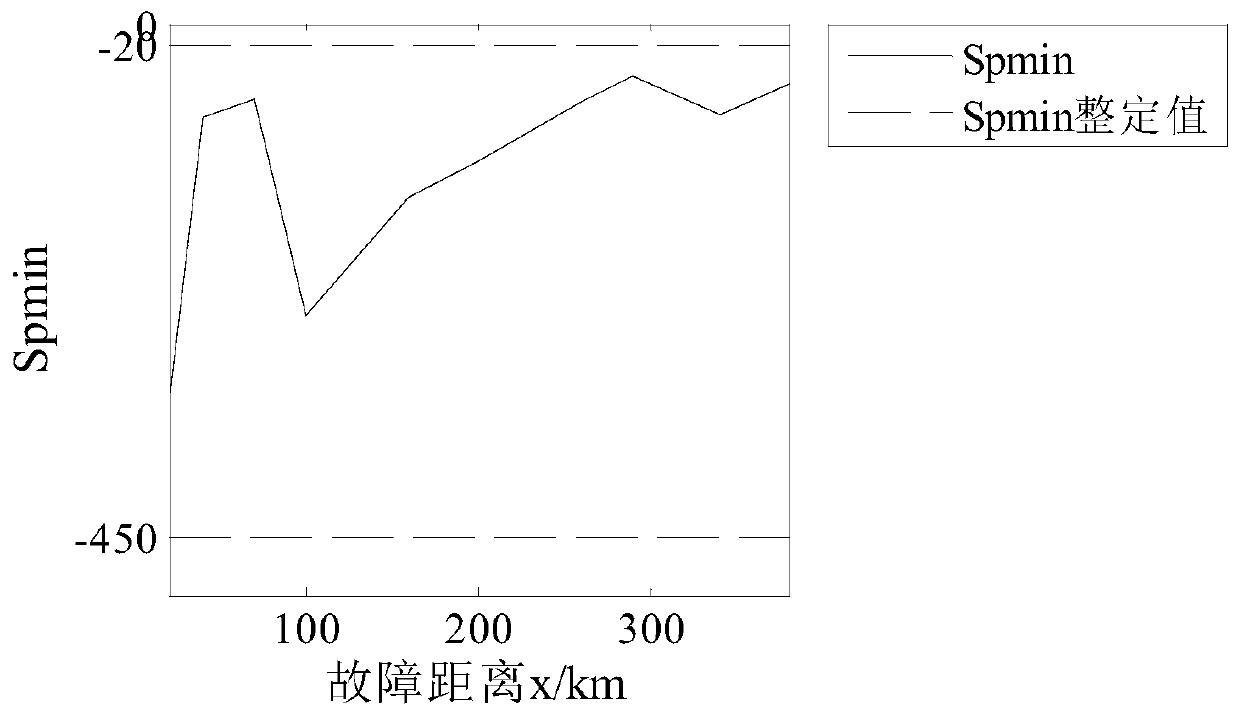
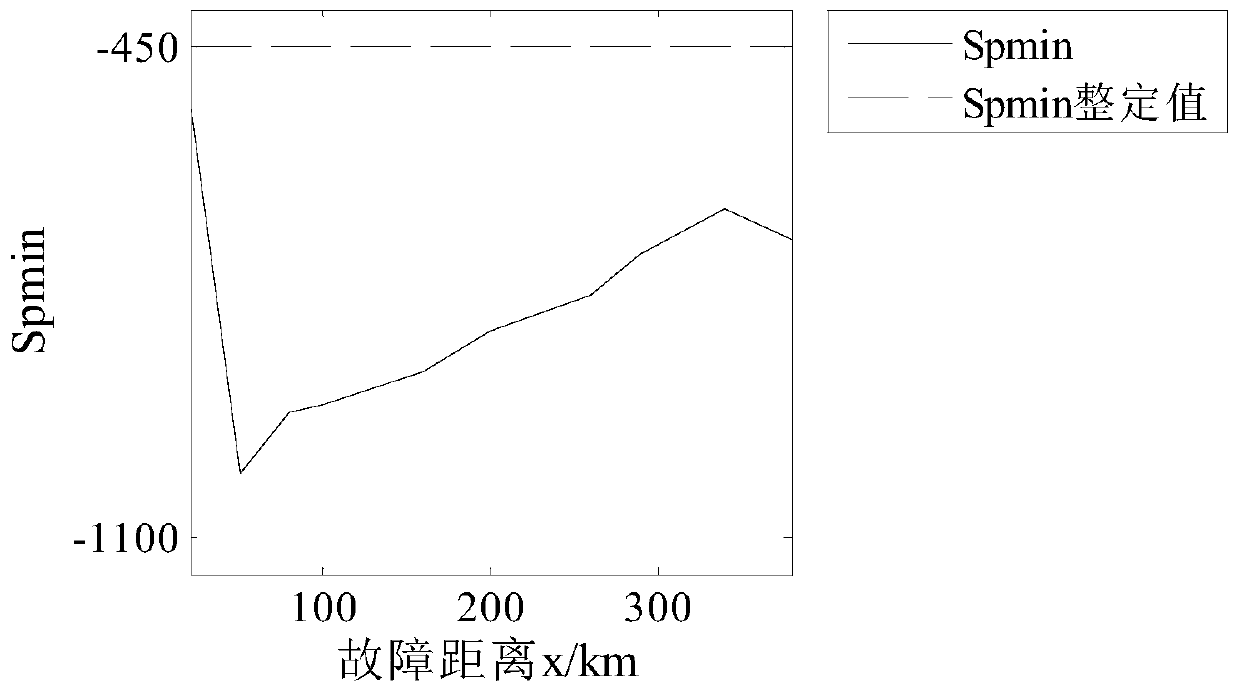
[0032] (1) Fault location: positive ground fault f 1 , 160km away from the measuring end; the fault start time is 0.4s; the sampling frequency is 10kHz.
[0033] (2) Acquire fault voltage and current data at the measurement point according to the first step in the manual.
[0034] (3) Acquire the fault voltage and curre...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Establish as attached figure 1 The MMC HVDC transmission system shown is used as a simulation model. The winding on the valve side of the connecting transformer adopts a delta connection without a neutral point, and the AC side of the connecting transformer adopts a star connection, and its neutral point is directly grounded. The DC side is grounded through the clamping resistor, which has a large resistance value. Its main function is to clamp the two-pole voltage and provide a potential reference point for the DC system during normal operation. The DC voltage is ±320kV, the transmission line is 400km, and M is the measurement terminal.
[0038] (1) Fault location: bipolar short circuit fault f 2 , 160km away from the measuring end; the fault start time is 0.4s; the sampling frequency is 10kHz.
[0039] (2) Acquire fault voltage and current data at the measurement point according to the first step in the manual.
[0040] (3) Acquire the fault voltage and...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3: Establish as attached figure 1 The MMC HVDC transmission system shown is used as a simulation model. The winding on the valve side of the connecting transformer adopts a delta connection without a neutral point, and the AC side of the connecting transformer adopts a star connection, and its neutral point is directly grounded. The DC side is grounded through the clamping resistor, which has a large resistance value. Its main function is to clamp the two-pole voltage and provide a potential reference point for the DC system during normal operation. The DC voltage is ±320kV, the transmission line is 400km, and M is the measurement terminal.
[0044] (1) Fault location: Three-phase short-circuit fault on the AC side of the rectifier station f3 ; The start time of the fault is 0.4s; the sampling frequency is 10kHz.
[0045] (2) Acquire fault voltage and current data at the measurement point according to the first step in the manual.
[0046] (3) Acquire the fau...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com