Three level gate monitoring
A grid control and grid technology, applied in program control, computer control, general control system, etc., can solve problems such as component aging, overheating, humidity, dust, mechanical stress, equipment failure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
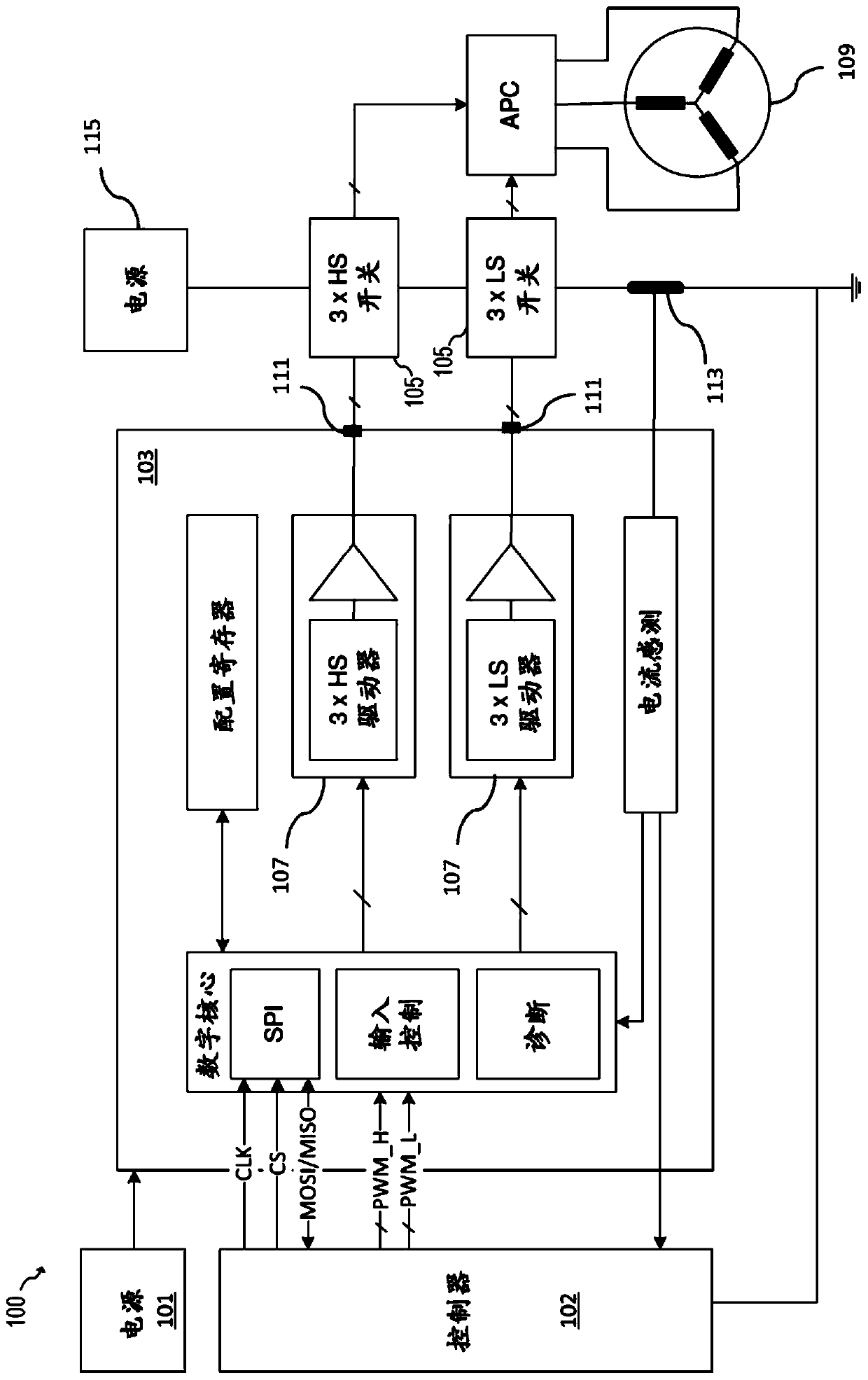
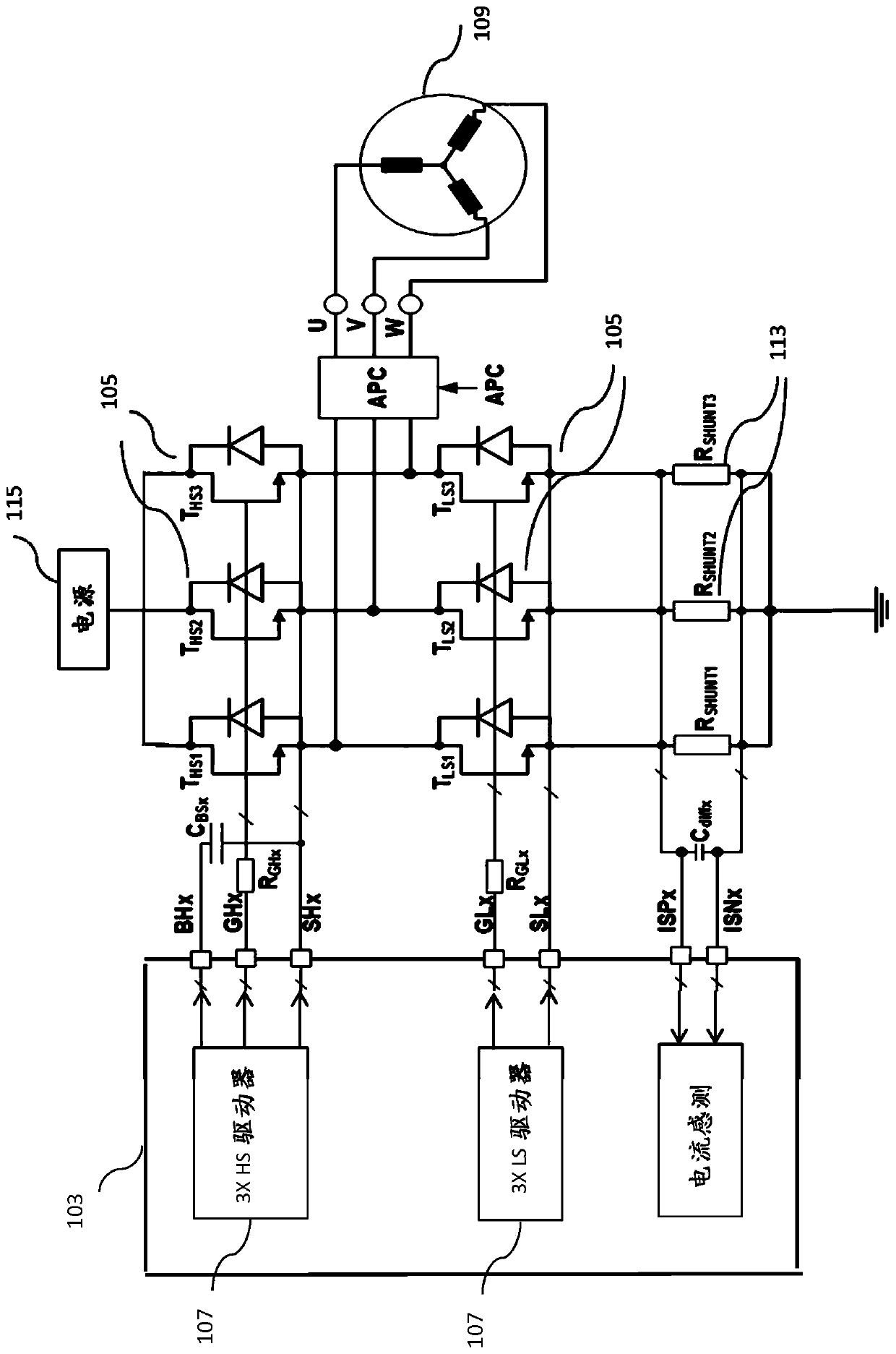
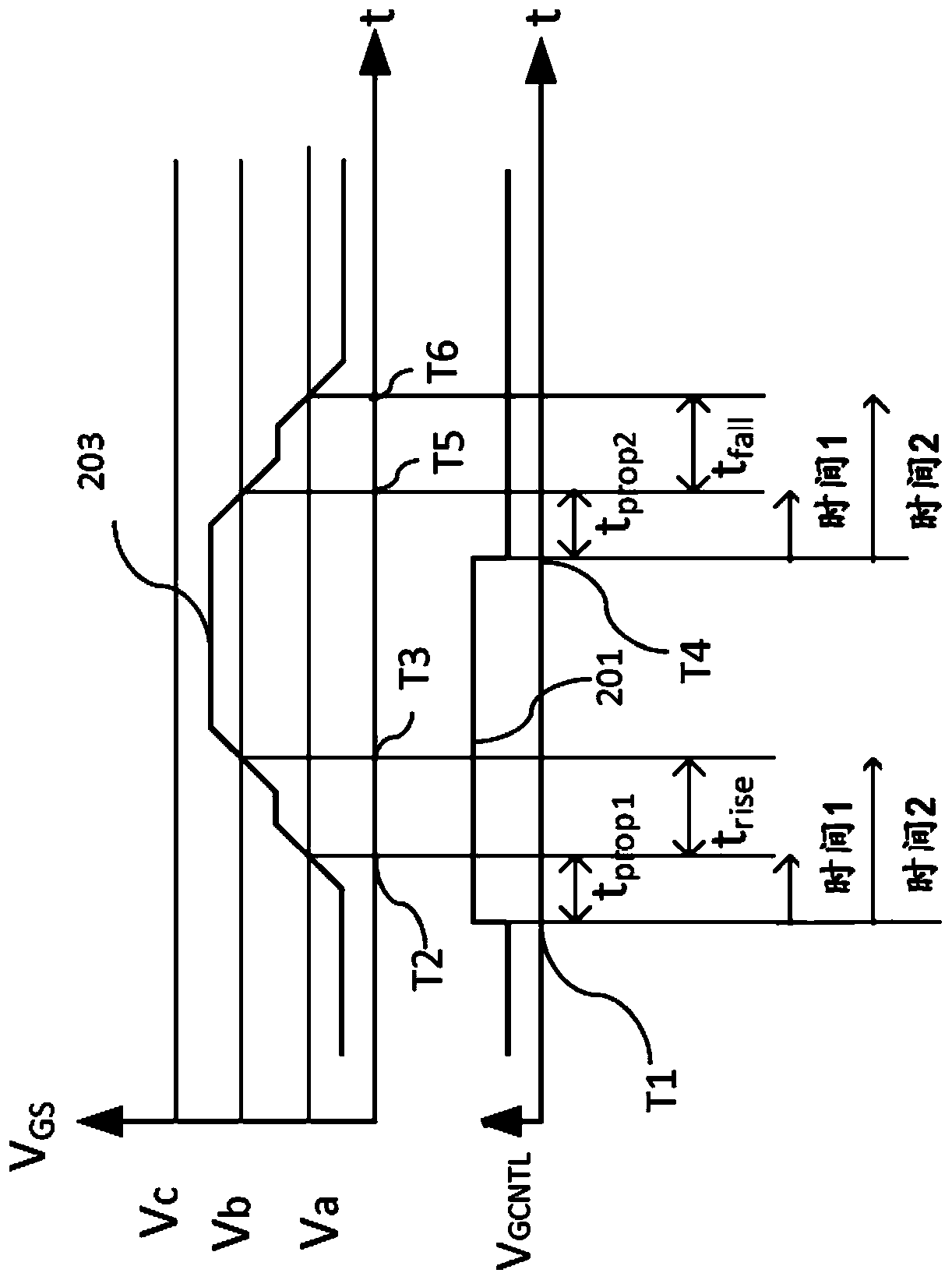
[0073] Example 1. In one embodiment, a method of monitoring the gate of a transistor comprises: monitoring the gate voltage of the transistor; and based on the monitoring, measuring the time at which the gate control signal is asserted and the gate voltage of the transistor versus a first voltage threshold a first time difference between the moments of crossing; based on monitoring, measuring a second time difference between the moment when the gate voltage of the transistor crosses the first voltage threshold and the moment when the gate voltage of the transistor crosses the second voltage threshold; and determining Whether the first time difference falls within the first time window and whether the second time difference falls within the second time window.
example 2
[0074] Example 2. The method of Example 1, further comprising: asserting an error signal when the first time difference falls outside a first time window or when the second time difference falls outside a second time window.
example 3
[0075] Example 3. The method of Example 2, further comprising disabling a driver coupled to the gate of the transistor when the false signal is asserted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com