Organ image constructing method and system based on voxel model
A voxel model and construction method technology, applied in the field of organ images, can solve the problems of inaccurate display results, less information in cross-sectional images, and high cost of consumables, and achieve the effects of easy understanding, improving diagnostic efficiency, and reducing the number of images.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
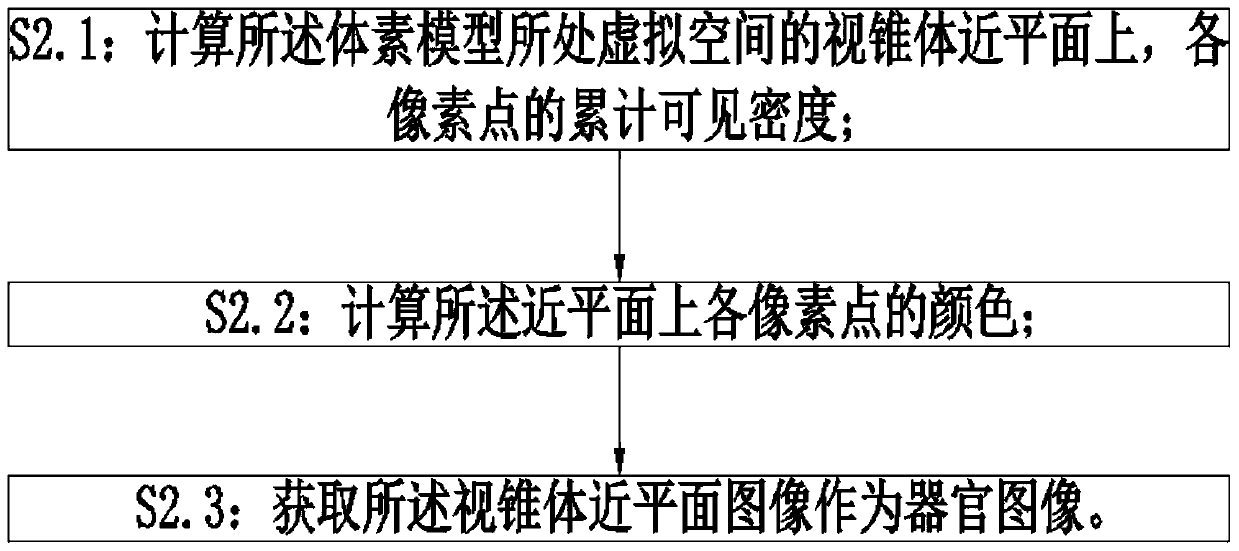
[0034] A method for constructing organ images based on voxel models, such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, including: S1: Model rendering: S1.1: Obtain the patient’s organ model; S1.2: Obtain voxel information according to the organ model, and the voxel information includes the density function ρ(p ), visibility function α(p), density gradient function and the virtual space position to obtain the voxel model; S2: model rasterization: S2.1: calculate the cumulative visible density S(τ) of each pixel on the near plane of the viewing cone in the virtual space where the voxel model is located; S2. 2: Calculate the color S' of each pixel on the near plane; S2.3: Acquire the near plane image as the organ image.
[0035] In a preferred embodiment, the organ model is a CT model, and the density function of voxels is: Among them, g p is the gray level of voxel P in the CT model; the visibility function α(p)=1.
[0036] The definition of a voxel is: in the virtual space, the v...
Embodiment 2
[0054] In a preferred embodiment, a method for constructing an organ image based on a voxel model is different from Example 1, such as figure 2 and Figure 5 As shown, it also includes S1.2.0: S1.2.0: Obtain the ρ(p) and α(p) conditions that need to be met for the voxels used for display; the voxels that ρ(p) and α(p) satisfy the conditions form a set U; In S1.2, a ray is made from the observation point in the virtual space to the pixel point, and the ray passes through n voxels p of the voxel model from near to far i (i=1,2,3...n); k(0n The original visibility function V n for: Voxel p after conditional screening n The final visibility V n 'for: In , the calculation method of cumulative visible density S(τ) is:
[0055] The colors and densities of voxels corresponding to tissues such as muscles, bones, and skin are quite different, and voxels with the same or similar densities correspond to different types of tissues. Doctors can select the displayed voxels throug...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In a preferred embodiment, a method for constructing an organ image based on a voxel model, such as figure 2 and Figure 10 As shown, the difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 is that S1.2.0 is also included: S1.2.0: Obtain the information of the virtual plane S, including the point P that the virtual plane S passes through S , the normal vector is N S ; In S1.2, a ray is made from the observation point in the virtual space to the pixel point, and the ray passes through n voxels p of the voxel model from near to far i (i=1,2,3...n); for voxel p, k (0n The raw visibility function V of n for: The final visibility Vn' of voxel pn after condition filtering is: In S2.1, the calculation method of cumulative visible density S(τ) is:
[0063] Such as Figure 11 As shown in , the virtual plane is the section, and the voxel points located on the other side of the normal vector direction of the plane are displayed to realize the display of the model section.
[0064] The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com