Heat-conducting insulating material mixed with epoxy resin and used for air-core reactor, and preparation method of heat-conducting insulating material
A technology of heat-conducting insulating materials and air-core reactors, which is applied in the field of heat-conducting insulating materials, can solve the problems of high temperature of insulating materials, complicated preparation process, burning of insulating materials, etc., and achieve the goal of ensuring insulation and thermal conductivity, simple operation and simplified operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] According to the mass fraction of 1.1:1.0:2.0, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, and magnesium oxide are mixed to form an inorganic component, and then the inorganic component, bisphenol A epoxy resin, and phthalic anhydride are mixed according to the mass fraction Mix 15:100:50 and heat to 100°C, stir under 50kPa negative pressure for 20min, after casting, carry out segmental curing at 160°C for 6h to obtain thermally conductive insulating material A.
Embodiment 2
[0028] According to the mass fraction of 1.0:1.0:2.0, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, and magnesium oxide are mixed to form an inorganic component, and then the inorganic component, bisphenol A epoxy resin, and phthalic anhydride are mixed according to the mass fraction Mixed at 15:100:50 and heated to 100°C, stirred for 20min under 50kPa negative pressure, after casting, cured in sections at 160°C for 6h to obtain thermally conductive insulating material B.
Embodiment 3
[0030] According to the mass fraction of 1.0:1.0:2.0, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, and magnesium oxide are mixed to form an inorganic component, and then the inorganic component, bisphenol A epoxy resin, and phthalic anhydride are mixed according to the mass fraction Mixed at 15:100:50 and heated to 100°C, stirred for 20min under 50kPa negative pressure, after casting, cured in sections at 180°C for 8h to obtain thermally conductive insulating material C.
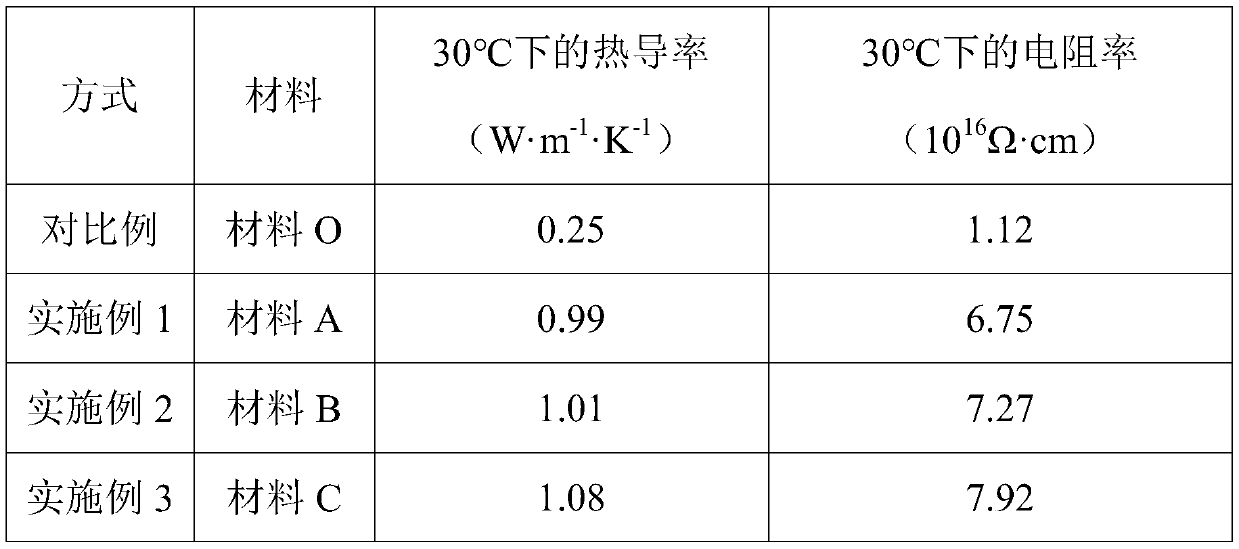
[0031] Table 1 The performance table of the thermally conductive insulating material obtained by comparative examples of the present invention and each embodiment
[0032]
[0033] As can be seen from the table, through the comparison of Comparative Examples and Examples 1-3, it can be seen that the thermal conductivity and resistivity of the thermally conductive insulating material obtained by the preparation method provided by the present invention at 30 ° C are higher than those without adding inorganic groups. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com