Method for disintegrating human pluripotent stem cells into macrophages
A macrophage, volume percentage technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as hindering clinical application, long differentiation cycle, and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
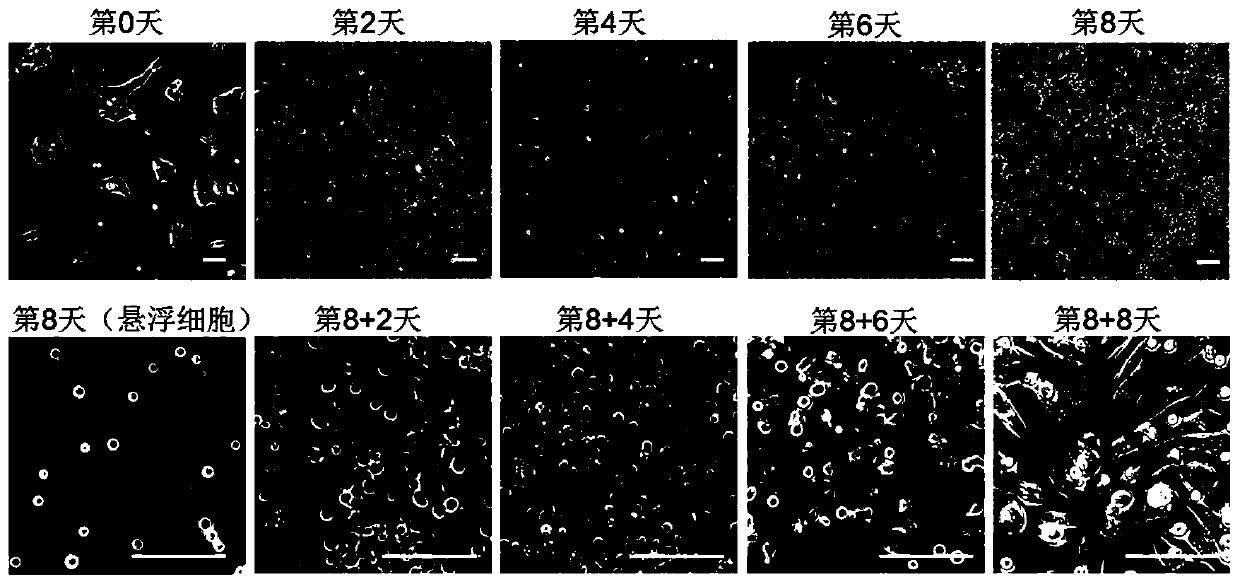
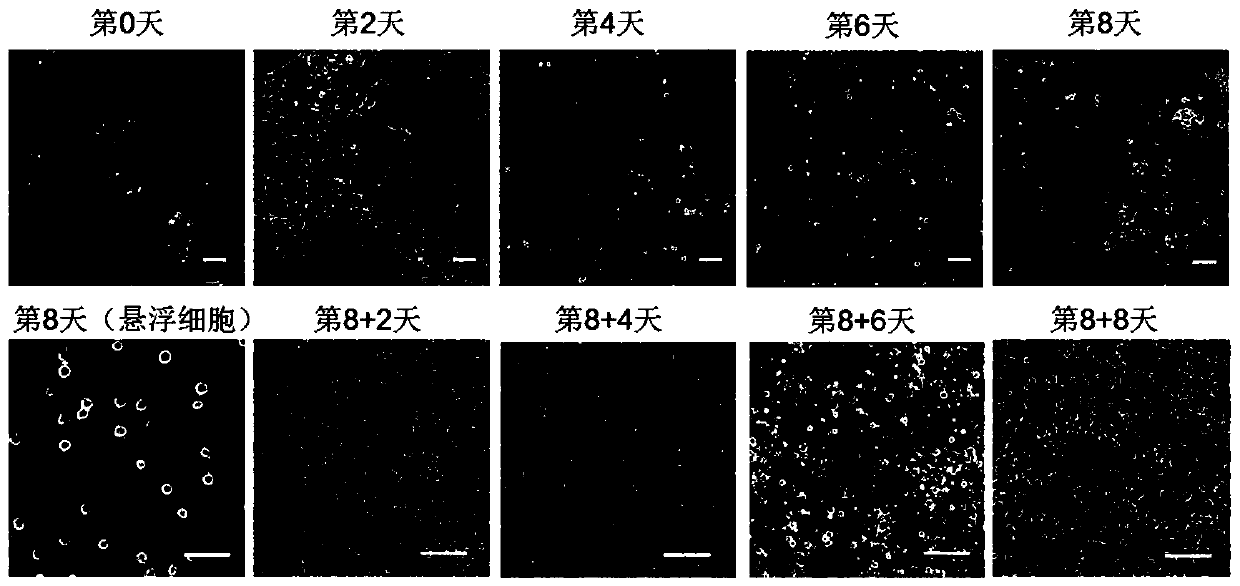
[0159] Example 1. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into macrophages
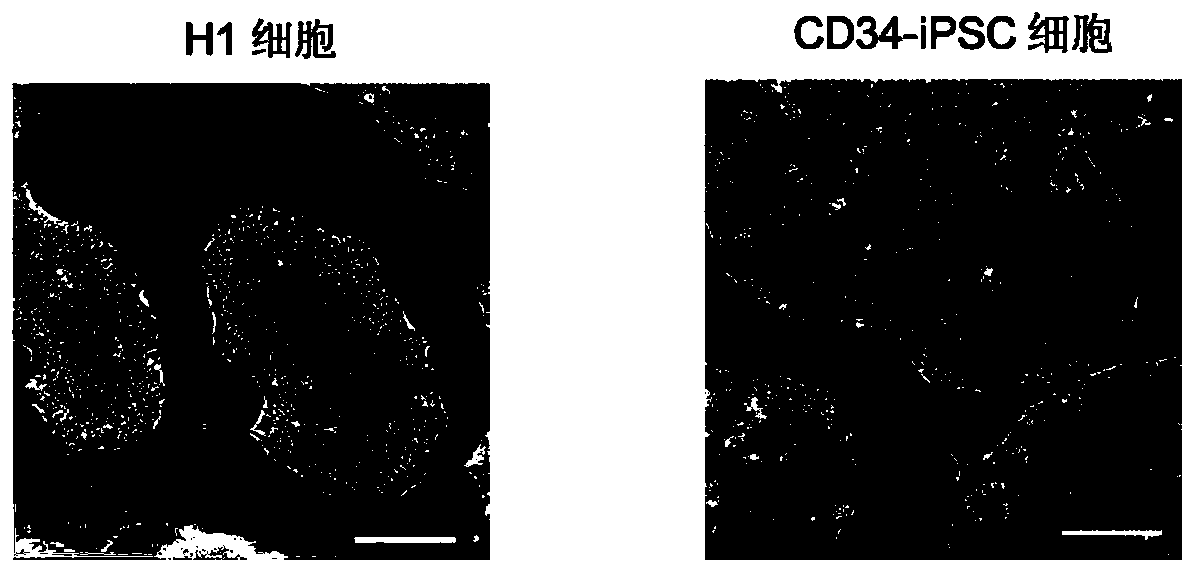
[0160] Two types of human pluripotent stem cells were used in this example, namely H1 cells and CD34-iPSC cells.
[0161] 1. Inoculate human pluripotent stem cells in a 6-well plate (2.5×10 per well 5 cells) were cultured in TeSR-E8 medium at 37°C until the cell confluency was 70%-80%.
[0162] 2. After completing step 1, take the six-well plate, suck off the culture supernatant, and add PBS buffer preheated to 37°C to wash twice. At this point, the morphology of H1 cells and CD34-iPSC cells is shown in figure 1 (Scale bar 100 μm).
[0163] 3. After completing step 2, take the six-well plate, add 1ml of cell digestion solution Accutase to each well, let it stand at 37°C for 3-5min, then add an appropriate amount of RPMI 1640 basal culture medium to stop the digestion, and collect the cells by centrifugation.
[0164] 4. Inoculate the cells collected in step 3 on a petri dish (the petri dis...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Example 2, Detection of cells in the process of differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into macrophages
[0175] 1. Flow cytometric detection of cell A and cell B
[0176] 1. Get the cell A obtained in step 9 and the cell B obtained in step 12 in Example 1, and resuspend the cells in PBS buffer containing 5% (v / v) fetal bovine serum to obtain cell A suspension (containing 1 × 10 5 cells), cell B suspension (containing 1×10 5 cells).
[0177] 2. Add PE-labeled CD43 antibody (volume ratio 1:50) and APC-labeled CD34 antibody (volume ratio 1:50) to the A cell suspension in step 1, respectively, and add to the B cell suspension in step 1 PE-labeled CD43 antibody (volume ratio 1:50), APC-labeled CD34 antibody (volume ratio 1:50), FITC-labeled CD45 antibody (volume ratio 1:50), FITC-labeled CD14 antibody (volume ratio 1:50 ), APC-labeled CD11b antibody (volume ratio 1:50), PE-labeled CD163 antibody (volume ratio 1:50), incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes in the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com