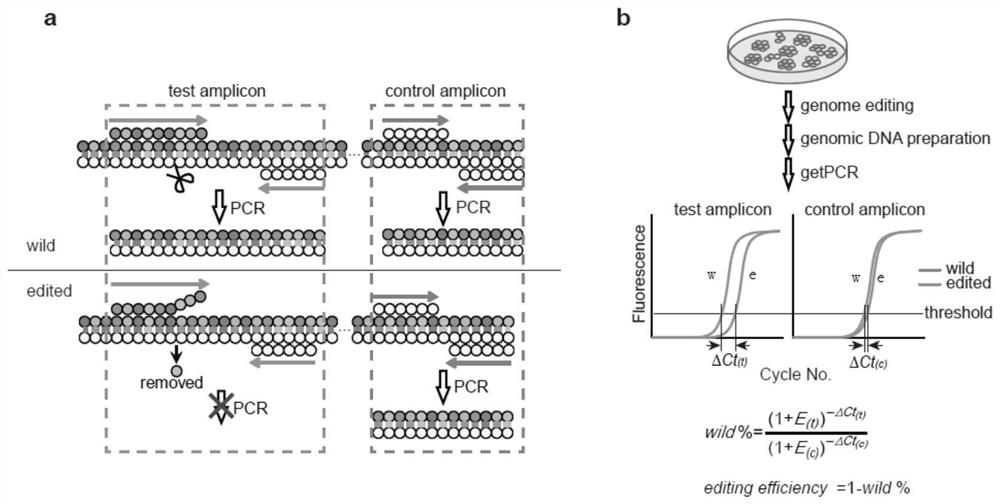
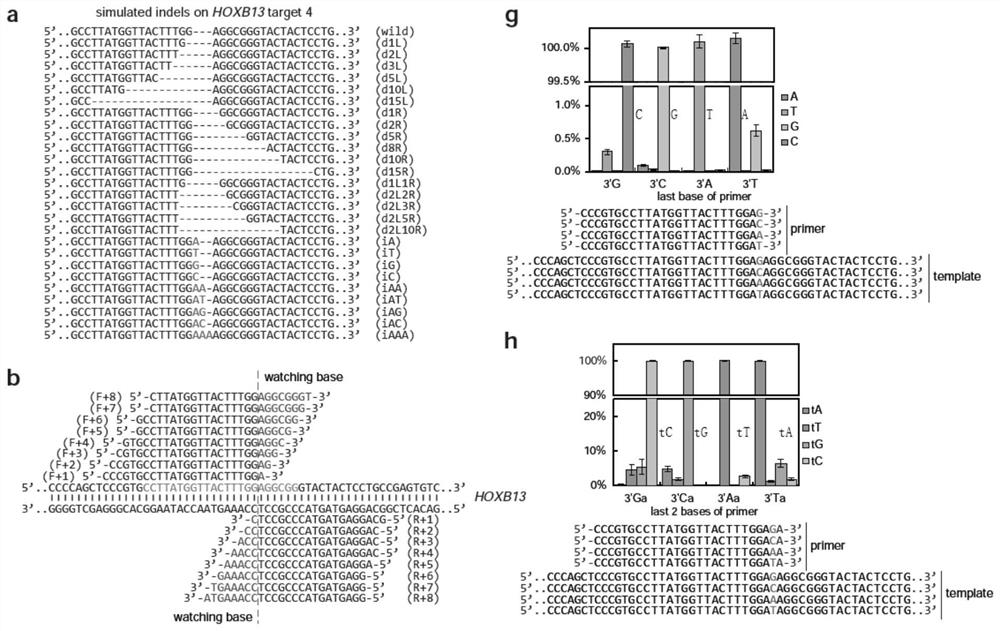
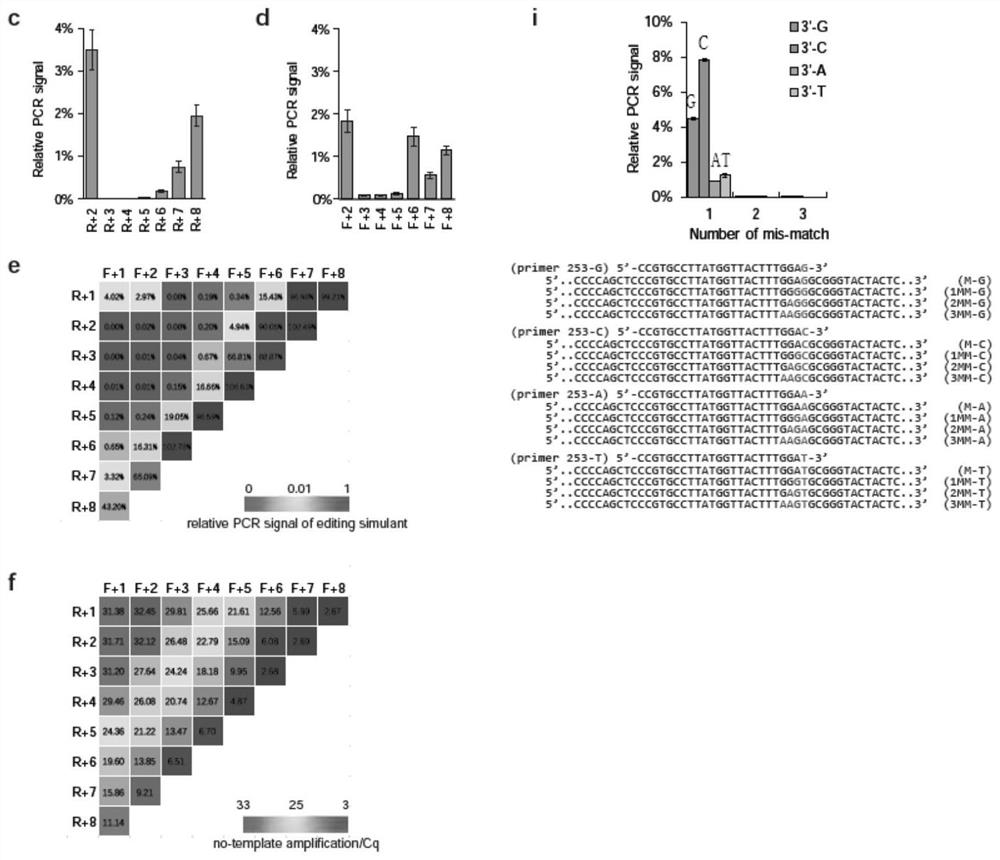
A genome editing detection method, kit and application
A genome editing and detection method technology, applied in the field of gene editing and detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome experimental steps and affecting accuracy, and achieve the effect of simple process and reliable quantitative results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0170] The design of value guard base in the embodiment 1 getPCR
[0171] In order to better apply the getPCR technology, in this embodiment, the design rules of the guarded bases are studied. Since most indels appear near the nuclease cleavage site, and indels smaller than 15 bp account for the main part, in addition, in order to better distinguish the indel sequence from the wild-type sequence, the number of bases in this embodiment is relatively small Insertions or deletions were investigated. In view of this, the inventors designed and constructed 26 plasmids, each with an indel mutant of 1-15bp, to simulate the nuclease-induced genome editing of the HOXB13 gene in vivo ( figure 2 a).
[0172] In this embodiment, two series of guarded bases are designed, and they respectively have one to eight guarded bases ( Figure 7 a-c), from which representatives with ideal amplification efficiency were screened out ( figure 2 b) to further check their discriminative ability, th...
Embodiment 2
[0175] Embodiment 2 runs the parameters of getPCR
[0176] Another factor that needs to be determined is the optimal parameter for getPCR operation. In this embodiment, the annealing temperature during the getPCR reaction is studied. For the four groups of guarded bases designed in Example 1, as the annealing temperature increases, compared with the indel template containing mismatched bases, the ability of getPCR to specifically amplify the wild-type template DNA increases significantly ( image 3 a-d). However, when the annealing temperature was increased above 4 °C above the Tm value, the PCR efficiency began to drop significantly. Since PCR amplification usually prefers the best PCR efficiency, this embodiment systematically evaluates the selectivity of each guarded base at the best PCR efficiency ( image 3 e-h). Interestingly, no matter how many guard bases or total bases the primer has, the best selectivity is usually observed when the annealing temperature is about ...
Embodiment 3
[0179] Example 3 Research on the Accuracy of GetPCR Quantitative Genome Editing
[0180] figure 2 Shown in a are the plasmids used to model insertion-deletion mutations (indels) caused by genome editing, which were first used to assess the ability of getPCR to quantify genome editing efficiency. In this example, twenty-six indel plasmids were mixed in equal parts, and then mixed with wild-type plasmids in a specific ratio to simulate indel frequencies of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100%. The indel frequency of the mixture was quantified and compared by getPCR and the classic Surveyor method. When the indel frequency is not higher than 20%, the quantitative results of the Surveyor method can truly reflect the expected value. However, as the indel frequency increases further, the observed value gradually deviates from the expected value ( Figure 4 a-b). In contrast, all 12 getPCR strategies using different guard bases, whether carrying 3, 4 or 5 guard bases on the guard bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com