CRISPR-Cas9 for targeting knockout of human intestinal cancer cell CNR1 gene, and specific sgRNA thereof
A colorectal cancer cell-specific technology, applied in the field of gRNA, can solve the problem that the molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer has not yet been clarified
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
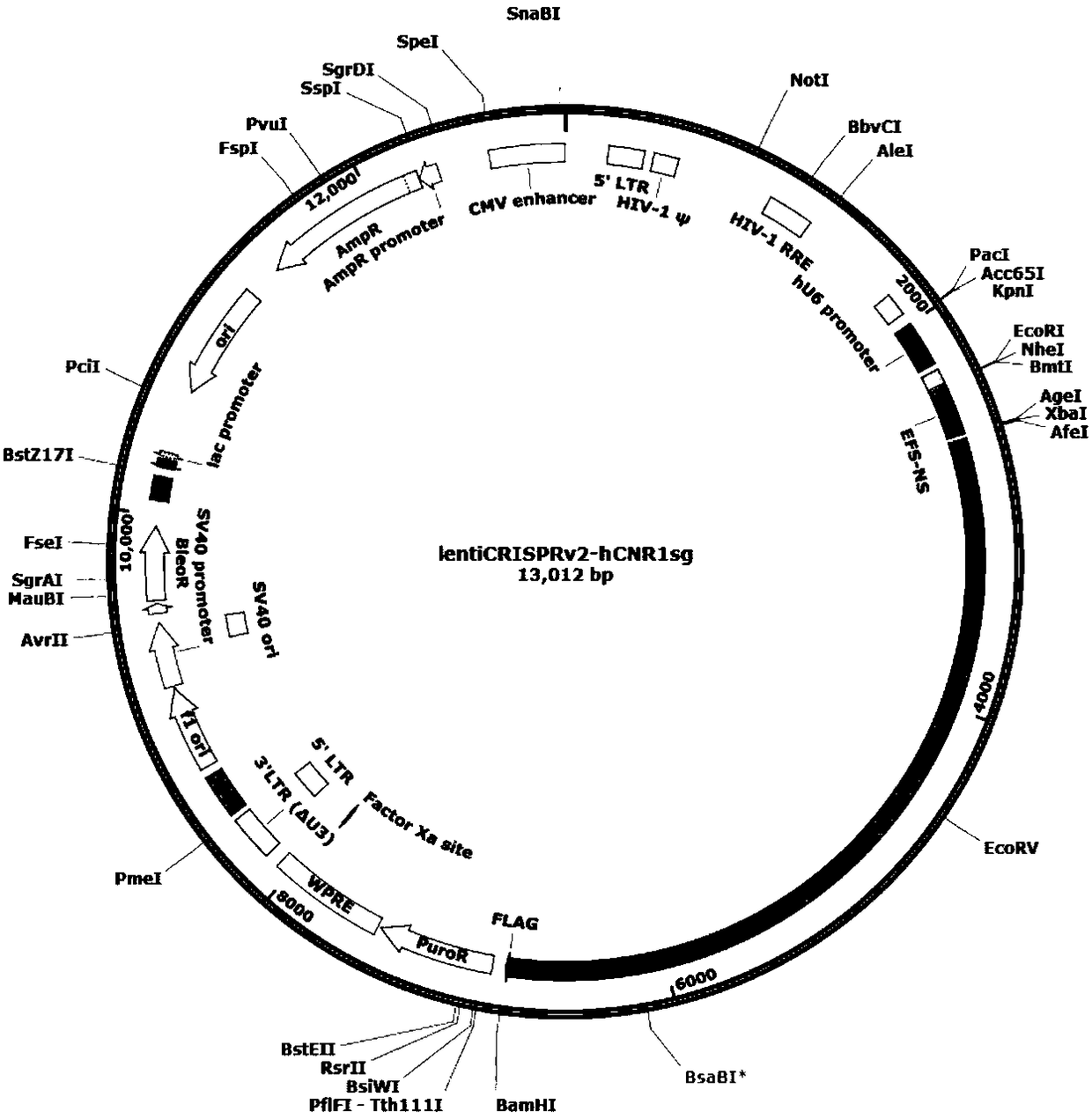
[0044] 1. Construction of a knockout CNR1 plasmid using CRISPR / Cas9 technology
[0045] 1.1 sgRNA oligonucleotide chain synthesis
[0046] Using the CRISPR online design tool (http: / / crispr.mit.edu / ) according to the scoring system, a 20bp sgRNA was designed on the second exon of CNR1, and no non-specific genes were verified by BLAST. ACCG was added to the 5' end of the coding strand template, and AAAC was added to the 3' end of the non-coding strand template to complement the cohesive ends formed after digestion with BsmBI, and a pair of CRISPR oligonucleotide chains were designed, as shown in Table 1.
[0047] Table 1 CNR1 targeting site and sgRNA oligonucleotide sequence
[0048]
[0049] 1.2 Vector construction
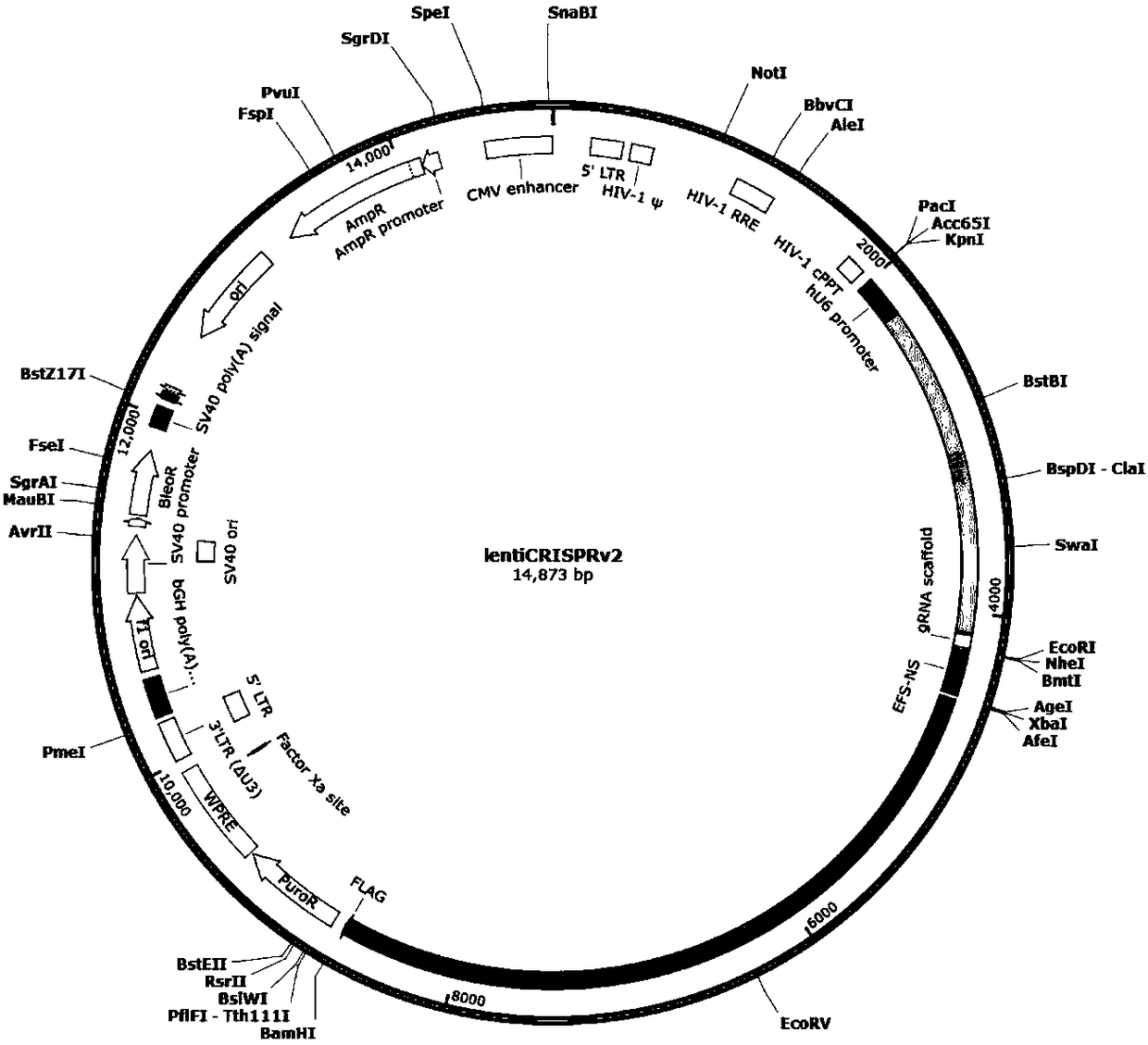
[0050] 1.2.1 Use BsmBI to digest 2 μg of Lenti-CRISPRv2 plasmid (purchased from Addgene) for 2 hours at 37°C. The enzyme digestion system is as follows:
[0051] 2μg (2μl)
Lenti-CRISPRv2
1μl
BsmBI (NEB)
5μl
10X Cutsmart
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com