An Efficient Calculation Method of Probabilistic Power Flow with High Dimensional Related Uncertainty Sources Based on Improved Nataf Transform
A technology of probabilistic power flow and calculation method, which is applied in the direction of AC networks with the same frequency from different sources, and can solve problems such as unsatisfactory calculation efficiency, time-consuming deterministic power flow calculation, and inability to analyze network operation status.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
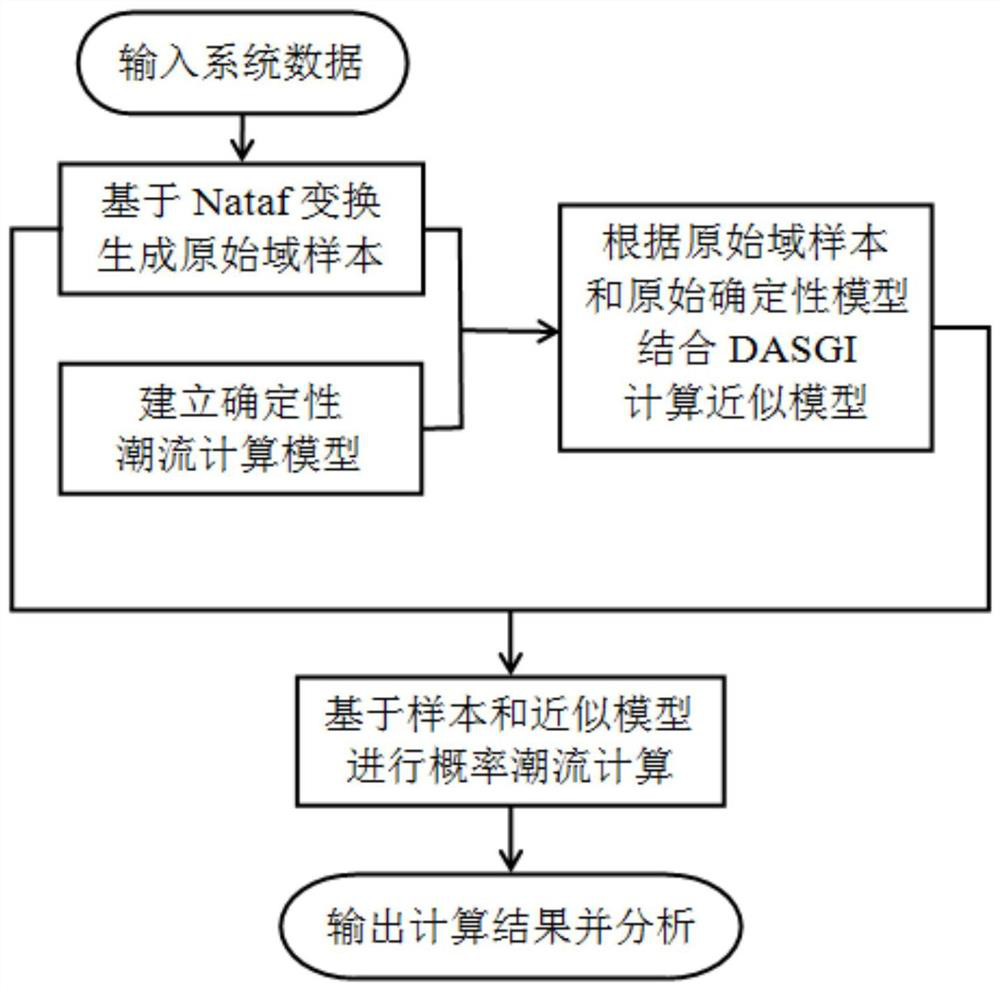
[0087] see figure 1 , based on the improved Nataf transform, an efficient calculation method of probability power flow with high-dimensional correlated uncertain sources mainly includes the following steps:
[0088] 1) Determine the random input variable X of the power flow calculation model and the Pearson correlation coefficient matrix C of the random input variable X X. The stochastic input variable X is the active power output of the renewable energy converted from the power system uncertainty source. The power system uncertainty sources include the wind speed of the wind power plant, the solar radiation intensity of the photovoltaic power plant, the tidal flow velocity of the tidal power plant and the load of the fluctuating load. The number of uncertain sources is n.
[0089] Further, the main steps to determine the random input variable X of the power flow calculation model are as follows:
[0090] 1.1) Determine the random input variable X=[X 1 ,X 2 ,...,X n ], ...
Embodiment 2
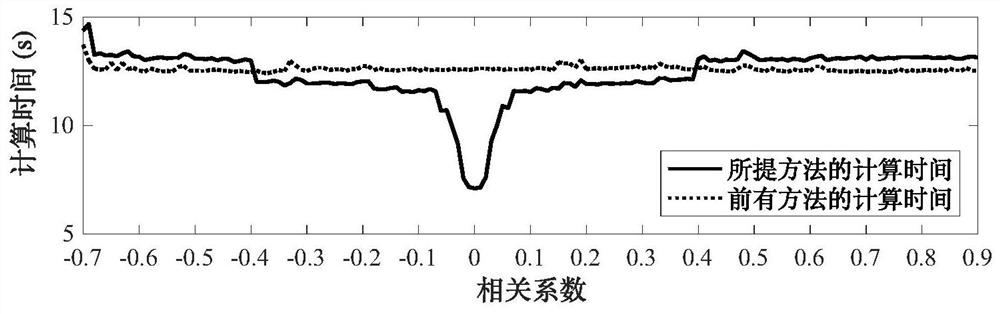
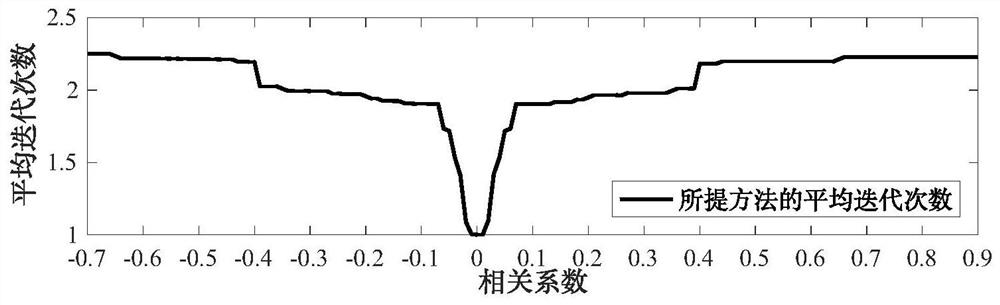
[0161] see Figure 2 to Figure 4 , an experiment to verify the efficient calculation method of probability power flow with high-dimensional correlated uncertain sources based on the improved Nataf transform, mainly includes the following steps:
[0162] 1) Based on IEEE118 nodes, establish a power system simulation model.
[0163] 2) Determine the random input variable vector X=[X 1 ,X 2 ,...,X n ] and the Pearson correlation coefficient matrix C of the random input variable vector X X : In the present embodiment, n=114, wherein the setting of variables is as follows: all active loads (99 in total) are set as random variables, and reactive loads are determined according to power factors consistent with the original calculation example. According to the node number, the first 33 active loads obey the normal distribution, the mean value is the original value of the example, and the standard deviation is 5% of the corresponding mean value, which is recorded as the first group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com