Novel offshore wind plant reactive power optimization method based on mean value variance mapping
A mean-variance, wind farm technology, applied in the field of reactive power optimization of offshore wind farms, which can solve problems such as increasing the risk of premature convergence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
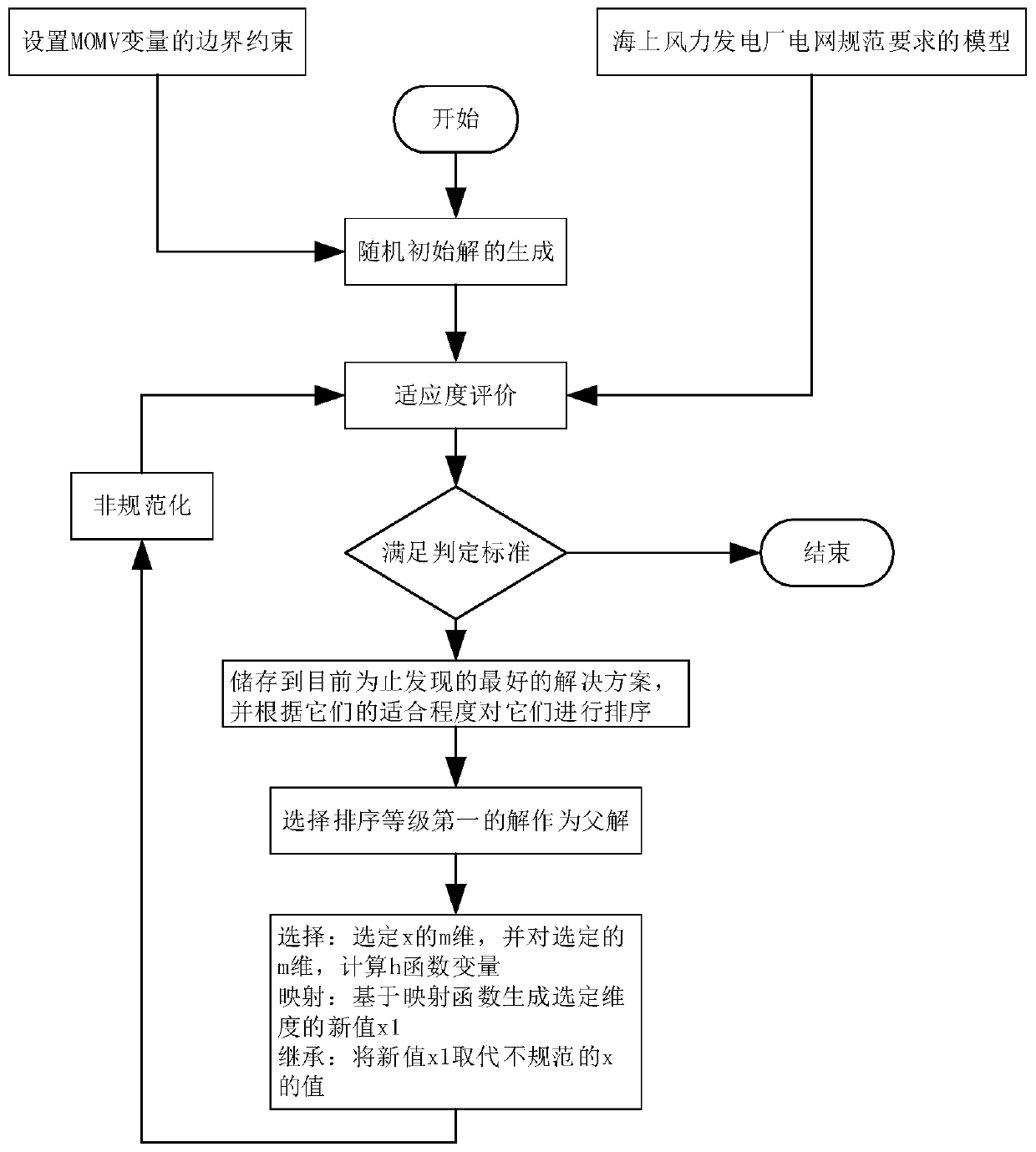
[0068] Embodiments of the present invention provide a new method for reactive power optimization of offshore wind farms based on mean-variance mapping, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0069] Step 1: Perform optimization on a given scenario, which includes a set of future operating points within a 24-hour time frame. The predicted wind speed results for the considered time period directly form a neural network (NN) based wind speed forecast and are received as input by the optimization algorithm.
[0070] Step 2: Determine the system objective function, decision variables and related constraints to form the original global optimization problem.
[0071] Step 3: Initial setting of MOMV optimization algorithm, fitness evaluation, archiving of solutions and proposal of new mapping functions to form offspring.
[0072] Step 4: Execute the evolution loop until the specified termination criteria are met.
[0073] In an optional embodiment, the optimization is performed on a g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com