Method for repairing plant community structure of Alternanthera philoxeroides invasive slash in Caohai wetland
A kind of technology of Neptera chinensis and plant community, applied in botany equipment and methods, water conservancy engineering, horticulture, etc., can solve problems such as restoration of plant community structure in untraceable land, so as to ensure the stability of wetland ecosystem, inhibit invasion, and restore species diversity sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
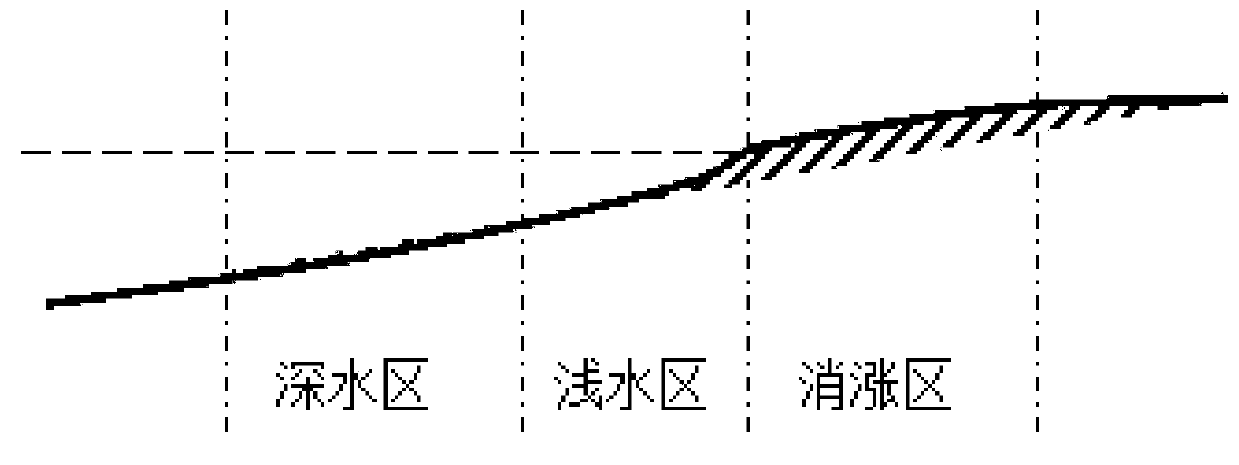
[0027] according to figure 1 A method for restoring the plant community structure of the invasive site of A. chinensis in Caohai Wetland is shown. The restoration method is specifically a method of replacing invasive alien plants with native plants with economic or ecological value according to the own law of plant community succession. Substituting species The native species of water onion, clover, water sedge, water sedge and Lishihe were selected from the natural distribution of Caohai Lake. The specific community construction method is as follows:
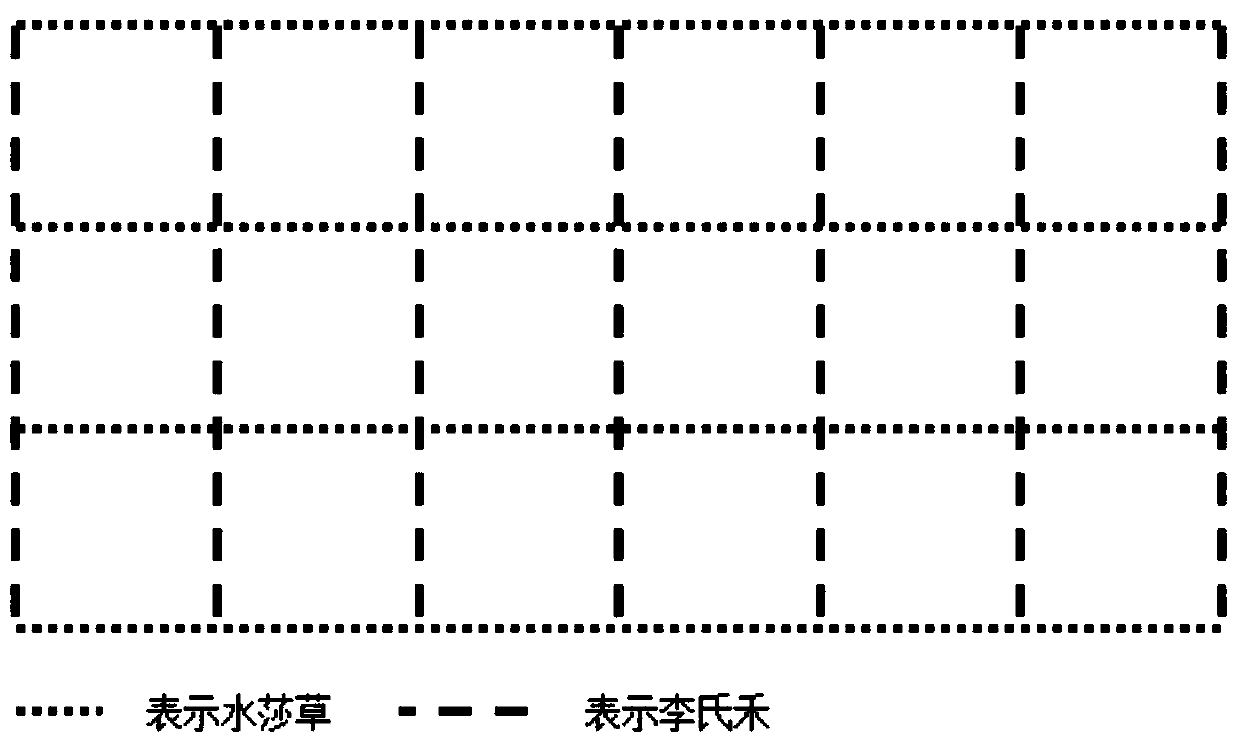
[0028] S1. Plant community construction in the ups and downs area: select the water sedge community and the Lishihe community, and in the lake water ups and downs area, that is, the area where the water body has not been submerged by the lake for more than half a year, plant in a grid format (such as figure 2 shown), the grid spacing is 100cm, and the plant-to-plant spacing is 20cm; and the water sedge community and Lishihe co...
Embodiment 2
[0032] according to figure 1 A method for restoring the plant community structure of the invasive site of A. chinensis in Caohai Wetland is shown. The restoration method is specifically a method of replacing invasive alien plants with native plants with economic or ecological value according to the own law of plant community succession. Substituting species The native species of water onion, clover, water sedge, water sedge and Lishihe were selected from the natural distribution of Caohai Lake. The specific community construction method is as follows:
[0033] S1. Plant community construction in the ups and downs area: select the water sedge community and the Lishihe community, and in the lake water ups and downs area, that is, the area where the water body has not been submerged by the lake for more than half a year, plant in a grid format (such as figure 2 shown), the grid spacing is 100cm, and the plant-to-plant spacing is 20cm; and the water sedge community and Lishihe co...
Embodiment 3
[0037] according to figure 1 A method for restoring the plant community structure of the invasive site of A. chinensis in Caohai Wetland is shown. The restoration method is specifically a method of replacing invasive alien plants with native plants with economic or ecological value according to the own law of plant community succession. Substituting species The native species of water onion, clover, water sedge, water sedge and Lishihe were selected from the natural distribution of Caohai Lake. The specific community construction method is as follows:
[0038] S1. Plant community construction in the ups and downs area: select the water sedge community and the Lishihe community, and in the lake water ups and downs area, that is, the area where the water body has not been submerged by the lake for more than half a year, plant in a grid format (such as figure 2 shown), the grid spacing is 100cm, and the plant-to-plant spacing is 20cm; and the water sedge community and Lishihe co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com