A smart damper with synchronous self-monitoring of force and displacement
A damper and self-monitoring technology, which is applied to the testing of instruments, measuring devices, and mechanical components, etc., can solve the problem of less actual data of the damper
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
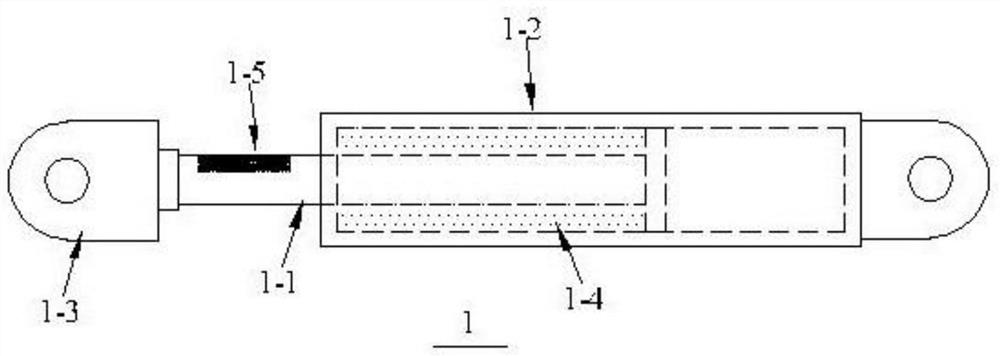
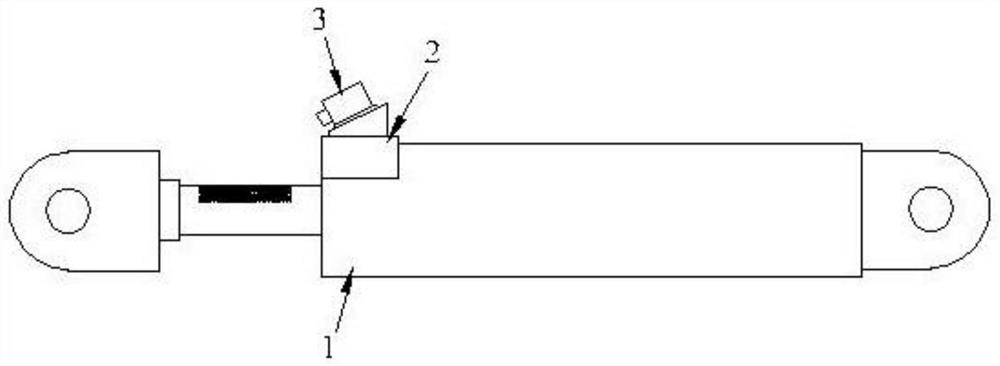
[0024] Such as Figure 1~2 Shown: a kind of intelligent damper of synchronous self-monitoring of force and displacement, comprises damper (1), displacement measuring frame (2), camera system (3), it is characterized in that: described damper (1) comprises piston ( 1-1), the cylinder (1-2), the connecting section at both ends (1-3), the damping medium (1-4) and the image speckle (1-5), the piston (1-1) is located in the cylinder ( 1-2) Inside, the damping medium (1-4) is in the cylinder (1-2), when the damper (1) is disturbed and works, the piston (1-1) forces the cylinder (1-2) The damping medium (1-4) moves, so that the damping medium (1-4) converts the external energy into heat energy and dissipates it. The connecting sections (1-3) at both ends connect one end of the piston (1-1) to the cylinder One end of (1-2), the minimum net cross-sectional size of the connecting section (1-3) at both ends must meet the requirements of the elastic state of the damper (1) in normal use,...
Embodiment 2
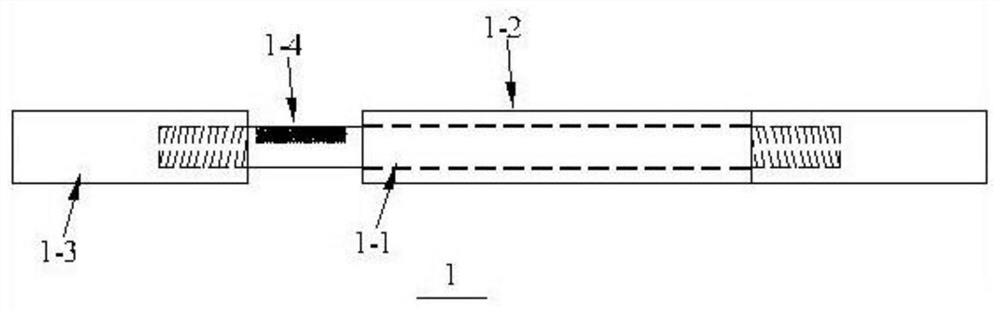
[0030] Such as Figure 3-4 Shown: this embodiment is the same as the rest of embodiment 1, the difference is that the damper (1) is an anti-buckling support damper, and the damper (1) includes a core component (1-1), an outer restraint Components (1-2), connecting segments at both ends (1-3) and image speckle (1-4), the core component (1-1) is located inside the outer constraint component (1-2), and the outer constraint component (1- 2) The length of the damper (1) is slightly shorter than that of the core component (1-1), and its inner dimension is slightly larger than the cross-sectional dimension of the core component (1-1). When the damper (1) works normally, its outer dimension needs to meet the requirements of the outer constraint component ( 1-1) Requirements of being in an elastic state, the cross-sectional size of the connecting section at both ends (1-3) is slightly larger than that of the core part (1-1), and the image speckle (1-4) is in the unconstrained part (1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com