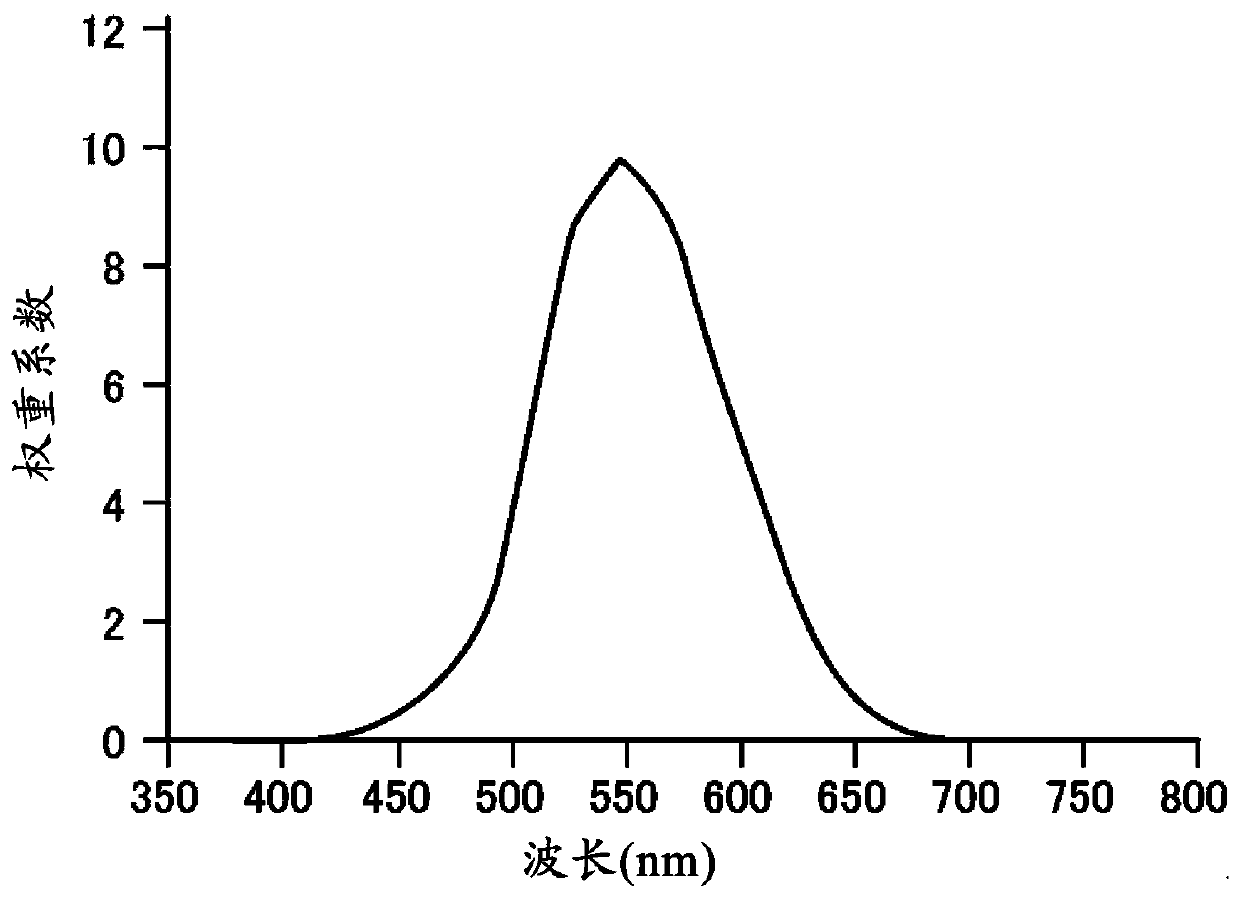
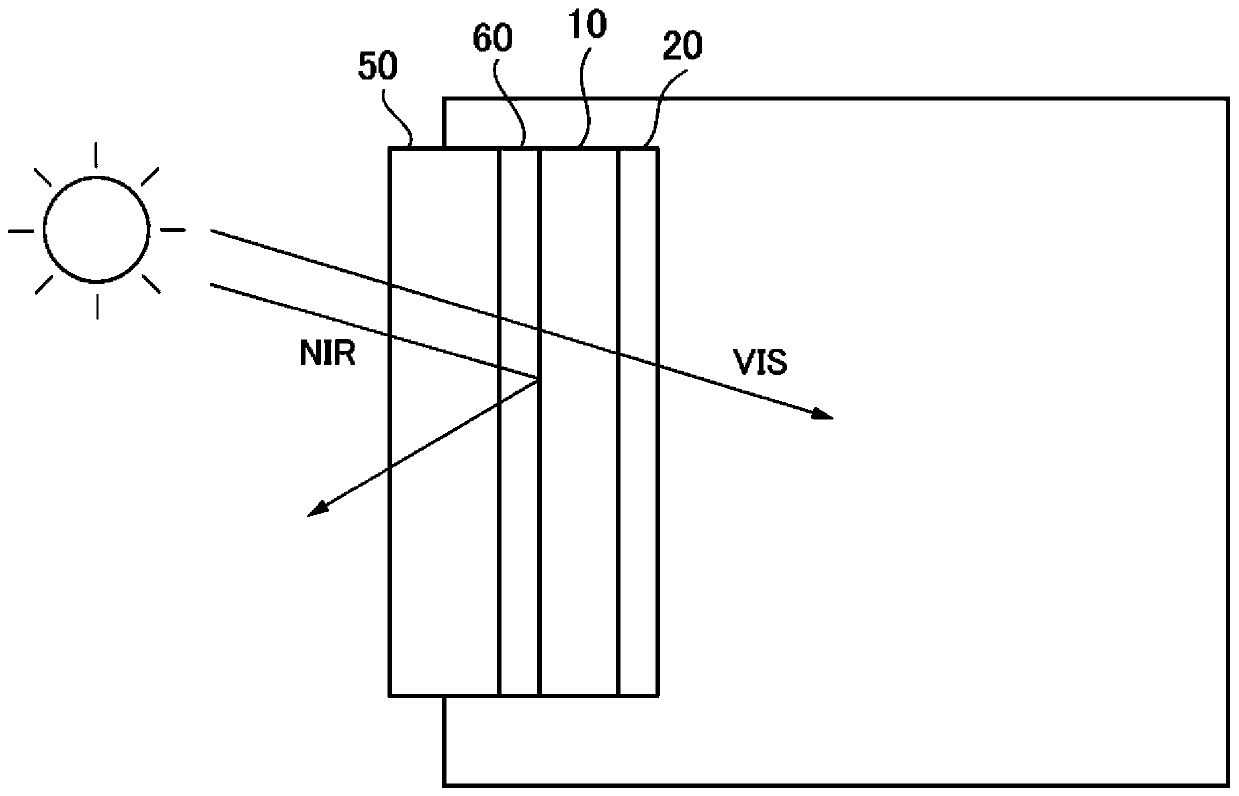
Infrared ray-reflective substrate
A reflective substrate and infrared technology, which is applied in optics, instruments, film/sheet adhesives, etc., can solve the problems of decreased light transmittance, poor visual recognition, and reduced visible light transmittance, and achieve low heat insulation coefficient, the effect of high visible light transmittance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0134] On one side of a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film substrate with a thickness of 50 μm, a titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), a silver alloy containing copper (2.5%) as an impurity with a thickness of 10nm, a titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), and the first laminate is formed on the substrate. Then, a photocurable urethane acrylate resin solution is applied on the first laminate, dried, and then irradiated with ultraviolet rays to cure the resin solution to form a transparent spacer layer. The amount of the resin solution was adjusted so that the thickness of the transparent spacer layer formed by curing the resin was 100 nm. For the cured transparent spacer layer, a titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), a silver alloy containing copper (2.5wt%) as an impurity with a thickness of 10nm, a titanium oxide (TiO 2 ) was bonded to a 17-μm-thick adhesive layer made of an acrylic adhesive to form the polarizing film laminate of Example 1. The layer structure of the polarizing film laminate of Example 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0136] The polarizing film laminate of Example 2 was laminated with the polarizing film of Example 1 only in the aspects where the thickness of the silver alloy metal layer of the first and second laminates was 12 nm and the thickness of the adhesive layer was 70 nm. different, but identical in other respects.
Embodiment 3
[0138] The polarizing film laminate of Example 3 differs from the polarizing film laminate of Example 1 only in that the silver alloy metal layers of the first and second laminates have a thickness of 12 nm, and is the same in other respects.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com