Optical lens
A technology of optical lens and optical imaging lens, which is applied in the field of optical lens, can solve the problems of poor distortion control, large volume, and low relative illumination, and achieve the effects of reducing temperature variation, good system stability, and overall system length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
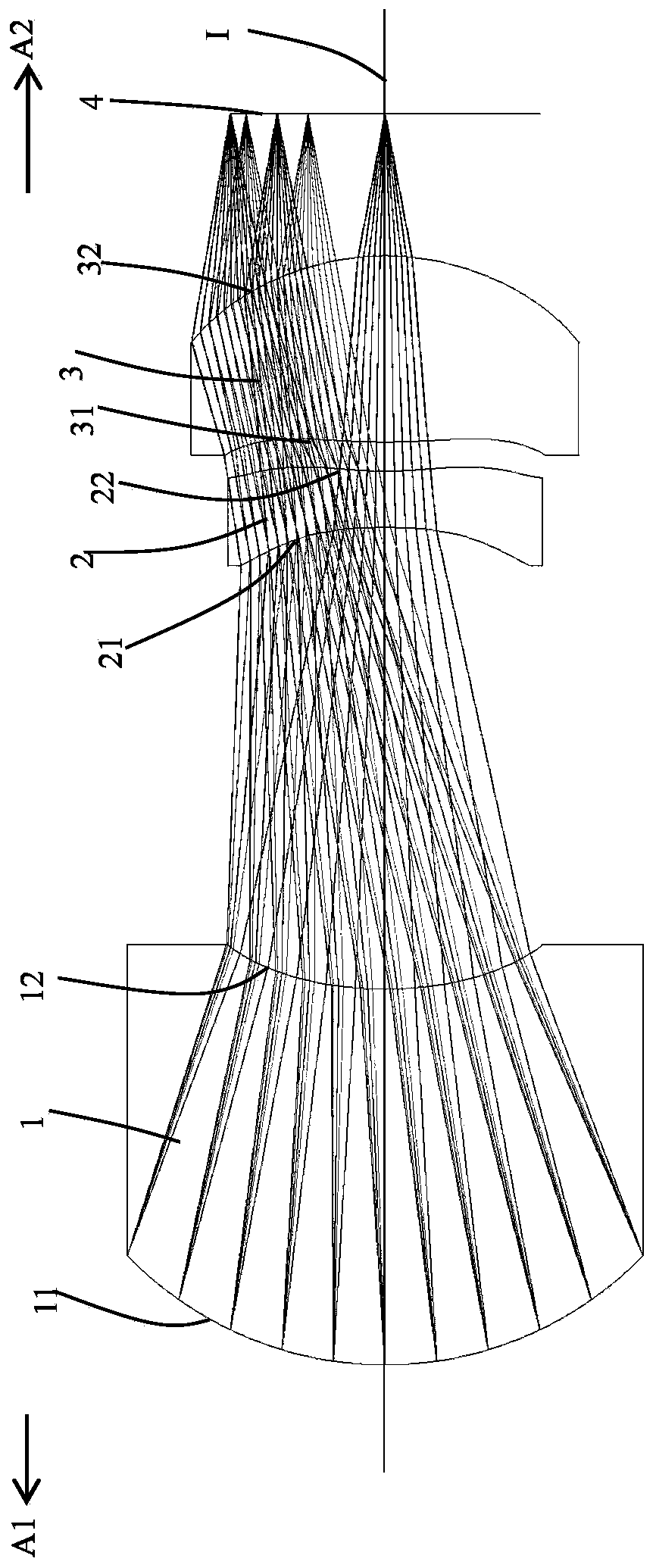
[0136] Such as figure 1 As shown, an optical lens is used to project light from a light source to an object through the optical lens. The direction toward the light source is the image side A2, and the direction toward the object is the object side A1. The optical lens is from the object The side A1 to the image side A2 sequentially include a diaphragm (not shown in the figure), a first lens 1, a second lens 2, a third lens 3, and a projection surface (ie, a light source) 4 along an optical axis I; the projection surface 4 emits The light from the third lens 3, the second lens 2, the first lens 1 and the diaphragm are projected onto the subject in sequence. The object side and an image side facing the image side A2 through which the imaging light passes.
[0137] The first lens 1 has a positive refractive power, the object side 11 of the first lens 1 is a convex surface, and the image side 12 of the first lens 1 is a concave surface; the second lens 2 has a negative refractiv...
Embodiment 2
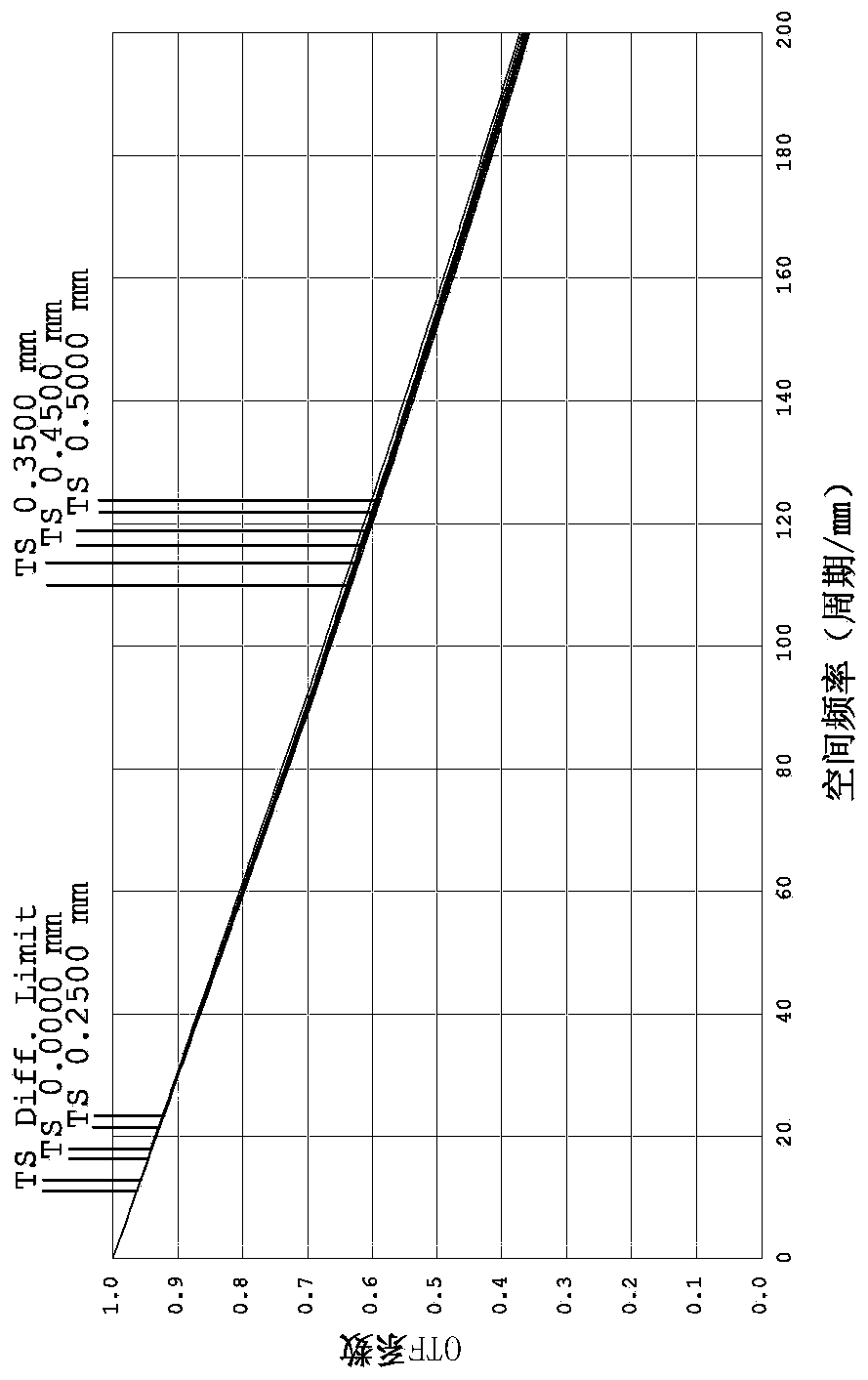
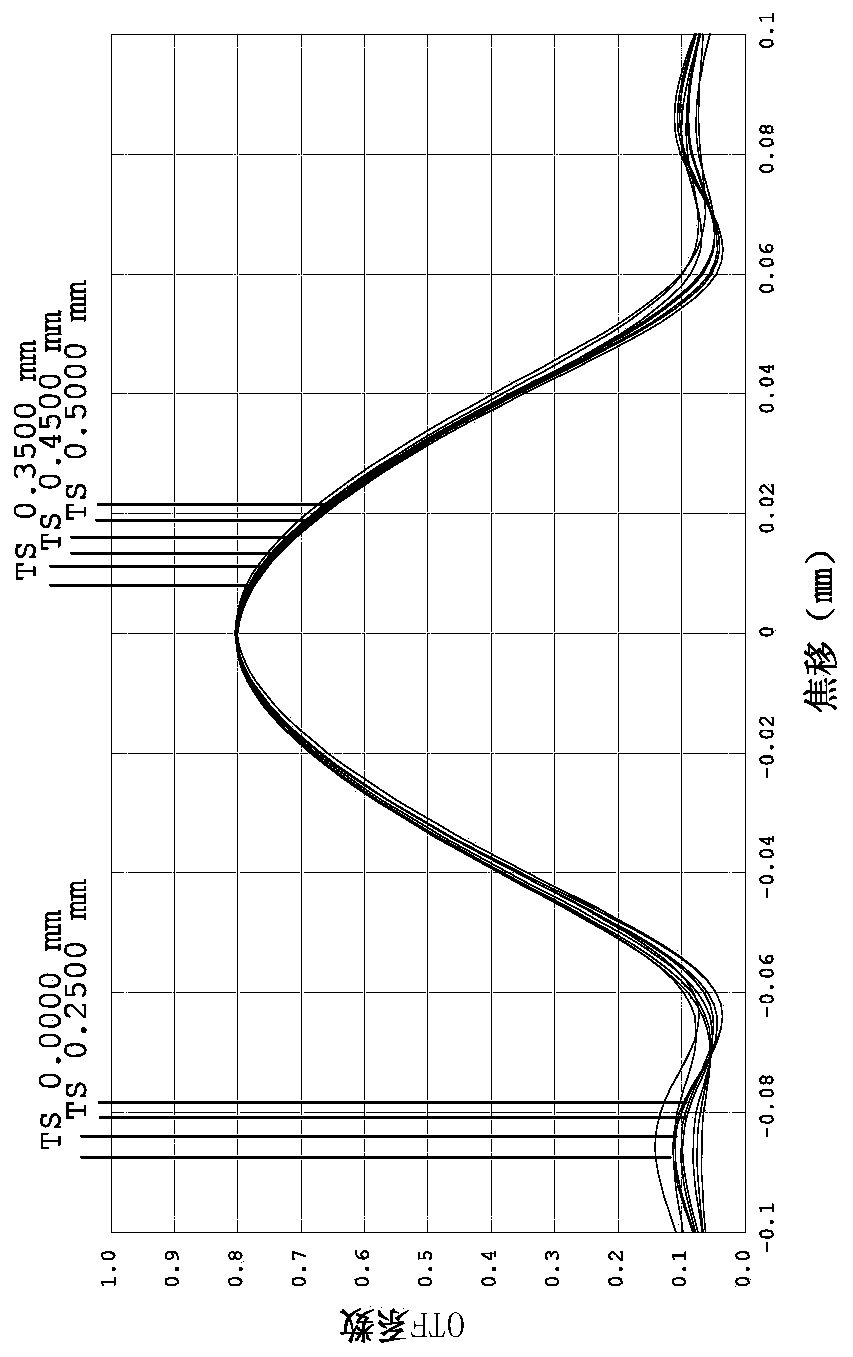
[0162] Such as Figure 17 As shown, this embodiment and the embodiment 1 have the same concave-convex surface shape and refractive index of each lens, and only the optical parameters such as the radius of curvature of each lens surface and lens thickness are also different.
[0163] The detailed optical data of this specific embodiment are shown in Table 2-1.
[0164] Detailed optical data of Table 2-1 Example 2
[0165] surface Aperture radius (mm) Radius of curvature (mm) Thickness (mm) material Refractive index Dispersion coefficient focal length(mm) - subject surface 49.81 INF 450 - 0.88 INF 0.100 11 first lens 0.84 1.226 1.216 M-NBFD130 1.8061 40.7306 3.82 12 0.51 1.165 1.340 21 second lens 0.45 -1.839 0.241 ZEONEX_330R 1.5094 56.4745 -1.29 22 0.52 1.023 0.111 31 third lens 0.54 1.674 0.660 ZEONEX_T62R 1.5365 55.9807 1.25 32 0.61...
Embodiment 3
[0173] Such as Figure 33 As shown, this embodiment and the embodiment 1 have the same concave-convex surface shape and refractive index of each lens, and only the optical parameters such as the radius of curvature of each lens surface and lens thickness are also different.
[0174] The detailed optical data of this specific embodiment are shown in Table 3-1.
[0175] Detailed optical data of the third embodiment of table 3-1
[0176] surface Aperture radius (mm) Radius of curvature (mm) Thickness (mm) material Refractive index Dispersion coefficient focal length(mm) - subject surface 49.72 INF 450 - 0.88 INF 0.100 11 first lens 0.84 1.295 1.190 D-ZF93 2.0017 20.7054 4.06 12 0.49 1.066 1.392 21 second lens 0.46 -1.690 0.238 ZEONEX_330R 1.5094 56.4745 -1.40 22 0.52 1.266 0.111 31 third lens 0.55 1.536 0.619 ZEONEX_T62R 1.5365 55.9807 1.25 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com