Non-dispersive water flow path simulation method based on DEM and flow collection
A simulation method and non-dispersive technology, applied in CAD numerical modeling, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve optimal water flow path
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
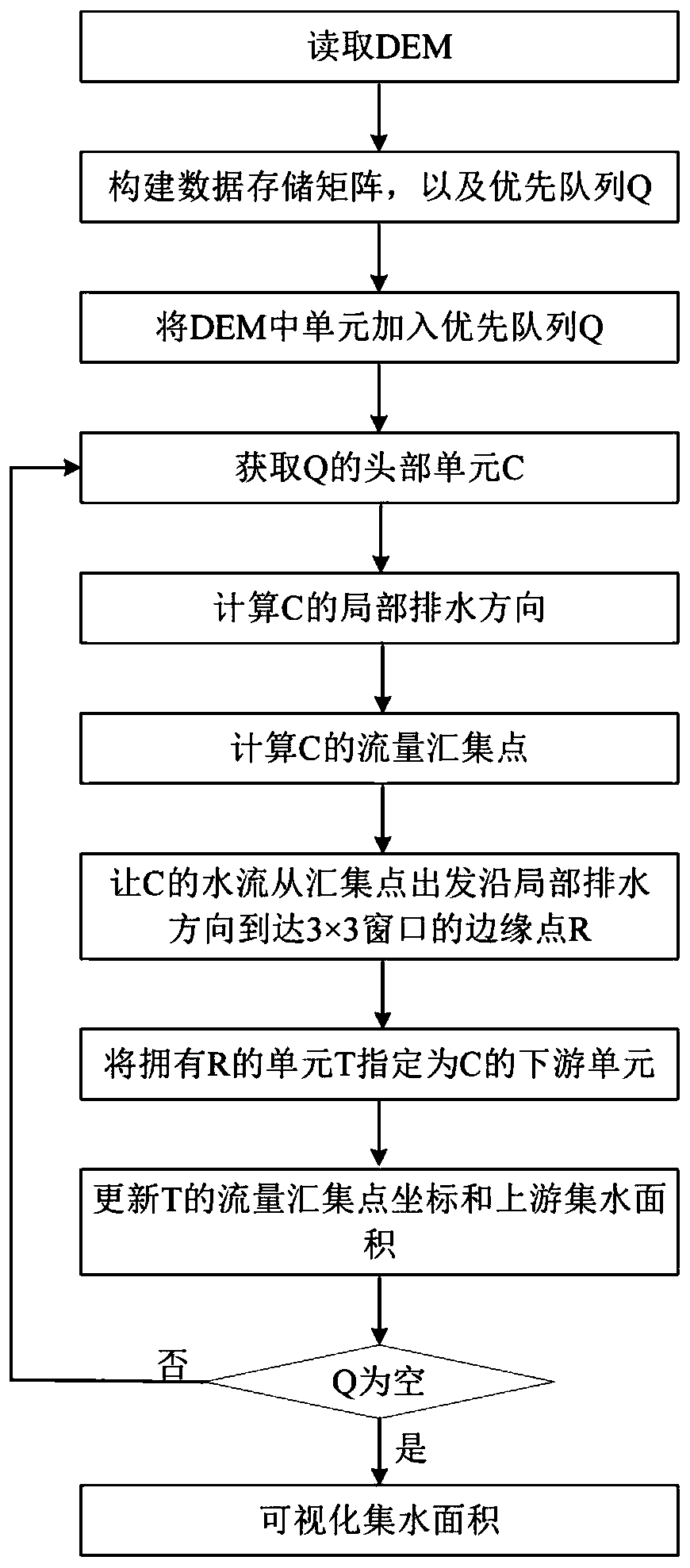
[0083] see Figure 1 to Figure 7 , the technical solution provided by the present invention is, in order to better realize the above-mentioned purpose of the invention, the present invention also provides a non-dispersive water flow path simulation method based on DEM and flow collection, wherein, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
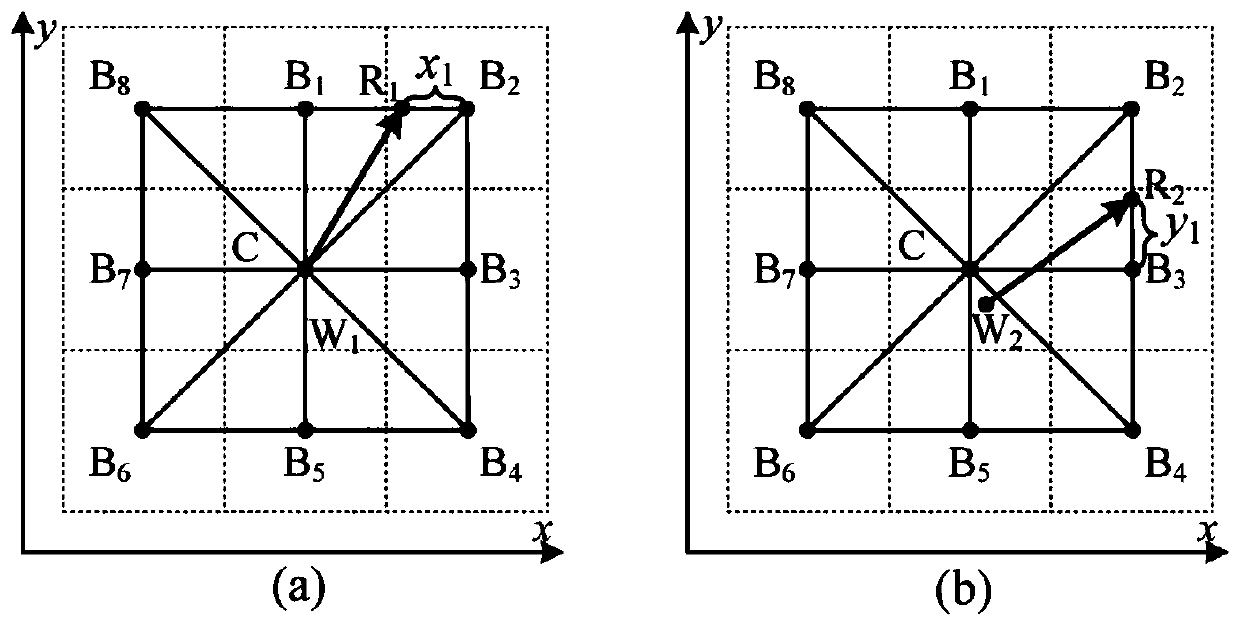
[0084] Step S1. Load the DEM elevation data, read the DEM data as a two-dimensional array A, and create four arrays M, N, L, and S with the same number of rows and columns as A, where M and N are used to store the data of each grid respectively The abscissa X of the relative coordinates between the water flow collection point and the center point, the coordinate value of the ordinate Y, L is used to record the upstream catchment area of each unit, S is used to record the direction of the center point of the downstream unit, M, N, All values in the first column, last column, first row, and last row in L and S are assigned invalid ...
specific example 1
[0116] by Figure 5 Take the 5×5 DEM as an example. In this example, the invalid value is set to -9999, and the local drainage direction is provided by the Dinf method. The processing flow and results are as follows Image 6 shown; the specific steps are as follows:
[0117] Step S1, read the DEM data as an array A (Figure (6a)), create an array M ( Image 6 (d)), N( Image 6 (e)), L( Image 6 (f)), S( Image 6 (g)), assign invalid values to the first column, last column, first row, and last row in M, N, L, and S, and create a priority queue Q sorted by unit from high to low ( Image 6 (b));
[0118] Step S2, except the first column, the last column, the first row, and the last row, scan the remaining cells in the array A, and judge whether each cell of the array A is an invalid value -9999, and this step does not find an invalid value cell, Then determine whether there are invalid value units in the 8 adjacent units around the unit. Here, unit B4 in A is found to be ...
specific example 2
[0126] by Figure 7 (a), Figure 7 Take the plane and concave DEM in (b) as an example, the size of the two DEMs is 51×51, the elevation distribution has been marked in the figure, and the traditional D8 method, D8-LTD method and the present invention are used to obtain the two surfaces respectively The non-diffusion flow path of , the visualized flow path is as Figure 7 (c)-7(h), Figure 7 The black line in the figure is the water flow path, and the gray line is the contour line. The ideal water flow path should flow perpendicular to the contour line. It can be found that the water flow path obtained by the D8 method is very straight and not perpendicular to the contour line ( Figure 7 (c), 7(d)), although D8-LTD is well applied on a plane, the water flow path can be roughly perpendicular to the contour line ( Figure 7 (e)), but the water flow path obtained by this method on the concave surface has a phenomenon of disordered crossing ( Figure 7 (f)), the present inven...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com