Production method for smelting crude iron by using industrial wastes
A production method and technology of industrial waste, applied in the field of smelting, to achieve the effect of large output, good elasticity, and increased smelting volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
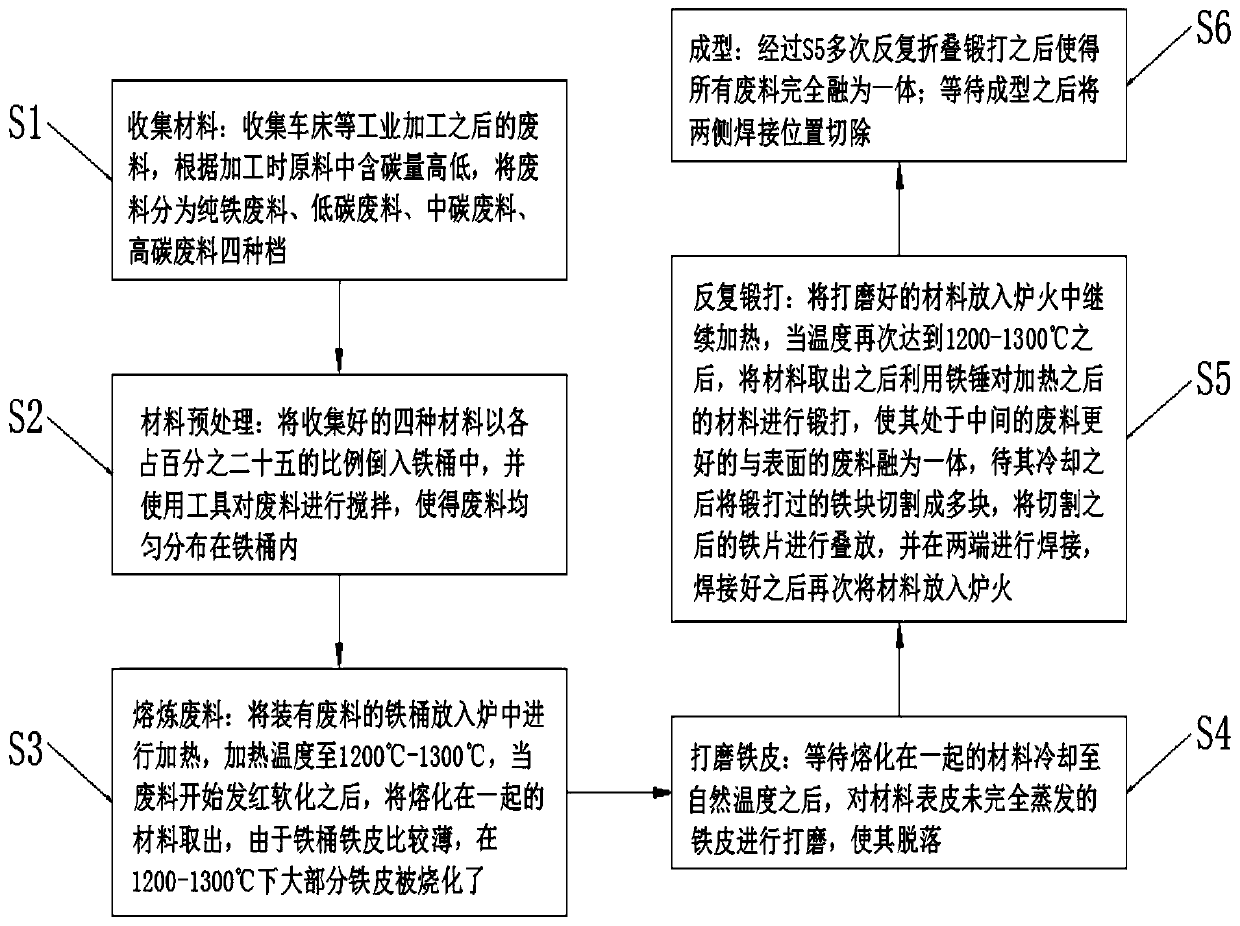
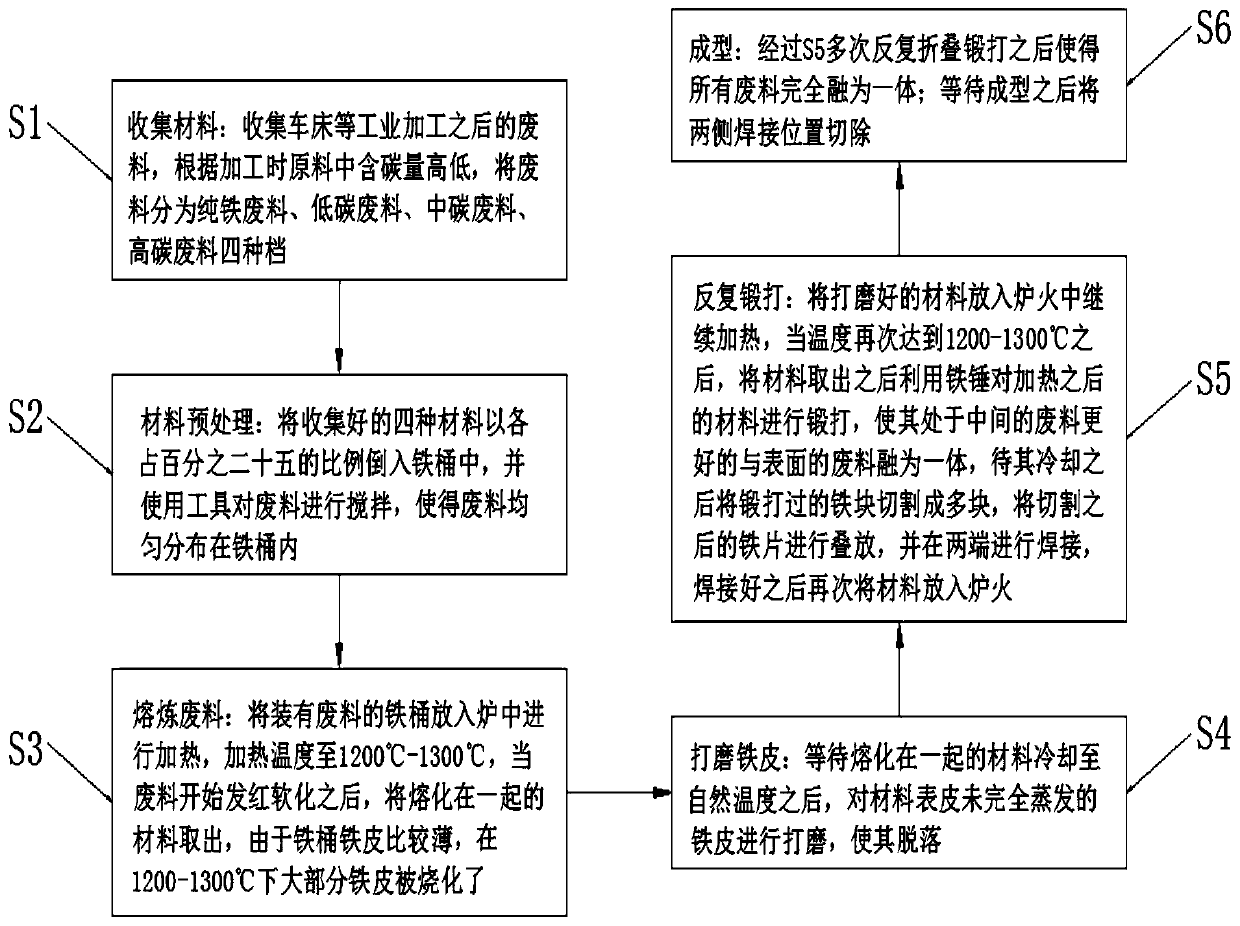
[0024] Embodiment one, such as figure 1 As shown, a production method of utilizing industrial waste to smelt crude iron according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0025] S1: Collecting materials: collect waste after industrial processing such as lathes, and divide the waste into four categories: pure iron waste, low-carbon waste, medium-carbon waste, and high-carbon waste according to the carbon content in the raw materials during processing;
[0026] S2: Material pretreatment: Pour the four collected materials into the iron drum at a ratio of 25% each, and use tools to stir the waste so that the waste is evenly distributed in the iron drum;
[0027] S3: Smelting waste: Put the iron drum containing the waste into the furnace to heat it to 1200°C-1300°C. When the waste starts to turn red and soften, take out the melted materials. Since the iron sheet of the iron drum is relatively thin , at 1200-1300°C, most of the iron sheet is burnt;...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment two, such as figure 1 As shown, in S5, the forged iron block is generally cut into three to six pieces.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment three, such as figure 1 As shown, in S6, the number of times of folding and forging is generally three to six times, which can avoid the effect of losing the hairy iron and cow hair pattern due to too many times.
[0033] In order to facilitate the understanding of the above-mentioned technical solution of the present invention, the working principle or operation mode of the present invention in the actual process will be described in detail below.
[0034] Generally speaking, it is more environmentally friendly to use the waste after industrial processing for processing. On the one hand, it is more environmentally friendly to reuse the waste. On the other hand, the waste after industrial processing can be continuously obtained, which is more convenient than salvaging iron sand in the river, and the output is larger; because The waste after industrial processing is used, and the sword cast after forging also has the effect of hairy iron and cow hair; because ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com