Quantitative detection method for sulfonamide-antibiotic-resistant genes in seawater bathing spot
A quantitative detection method and antibiotic resistance technology, applied in the field of detection, can solve the problems of late resistance genes, little attention, serious problems, etc., and achieve the effect of high amplification efficiency, high measurement accuracy and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
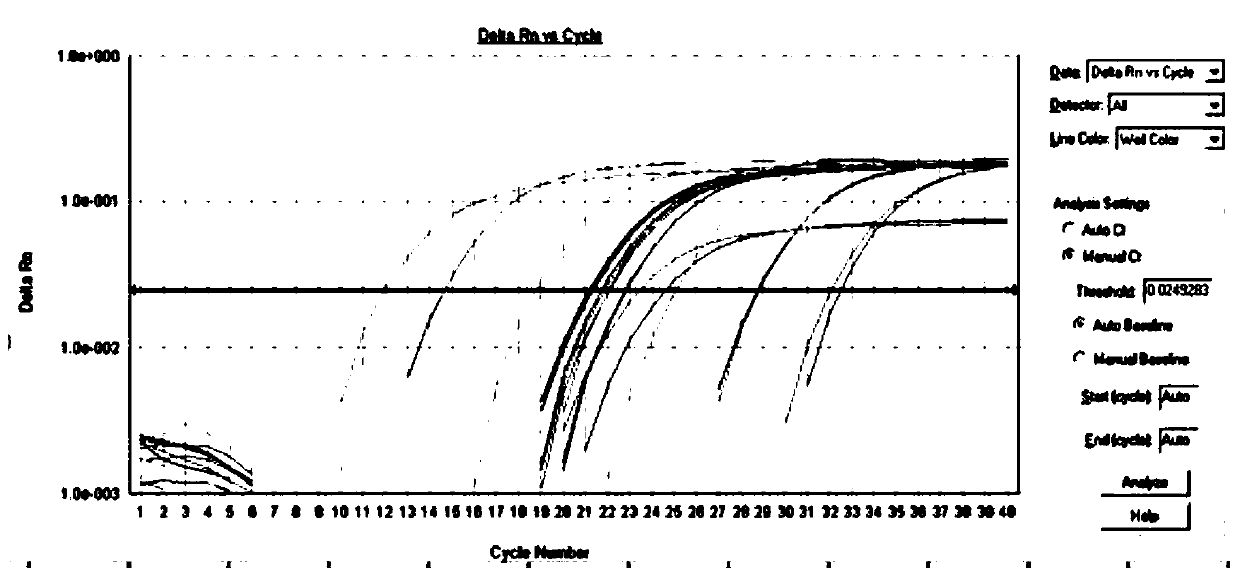
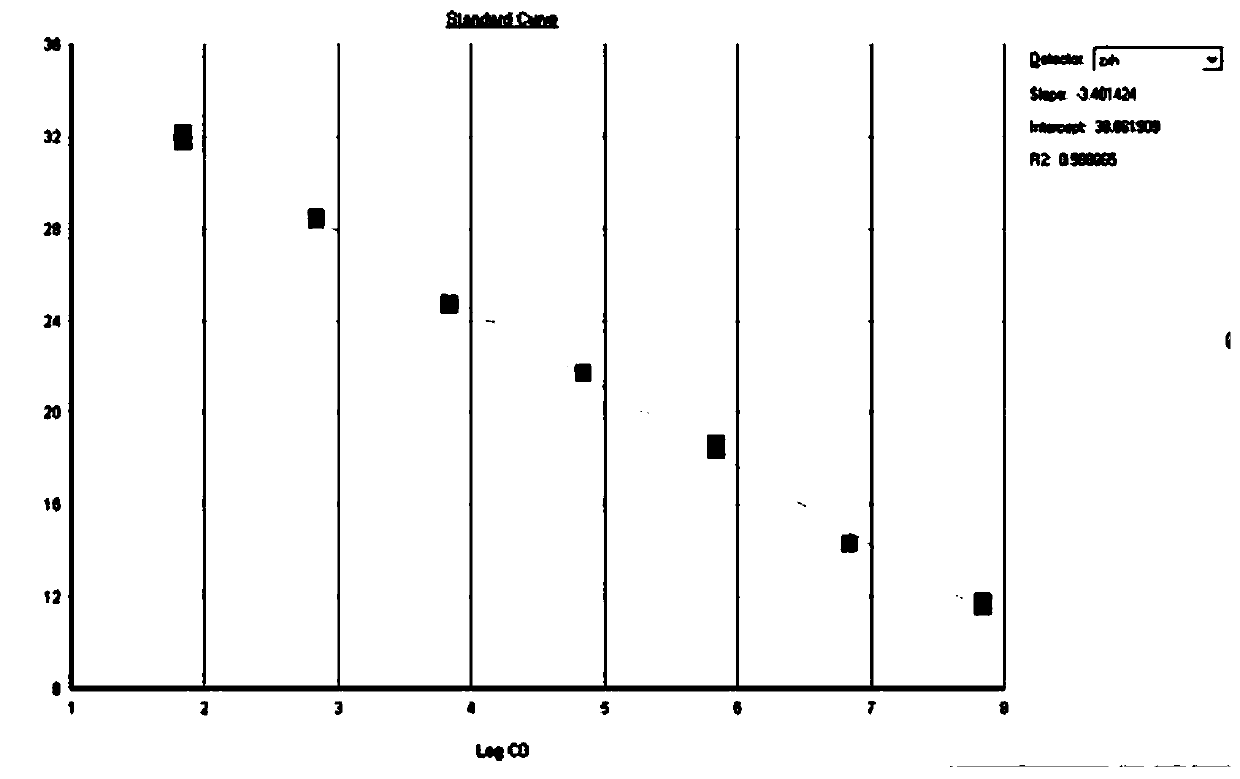
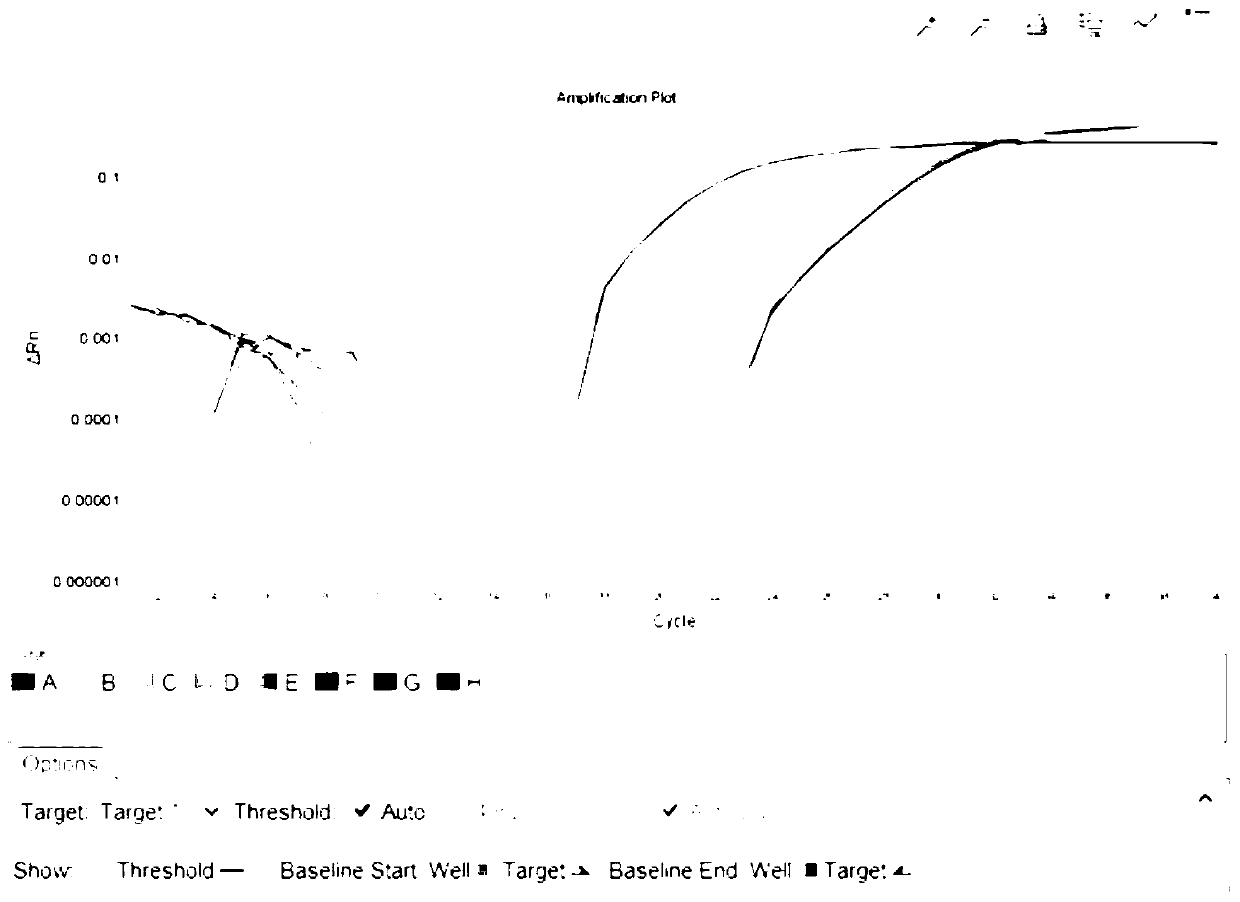
[0040] This example specifically illustrates the quantitative detection method for determining the resistance genes sul1 and sul2 of sulfonamide antibiotics in a bathing beach.
[0041] Step 1: Collection method of water samples and sediments in beach
[0042] Water samples: Water samples were collected in sterilized 5L polyethylene buckets. It is advisable to take surface water when collecting, and collect 3 barrels at each sampling point as 3 samples in parallel, and mark the serial number, collection location, and collection time. Immediately after collection, put the water sample into an incubator filled with ice cubes, and bring it back to the laboratory for processing in time.
[0043] Sediment: The surface sediment is collected with a sterilized sampler and put into a sterile ziplock bag. Immediately after collection, the samples were placed in an incubator filled with ice cubes and brought back to the laboratory for processing in time.
[0044] Step 2: Sample transp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com