ACSL4 and application thereof in NASH
A technology of drugs and inhibitors, applied in the field of ACSL4 and its application in NASH, can solve the problems that limit the development of chronic liver disease treatment methods and complex effects, and achieve the effect of improving liver lipid accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
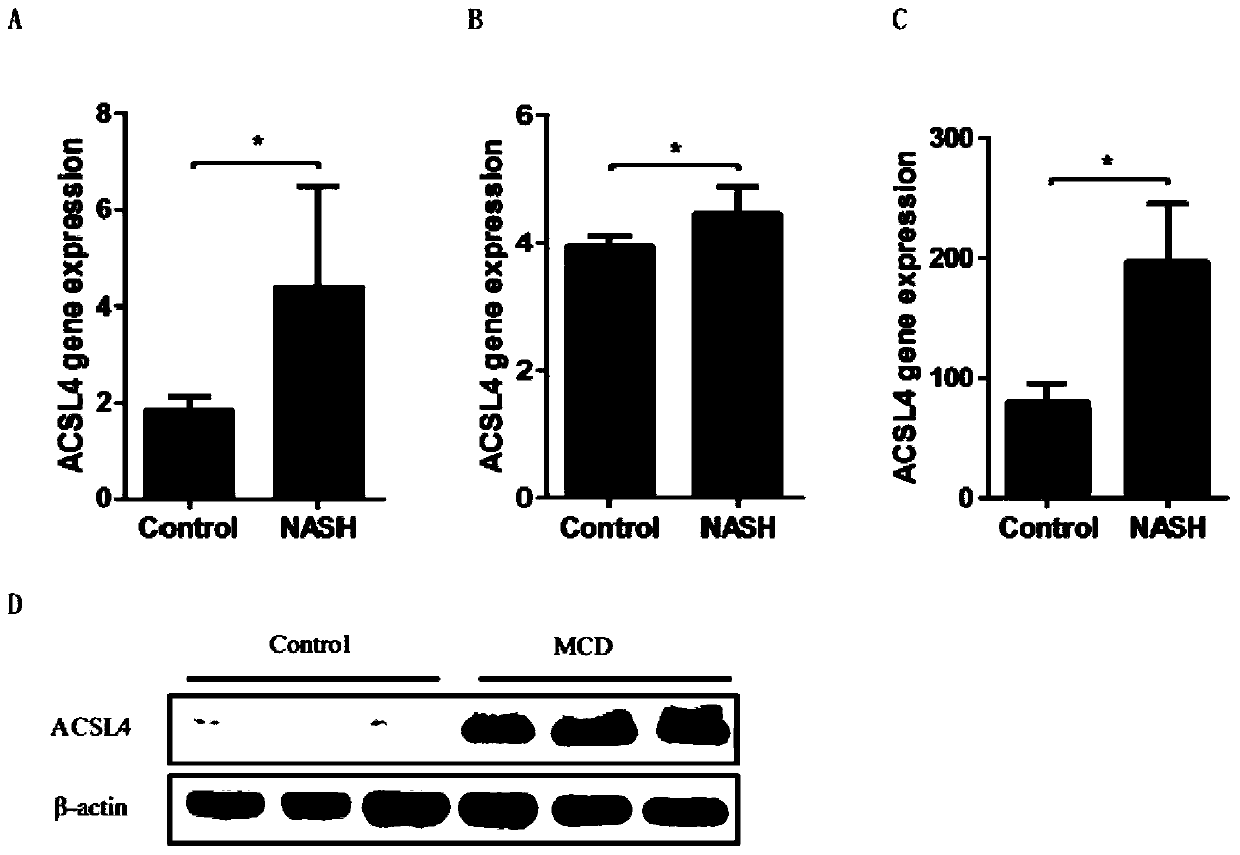
[0033] Such as figure 1 Shown is the GEO database (GSE48452, GSE63067, GSE89632) analysis showing that ACSL4 expression was significantly higher in NASH patients than in controls (Panels A-C). For the above database analysis results, a diet-induced NASH mouse model was used for verification. The mice were fed with MCD feed for 8 weeks, and the expression of ACSL4 was detected by Western blot. It was found that the expression of ACSL4 was significantly up-regulated in the diet-induced NASH mouse model compared with the control group, which was consistent with the database analysis results (Figure D).
Embodiment 2
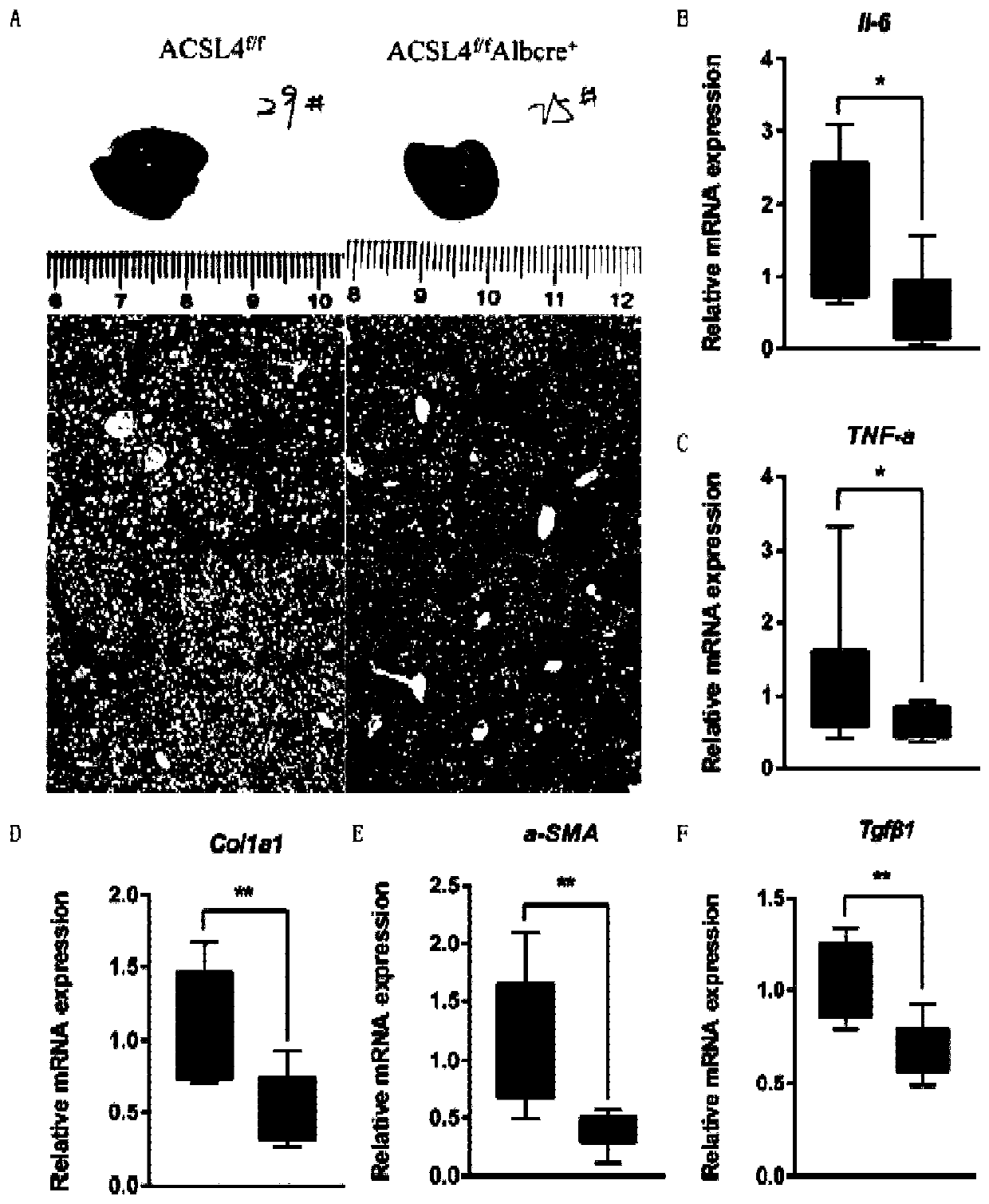
[0035] Such as figure 2 As shown, we constructed ACSL4 liver-specific knockout mice (ACSL4 f / f ; AlbCre + ), fed with MCD feed for 8 weeks, and the histopathological changes and fibrosis of the liver were detected by HE staining and Masson staining. The results showed that compared with the control group, ACSL4 f / f ; AlbCre + Lipid accumulation and liver fibrosis in the mouse liver were significantly improved (Panel A). Then, qPCR method was used to detect the expression of fibrosis and inflammation-related genes, and it was found that ACSL4 f / f ; AlbCre + Genes associated with fibrosis and inflammation were significantly downregulated in mouse livers (Panels B–F).
Embodiment 3
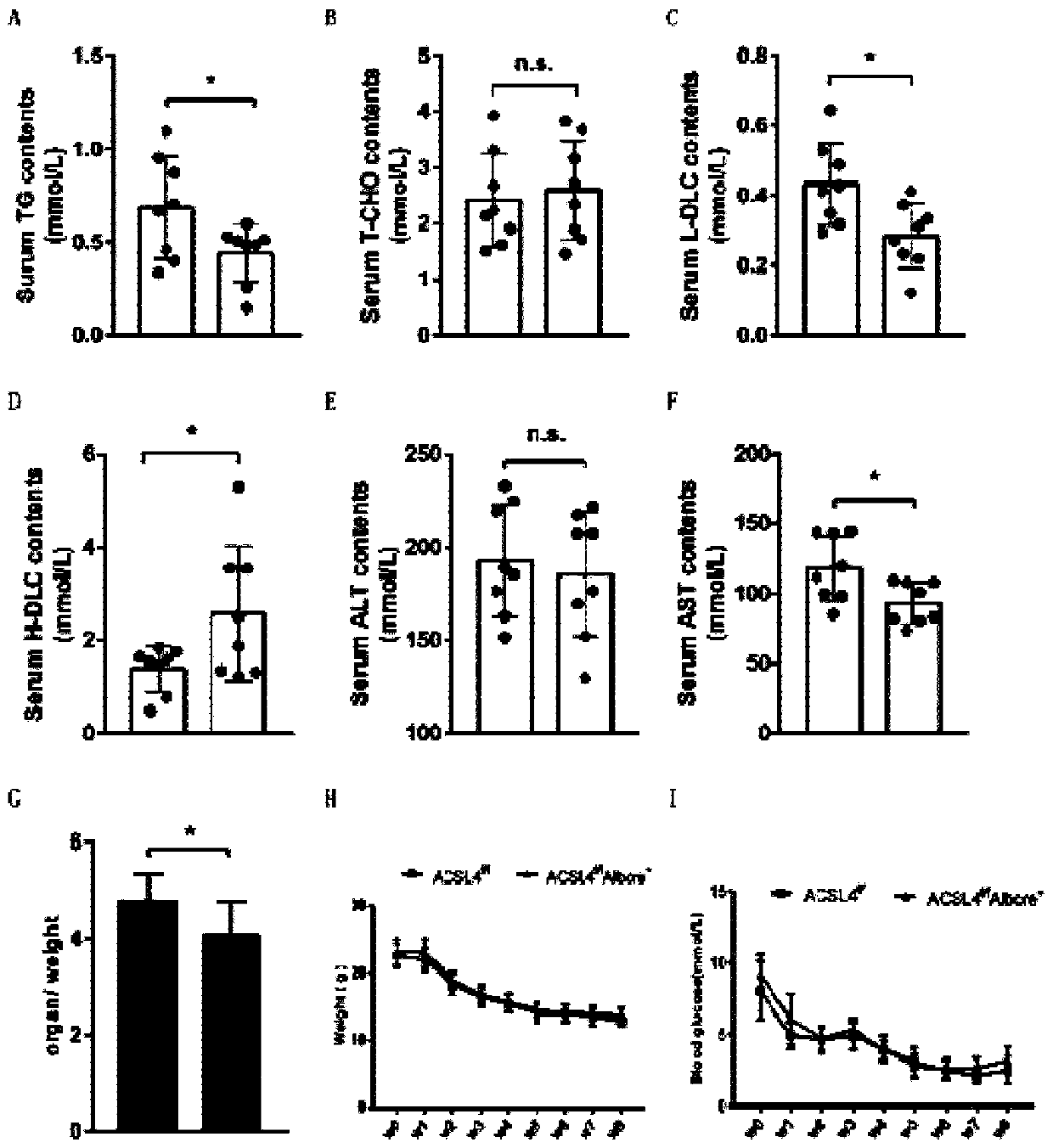
[0037] Such as image 3 As shown, the detection results of serum biochemical indicators showed that in the NASH model induced by MCD feed feeding for 8 weeks, ACSL4 f / f ; AlbCre + Blood triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein, and AST in mice were significantly improved (Figure A-F), and liver enlargement was reduced (Figure G). Since the MCD diet itself led to a decrease in body weight and blood glucose in mice, no significant changes in body weight and blood glucose-related indicators were detected (Fig. H-I). The above results suggest that liver-specific knockout of ACSL4 can significantly improve the abnormal blood lipids and liver function that usually accompany the progression of NASH.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com