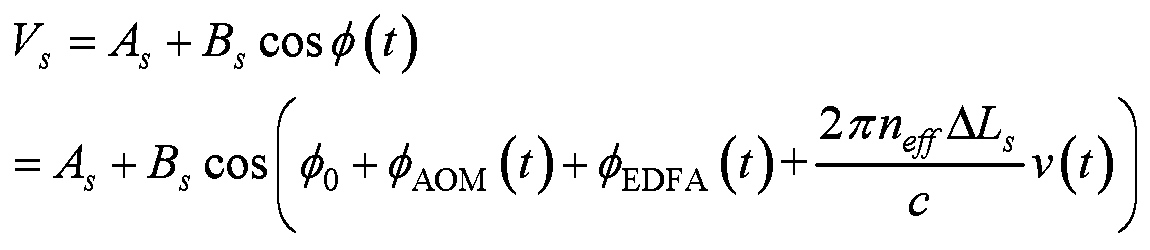Distributed optical fiber sensing system for low-frequency detection
A distributed optical fiber, sensing system technology, applied in measurement devices, geophysical measurements, and the use of wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve the problems of high noise, affecting the low-frequency characteristics of the system, and difficult to meet the detection of low-frequency weak vibration signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
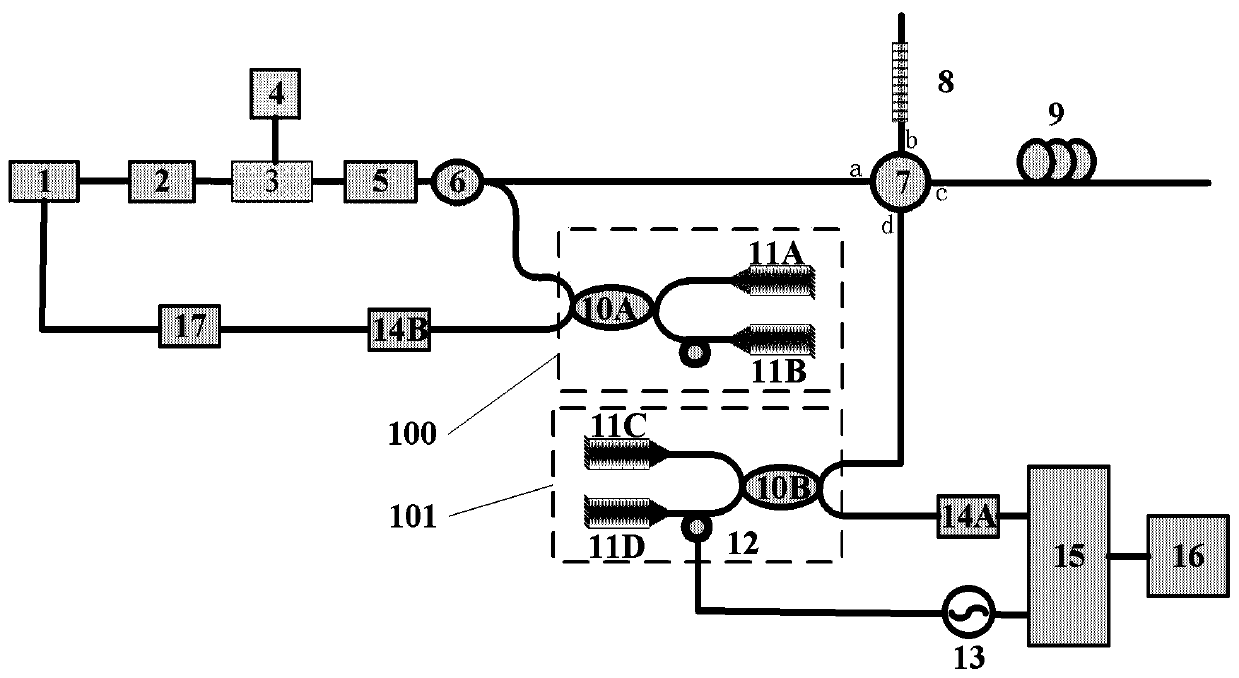
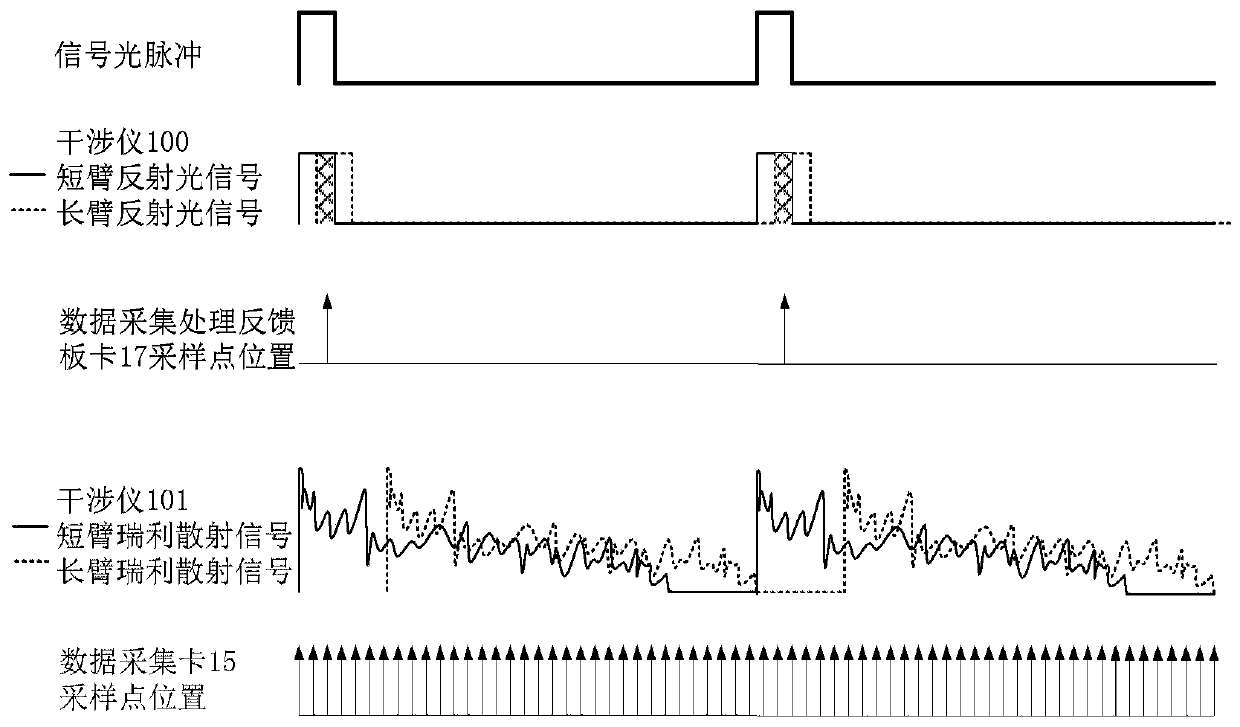
[0050] Specific embodiments of the present disclosure will be described in detail below, and it should be noted that the embodiments described here are only for illustration, and are not intended to limit the embodiments of the present disclosure. In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the embodiments of the present disclosure. It will be apparent, however, to one of ordinary skill in the art that these specific details need not be employed to practice the disclosed embodiments. In other instances, well-known structures, materials or methods have not been described in detail to avoid obscuring embodiments of the present disclosure.
[0051]Throughout this specification, reference to "one embodiment," "an embodiment," "an example," or "an example" means that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment or example is included in the present disclosure....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com