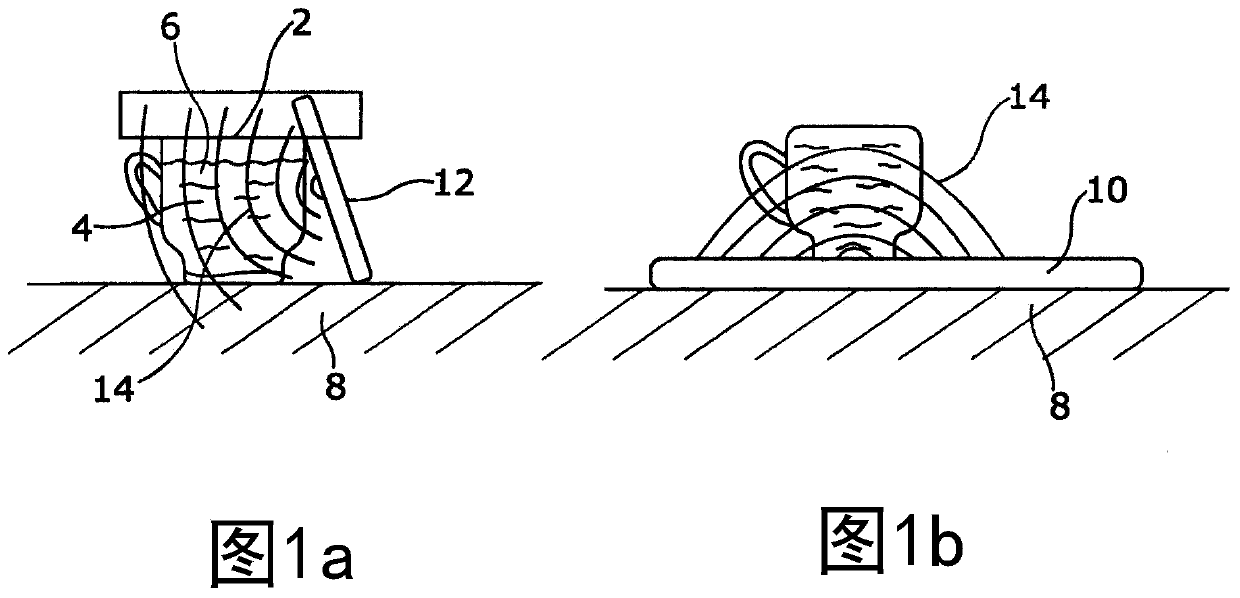
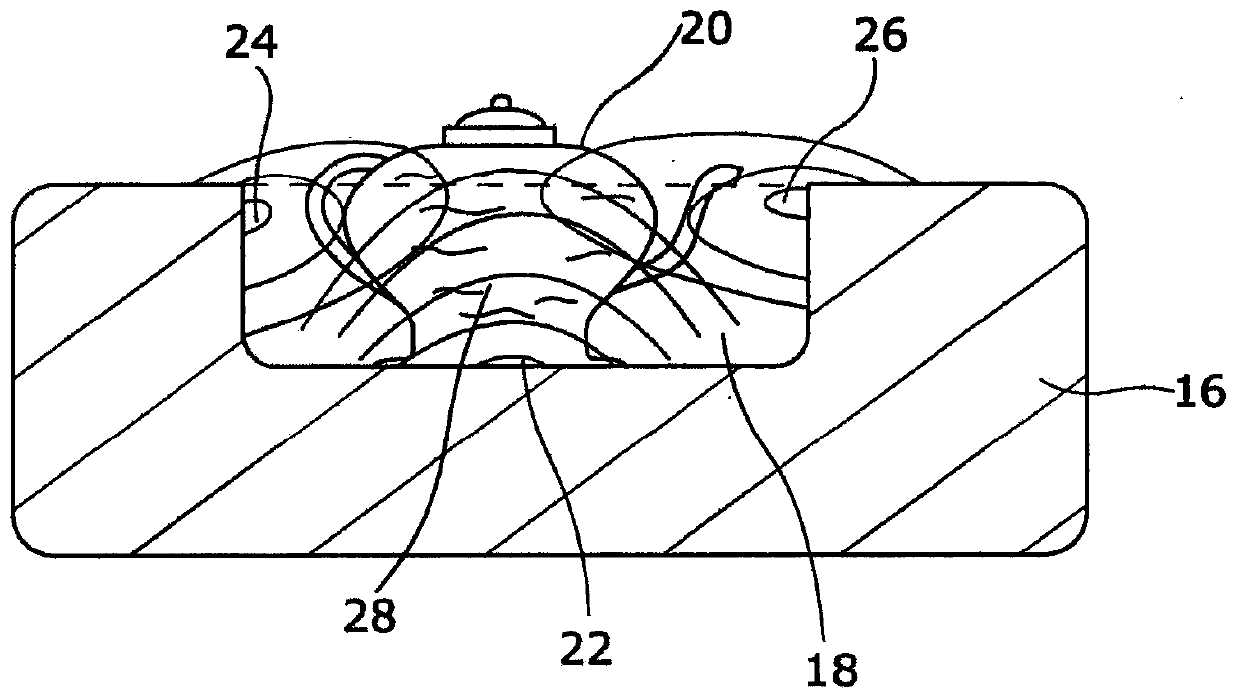
Method and apparatus for enhancement of aqueous extraction of plant material
A plant material and equipment technology, applied in the field of water-based extraction, can solve problems such as limited capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0034] Example 1 (Hot Brewed Japanese Sencha Green Tea) 83
[0035]A world-renowned tea master with special skill in the subtleties of Japanese green tea was commissioned to study the effect of pulsed radio signals from smartphones on the hot brewing of sencha. The master is equipped with a device in the form of a smartphone, and in particular a Samsung Galaxy S4 loaded with the control application according to the invention. In one embodiment, the application is an application known as apZap available from the Google (RTM) store.
[0036] The tea art master prepared 2 ceramic teapots for brewing by introducing 2.5g of sencha, then poured 160ml of water at 70 degrees Celsius on the leaves. A teapot was placed in another room, while another teapot was subjected to 15 1ms burst radio signals at 2.4GHz per second. These pulses were generated by activating the apZap and placing the smartphone next to the teapot.
[0037] During the operation of apZap, the mobile phone is placed...
example 2
[0039] Example 2, Hot Brewed Japanese Sencha Green Tea 102
[0040] Two Japanese green tea samples were produced by the same method as Example 1. Again, one sample was subjected to a pulsed EM signal from a Samsung Galaxy S4 using the apZap application. Another brew is done in a separate room away from any influence from the smartphone signal. After 4 minutes of infusion, each tea was sequentially separated from the leaves into two vials and labeled.
[0041] Visual evaluation of the two samples identified clear differences in color intensity. Compared to Control Sample 2, Sample 1 prepared in the presence of a 2.4 GHz pulse was several shades darker in yellow and green. Sample 1 appeared to be a "stronger" tea compared to Sample 2 (the control sample).
[0042] The samples are then sent to an analytical laboratory and coumarin content is assessed by a chromatographically validated procedure performed by an accredited laboratory specializing in the analysis of food and bev...
example 3
[0047] Example 3 Hot Brewed Echinacea and Raspberry Fruit Tea
[0048] Two samples of Downing Echinacea and Raspberry Fruit Tea were prepared for hot brewing. Place fruit tea bags in separate pyrex cups. Add 250ml of hot water from the previously boiled kettle to each cup. One cup was placed in a separate room while the other was subjected to a 2.4GHz pulse from a Samsung Galaxy S4 using the apZap app. The infusion was continued for 5 minutes, after which time the application was stopped and the color, taste and texture of the two samples were compared.
[0049] Summary of experimental evidence from examples
[0050] The use of a smartphone with a pulsed digital signal during the aqueous extraction of plant material during the tea making process (infusion process) enables enhanced extraction, providing higher concentrations of key compounds in the final tea (e.g. through increased pigmentation and As evidenced by chemical analysis of higher coumarin content). The use of a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com