Polymer mortar and preparation method thereof
A polymer and polymer emulsion technology, applied in the field of concrete materials, can solve the problem that the performance of polymer mortar cannot meet the construction requirements of CRTSII slab ballastless track filling layer construction requirements, and the polymer mortar does not meet the construction requirements and is far from meeting the requirements of the mortar performance standard. Mortar performance standards and other issues, to eliminate adverse environmental impacts, ensure construction efficiency and project quality, and meet the effects of early age strength and elastic modulus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1 (simulation ambient temperature 35 ℃):
[0032] A kind of polymer mortar, according to one cubic meter of concrete, comprises the following raw material components in parts by weight: 90 parts of rapid hardening sulfoaluminate cement, 45 parts of polymer emulsion, 2 parts of superfine powder, 5 parts of gypsum powder, 10 parts of expansion agent, 190 parts of sand, 30 parts of water, 1.0 part of powder water reducer, 0.5 part of polymer fiber, 0 part of hardening accelerator, 0.04 part of retarder and 0.3 part of defoamer.
[0033] The polymer emulsion is a styrene-butadiene emulsion with a viscosity of 80 mPa.s, a solid content of 50%, and a minimum film-forming temperature of 0°C.
[0034] The ultrafine powder is a mixture of ultrafine muscovite powder and calcium carbonate whiskers, wherein the fineness of the ultrafine muscovite powder is 1200 mesh, the aspect ratio of the calcium carbonate whiskers is 20:1, and the ultrafine muscovite whiskers The mas...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2 (simulation ambient temperature 20 ℃):
[0044] Different from Example 1, 95 parts of rapid hardening sulfoaluminate cement, 40 parts of polymer emulsion, 2.5 parts of superfine powder, 10 parts of gypsum powder, 8 parts of expansion agent, 200 parts of sand, 35 parts of water, powder 0.8 part of body water reducer, 0.8 part of polymer fiber, 0.02 part of hardening accelerator, 0.01 part of setting retarder and 0.5 part of defoamer, and other conditions remain unchanged.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 (simulation ambient temperature 5 ℃):
[0046] Different from Example 1, 100 parts of rapid hardening sulfoaluminate cement, 35 parts of polymer emulsion, 3 parts of superfine powder, 10 parts of gypsum powder, 5 parts of expansion agent, 210 parts of sand, 40 parts of water, powder 0.5 part of body water reducing agent, 1.0 part of polymer fiber, 0.05 part of hardening accelerator, 0 part of setting retarder and 0.8 part of defoamer, and other conditions remain unchanged.
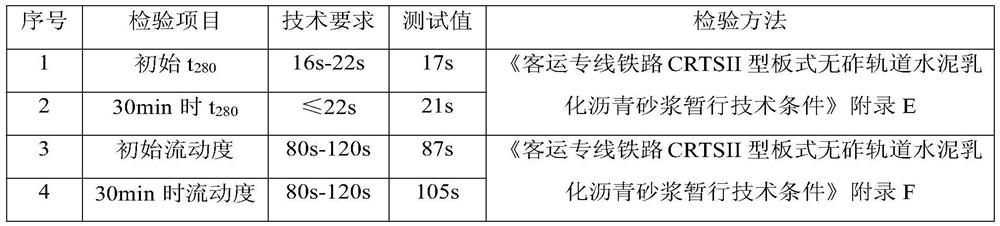
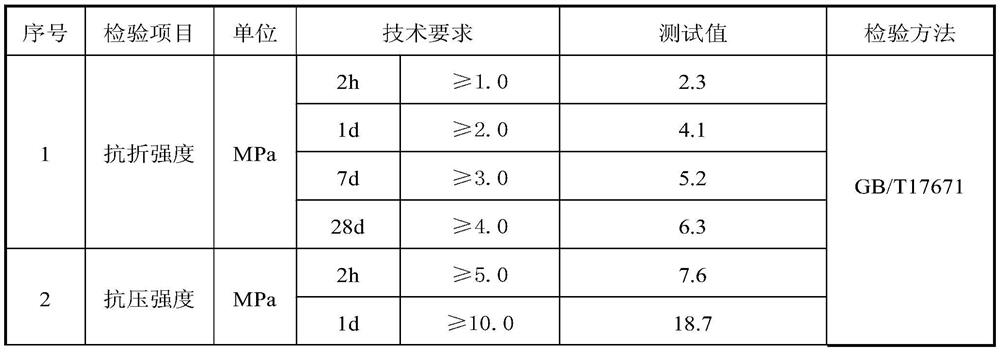
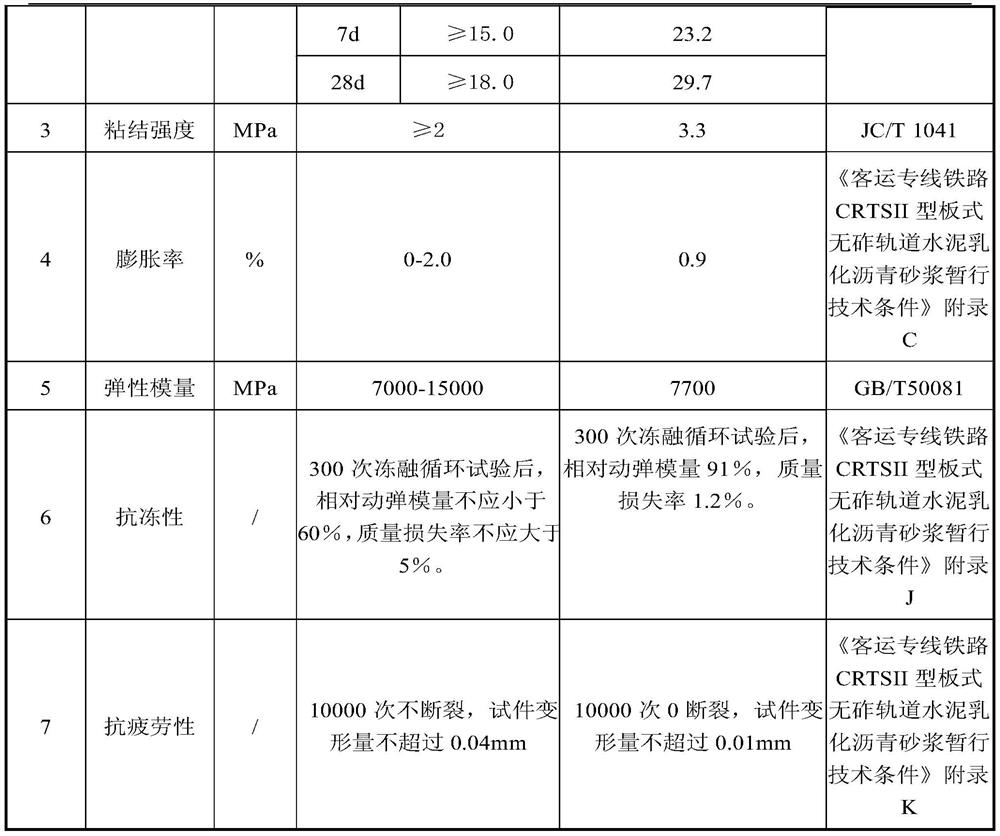
[0047] The performance test of the polymer mortar prepared by embodiment 1-3 all comprises two test phases, the first stage: the newly prepared polymer mortar (i.e. the polymer mortar before hardening), see Table 1, 3 and 5 (need Note that in Tables 1, 3 and 5 t 280 Refers to the time required for the expansion of the polymer mortar to reach 280mm); the second stage, the polymer mortar after hardening, see Tables 2, 4 and 6.
[0048] The performance result of the newly prepared polyme...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| minimum film forming temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com