Lithium secondary battery
A lithium secondary battery and electrode technology, applied in secondary batteries, lithium storage batteries, battery electrodes, etc., can solve problems such as heat concentration and deterioration, and achieve the effects of improving weight energy density, inhibiting deterioration, and stabilizing development goals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach >
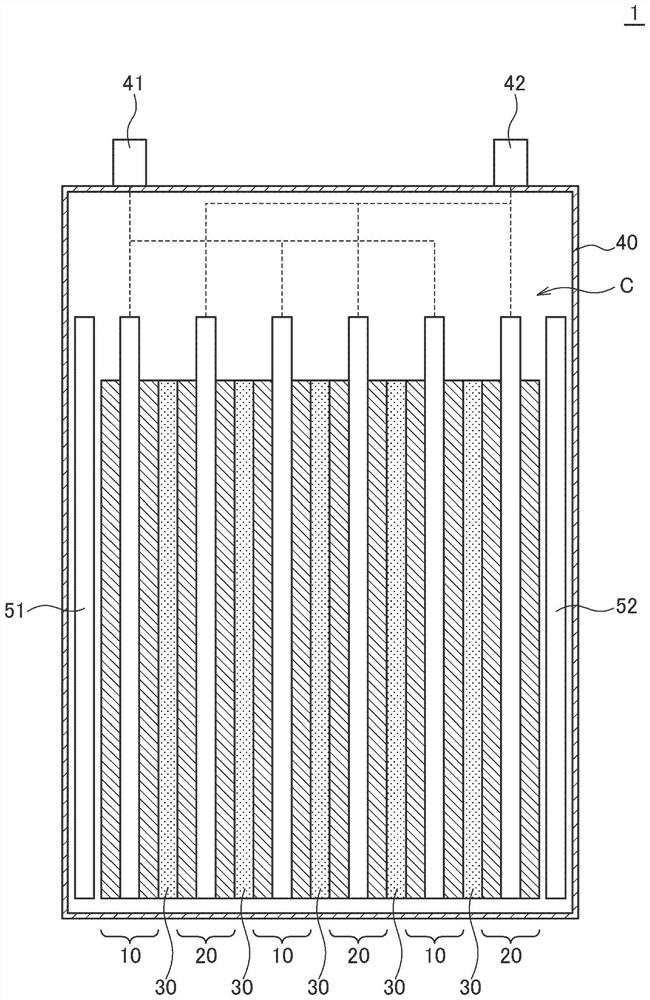
[0031] figure 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of lithium secondary battery 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the lithium secondary battery 1 of the first embodiment includes an electrode assembly C, an exterior body 40 that houses the electrode assembly C in a hermetically sealed state, and a pair of terminal electrodes 41 and 42 drawn out from the exterior body 40 . In addition, although not shown, a non-aqueous electrolytic solution is sealed together with the electrode assembly C in the exterior body 40 .
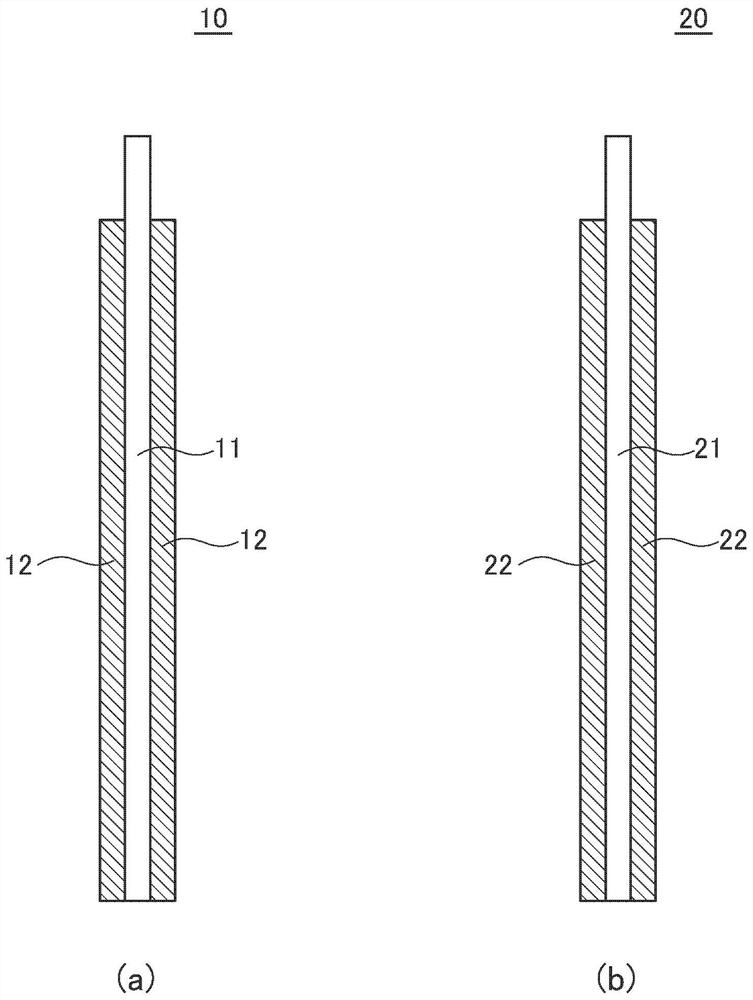
[0033] The electrode assembly C has a structure in which positive electrodes 10 and negative electrodes 20 are alternately stacked with a separator 30 interposed therebetween. figure 1 In the illustrated example, three positive electrodes 10 and three negative electrodes 20 are laminated, but the number of positive electrodes 10 and negative electrodes 20 is not limited to this. Also, it is not nece...
no. 2 approach >
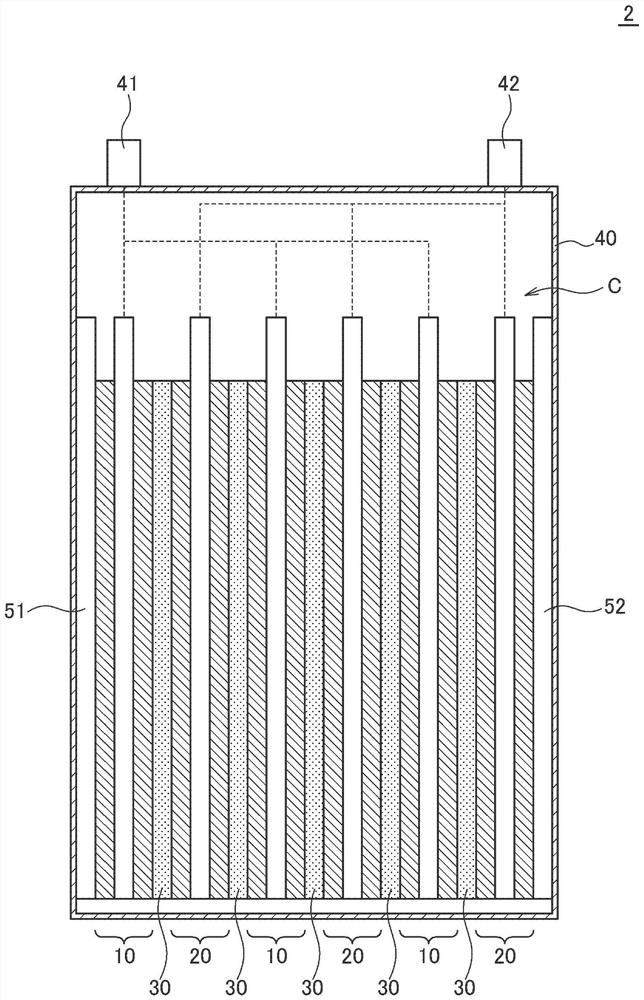
[0064] image 3 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a lithium secondary battery 2 according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0065] Such as image 3As shown, the difference between the lithium secondary battery 2 of the second embodiment and the lithium secondary battery 1 of the first embodiment is that the heat release layers 51 and 52 of the former are in contact with the electrode assembly C and the exterior body 40 structure. The rest of the structure of the lithium secondary battery 2 of the second embodiment is the same as that of the lithium secondary battery 1 of the first embodiment, and therefore, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same elements, and overlapping descriptions are omitted.
[0066] As exemplified in this embodiment, in the present invention, the heat dissipation layer may be in contact with the electrode assembly and the exterior body. Accordingly, the heat inside the electrode assembly is efficiently dissipated to...
no. 3 approach >
[0068] Figure 4 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a lithium secondary battery 3 according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0069] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the lithium secondary battery 3 of the third embodiment is different from the lithium secondary battery 2 of the second embodiment in that the former has an adhesive layer 61 between the heat release layers 51 and 52 and the exterior body 40 , 62. Other configurations of the lithium secondary battery 3 of the third embodiment are the same as those of the lithium secondary battery 2 of the second embodiment, and therefore, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same elements, and overlapping descriptions are omitted.
[0070] As exemplified in this embodiment, in the present invention, another layer such as an adhesive layer may be provided between the heat release layer and the electrode assembly.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com